What is it discoid eczema?
Discoid eczema is a common type of eczema /dermatitis, in which there are scattered, rounded plates of eczema Eczema can cause intense itching. Discoid eczema is also called nummular dermatitis.
What is the cause of discoid eczema?
The cause of discoid eczema is unknown. Some cases are associated with Staphylococcus aureus infection.
the eruption can be precipitate by:
- A located Injuries such as scratches, insect bites, or thermal burns.
-
Impetigo or wound infection
- Contact dermatitis
- Dry Skin
-
Varicose veins (varicose eczema)
- other skin problem
Who gets discoid eczema?
Discoid eczema can affect children and adults. It is slightly more common in adult men than in women. In men older than 50 years, there is an association with chronic alcoholism.
Discoid eczema can occur in atopic eczema, eczema craquelé and secondary eczematization.
What are the clinical features of discoid eczema?
There are two forms of discoid eczema:
- exudative acute discoid eczema: oozy papules, blisters and plaques
- Dry discoid eczema: subacute or chronic erythematousdry plates
Both forms of discoid eczema usually affect the extremities rather than the trunk, but the eruption maybe extended. Although often bilateral, the distribution It is often asymmetric.
Individual plates are ok circumscribed, mostly 1–3 cm in diameter, and swollen. Most patches are round or oval, hence the name "discoid" or "numular" (coin-shaped). Plaques are usually very itchy, but sometimes they don't itch at all. The skin between the patches is usually normal, but may be dry and irritable.
Severe discoid eczema can be generalized, with numerous small and large itchy lesions appearing all over the body due to an autoeczematization reaction.
The patches can be lightened without leaving a sign. However, on darker skin, the marks can persist for months. These can be dark brown (post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation) or paler than the surrounding skin (post-inflammatory hypopigmentation)
exudative discoid eczema
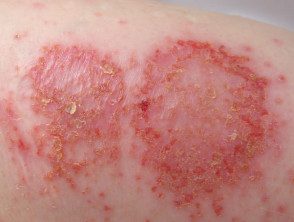
Discoid eczema
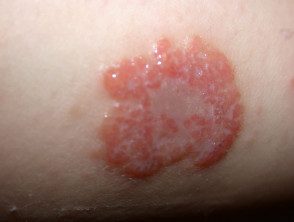
Discoid eczema
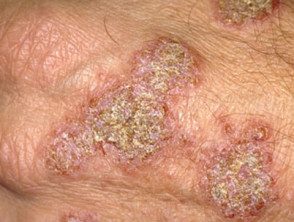
Discoid eczema
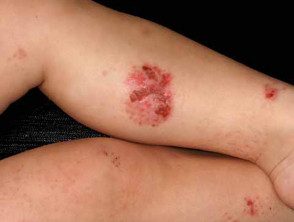
Infected nummular atopic dermatitis
See more images of discoid eczema.
How is discoid eczema diagnosed?
In most cases, the appearance of discoid eczema is quite characteristic.
- Bacterial swabs can reveal Staphylococcus aureus colonization or infection.
- Scrapings are commonly taken for mycology, as discoid eczema can be very similar to tinea corporis (ringworm infection).
- Patch tests are sometimes done to see if there might be a contact allergy responsible for dermatitis. In most cases, a specific allergy cannot be found.
What is the treatment for discoid eczema?
As discoid eczema is associated with loss of skin barrier function, it is important to:
Protects the skin from injuries.
As this type of dermatitis often begins as minor skin lesions, protect all of your skin carefully. If hands are affected, use gloves and tools to ensure skin is not irritated by friction, detergents, solvents, other chemicals, or excessive water.
Apply emollients frequently
Emollients include bath oils, soap substitutes, and moisturizers. They can be applied to dermatitis as often as needed to relieve itching, climbing and dryness. Emollients should also be used on unaffected skin to reduce dryness. It may be necessary to try several different products to find one that suits you. Many people find one or more of the following helpful: glycerin and cetomacrogol cream, white soft paraffin / mixed liquid paraffin, fat cream, wool fat lotions.
Anti-inflammatory treatments include:
Current steroids
Topical steroids are anti-inflammatory creams or ointments available by prescription that can clear dermatitis and reduce irritation. The strongest products are applied to the patches only once or twice a day for 2 to 4 weeks. They repeat from time to time. Mild ones like hydrocortisone are safe for daily use if needed.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics (most often flucloxacillin) are often prescribed if the dermatitis is blistering, sticky, or crusty. Sometimes discoid eczema clears up completely with oral antibiotics, only to recur when they are stopped.
Other treatments sometimes prescribed for severe discoid eczema include:
Oral antihistamines
Antihistamine pills can reduce itching in some patients with discoid eczema. They do not lighten the rash.
Ultraviolet radiation (UV) treatment
Phototherapy several times a week for 6 to 12 weeks can reduce the extent and severity of discoid eczema.
steroid injections
Intralesional steroids are sometimes injected into one or two particularly difficult areas of discoid eczema. This treatment is not suitable for multiple injuries.
oral steroids
Systemic Steroids are reserved for severe and extensive cases of discoid eczema. They are usually prescribed for a few weeks while continuing steroid creams and emollients in residual dermatitis.
Other oral treatments
Persistent and troublesome discoid eczema is occasionally treated with methotrexate, azathioprine, or cyclosporine. These medications have significant risks and side effects and require careful monitoring by a specialist. dermatologist. They may be more suitable in many cases than steroids in the long term.
Discoid eczema can usually be controlled with the above measures, although it tends to recur when treatment is stopped. In most patients, discoid eczema eventually clears up completely.

