Ad
Skin cancer
Application to facilitate skin self-examination and early detection. read more.
Introduction
Electrical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) is used by a portable point-of-care device called Nevisense™ (Scibase AB, Stockholm, Sweden) to objectively analyze lesions with suspected melanoma.
Nevisense™ Electrical Impedance Spectroscopy*
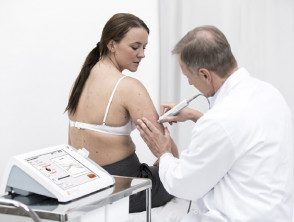
Nevada procedure
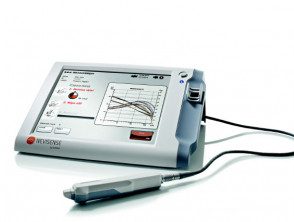
Nevisense device
* Images provided by Scibase
What is electrical impedance spectroscopy?
Visual examination is usually sufficient in identifying most skin types injury. However, when it comes to atypical injuries, a clinical diagnosis based on visual examination alone can pose a challenge, leading to unnecessary splits or even evil faults.
Dermatoscopy uses a portable skin surface microscope to examine skin lesions. In expert hands the chance of a correct diagnosis increases, but requires considerable training and experience.
In the spectrometric analysis of skin lesions, a computer program is used that calculates and extracts information about the cells and structures of the skin. The method uses a beam of light that penetrates below the surface of the skin. Clear images taken with a digital camera or handheld scanner are fed into a computer for detailed analysis.
In electrical impedance spectroscopy, the different electrical properties of human tissue are used to classify cellular structures and therefore detect malignant tumors.
SciBase electronic impedance spectroscopy is a patented technology developed at the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm, Sweden.
How electrical impedance spectroscopy worked?
- Skin tissues have different electrical properties under different medical conditions.
- Based on this, it is possible to identify a condition, such as melanoma, using Nevisense's unique EIS method.
- Electrical impedance spectroscopy It is a measure of the overall resistance within the tissue to alternating currents of various frequencies.
- An electrical signal is applied across the skin lesion using an innovative electrode system at the tip of the Nevisense™ probe.
- The frequencies used by Nevisense™ (1 kHz – 2.5 MHz) relate to clinically relevant properties, such as the composition of intra- and extracellular environments, the shape and size of cells, and the composition of the cell membrane.
- To cover the lesion in both width and depth, measurement is performed at 35 frequencies and four depth settings over the lesion in a total of 10 permutations.
- At first, a reference measurement is made on healthy skin near the lesion.
- This procedure is repeated in the lesion to be examined.
- Nevisense's advanced algorithm classifies the lesion based on measurement data from both the lesion and the reference.
- The Nevisense™ classifier provides an EIS score output on the Nevisense™ screen that reflects the degree of atypia identified by the method
- The results of visual inspection of suspected melanoma can be added to the objective information provided by Nevisense™ to reach a more informed clinical decision.
What are the advantages of electrical impedance spectroscopy analysis?
Electrical impedance spectroscopy The analysis complements doctors' visual examinations, particularly in cases of cutaneous lesions with unclear clinical signs of melanoma. Benefits included:
- A quick and simple procedure.
- Greater diagnostic precision
- Objective analysis
What clinical evidence supports the effectiveness of electrical impedance spectroscopy?
- Electrical impedance spectroscopy has been evaluated for more than a decade, from development and proof of principle to clinical studies in skin Cancer and benign skin lesions.
- In a multicenter study, a prospective, blinded study conducted at 5 US and 17 European research sites, a total of 1,951 subjects with 2,416 injuries were enrolled in the study.
- All eligible skin lesions in the study were examined with the Nevisense™ Electrical Impedance Spectroscopy System and by excision. biopsy subject to histopathological assessment.
- 1,943 injuries were evaluable for the primary efficacy endpoint (including 265 melanomas48 basal cell carcinomas and seven scaly cell carcinomas).
- The results of the pivotal study showed a sensitivity of 97% for evil one melanoma and specificity of 34,4%.
- The observed sensitivity for non-melanoma skin cancer was 100%.
- The positive and negative predictive values of Nevisense™ were 21.1% and 98.2%, respectively.
- The observed sensitivity and specificity for melanoma from investigational site histopathologists were 85.0% and 98.1%, respectively.
- not serious adverse events or unexpected adverse effects of the device were observed throughout the study.
- However, there is insufficient data to determine the role of Navisense™ in the treatment of patients with melanoma.
What is the clinical use of electrical impedance spectroscopy?
- The Nevisense™ EIS System is intended for use on skin lesions with one or more clinical or historical features of melanoma.
- The system is designed to be used when a clinician chooses to obtain additional information when considering excision.
- It is not intended to be used to confirm a clinical diagnosis of melanoma.
- It should be used by doctors trained in the clinical diagnosis of skin cancer.
What are the indications for electrical impedance spectroscopy?
- Electrical impedance spectroscopy It is indicated for use in primary skin lesions with a diameter between 2 mm and 20 mm.
- Lesions must have intact skin (i.e., non-ulcerated lesions and no bleeding).
- The injuries should not be in hair-Covered areas.
- The device should not be used on palms, soles, genitals, eyes or mucous membrane zones
- The lesions must be devoid of scars or recent trauma.


