Introduction
The physical characteristics of hair, skin and eye color, freckles, melanocytic naevi and the skin's response to the sun is influenced by gene polymorphisms.
Sun exposure stimulates tanning, where melanocytes produce the biopolymer melanin and transfer it to keratinocytes.
Which is the IRF4 gene?
Interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4) gene belongs to a family of DNAthat bind to proteins that play an important role in the development and function of the immune system [1].
IRF4 polymorphisms have been independently associated with pigmentation and age-specific effects on melanocytic nevus count in populations derived from Europe [2,3].
a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) within intron 4 of IRF4, rs12203592 * C/T, plays an important role in pigmentation.
IRF4 It is one of only 2 genes, With tyrosinase (TYR), known to affect the skin, eyes, hair and along with melanocortin 1 receiver (MC1R), freckled. IRF4 independently affects nevus counts throughout the body [4].
IRF4 It is predominantly expressed in blood cells with key functions in lymphoid, myeloid and dendritic cell lineages and adipocytes. IRF4 It is also expressed in melanocytes in nevi and primary melanomas [5,6].
What are the variants of IRF4?
Asian and African populations are fixed for ancestral rs12203592*C allele, being monomorphic. In European populations, the rs12203592*T allele is found at an allele frequency of around 17%. This allele frequency is from 40% in Ireland.
Which are the IRF4-related phenotypes?
The rs12203592*T allele was statistically significantly associated with dark hair color, light eye color, and decreased tanning ability [2,3,7]. Figure 1 shows the frequency of this phenotype by rs12203592 genotype in 1200 individuals from south-east Queensland. Figures 2, 3 and 4 demonstrate the blue eye and freckle phenotype of IRF4 rs12203592 *T/T patients. IRF4 It has also been one of the few genes linked to hair aging. [8].
Phenotype of individuals
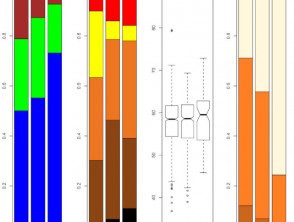
Figure 1. Eye color, hair color, whole-body nevus counts and tanning ability in 1200 IRF4 rs12203592 C/C, C/T and T/T in the Brisbane Naevus Morphology Study. The IRF4 rs12203592*T/T genotype demonstrates a strong association with blue eyes and a reduced tanning response.
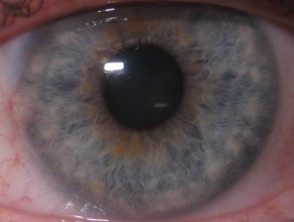
Figure 2. Clinical images of an IRF4 rs12203592*T/T study participant with a history of amelanotic nodular melanoma.
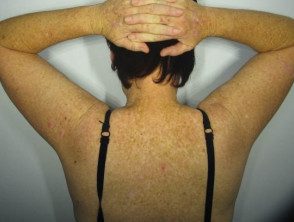
Figure 3. Clinical images of an IRF4 rs12203592*T/T study participant with a history of amelanotic nodular melanoma.
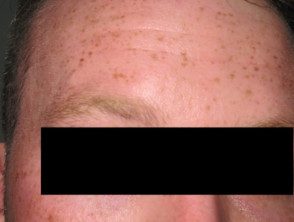
Figure 4. Light skin and freckle phenotype in an IRF4 rs12203592* participant in the T/T control study
A strong genotype by age interaction for total body nevus count has also been reported for this SNP, which is also a predictor of melanoma risk (Table 1). Compared to rs12203592 * C/C or C/T carriers, homozygous Individuals with T/T have higher nevus counts in adolescence, which reverses with age so that adults have lower nevus counts. The rs12203592*T allele was also associated with a decreased increase count (papular and dermal) melanocytic naevi and increased counts of flat nevi (compound and junctional) [3].
The Nevi Study in Children (SONIC) identified five significant associations (p <0.005) entre IRF4 rs12203592 variants and the clinical appearance of nevi. SNPs in IRF4 showed significant associations with globular patterns [9]. the IRF4 The rs12203952 polymorphism was very strongly associated with nevus counts (p <0,0001). T alleles, compared to C, are linked to higher nevus counts at any level of sun exposure.
What are the clinical characteristics of IRF4 variants?
Table 1: clinicopathological characteristics and IRF4 phenotype associations
| IRF4 rs12203592*C=83% | IRF4 rs12203592 * T = 17% |
| Low nevus count in adolescents a,e,f | High nevus count in adolescents a,e,f |
| High nevus count in adults a,e,f | Low nevus count in adults a,e,f |
| Darker skin color yes | Lighter skin color yes |
| Brown/dark eye color yes | Blue/light eye color b,g |
| Better tan yes | Reduced tan yes |
| Melanoma nevus remnant yes | Solar melanoma elastosis yes |
| Melanoma with minor Breslow thickness C | Melanoma with increased Breslow thickness C |
| Increased survival in melanoma. re | Reduced survival in melanoma re |
| lower incidence of nodular melanoma h | Increased incidence of nodular melanoma h |
Table 1: rs12203592 *T carriers have a reduced number of naevi with age, a fairer phenotype, and an increase in Breslow melanoma thickness with located chronic UV Sun damage.
a (Duffy et al. 2010) [3], b (Gibbs et al.2016) [7], c (Gibbs et al.2017) [10], d (Potrony et al.2017) [11], e ( Kvaskoff et al. 2011) [12], f (Orlow et al. 2015) [9], g (Peña-Chilet et al. 2013) [13], h (Rayer et al. 2019) [16]
As they are IRF4 variants diagnosed?
Genetic test for IRF4 Variants are most often performed for research purposes and forensic analysis of DNA samples. [14]. As of 2019, the entire coding region is evaluated on an Illumina Infinium HumanCoreExome-24 Microarrays or by bidirectional Sanger sequence analysis of intron 4.
Does IRF4 Does state affect patient management?
People likely to carry IRF4 rs12203592 * T variants have a phenotype that demonstrates a high nevus count in adolescents, lighter skin and eye color, and a reduced ability to tan. Melanomas in these patients are frequently associated with solar elastosis, increased Breslow thickness (Figure 3) and reduced melanoma survival.
Sun protection includes wearing sun-protective clothing outdoors, applying sunscreen at regular intervals, and avoiding severe or frequent sunburns.
The people who carry the IRF4 A variant gene should be advised to arrange skin checks by a trained healthcare professional. Education on skin self-examination should emphasize lesions that enlarge or change color, shape, and structure. Knowledge of the ABCDE characteristics of melanoma can be helpful; These features are:
- Asymmetry
- Border irregularity
- Color variation
- Diameter >6mm (large size)
- Evolution (change).
The proposed addition of “EFG” (Elevated, firm and growing for more than a month) to the ABCD acronym aids clinical evaluation of lesions. This may be particularly relevant for patients with IRF4 rs12203592 * T/T genotype, whose melanomas are associated with increased Breslow thickness [15].

