What are they venous malformations?
Venous malformations are a type of vascular nevus or birthmark. They are due to malformed dilated veins and are not cancerous. They appear as skin-colored, blue, or purple swellings anywhere on the body, and there are often prominent veins near the surface of the skin. I like it capillary vascular malformations (port-wine stains), venous malformations are always present at birth, although they may become more apparent over time. They can range in size from a small spot to occasionally involving an entire limb. Unlike cavernous hemangiomas, grow in proportion to the overall growth of the child.
Glomuvenous malformation
Glomuvenous malformation is also known as glomangioma or glomangiomatosis. These differ from standard venous malformations by being multiple in appearance, slightly raised, blue or bluish-purple in color. There are characteristic features of this injury on the skin biopsy (histology) Glomuveous malformations can be inherited as a autosomal dominant trait, which means that half of the children of an affected person will have a tendency to develop these lesions to a variable degree. They are due to a mutation in the glomulin gene.
Glomuveous malformations must be distinguished from glomus solitary tumors, which usually occur under or next to a nail in an adult, and are not inherited. They are small, but exquisitely tender blue or purple. nodules with a fibrous border An x-ray may show underlying erosion of the bone Tumors of the glomus solitarius are due to a proliferation of glomus cells; The diagnosis is confirmed by skin biopsy.
arteriovenous malformation
An arteriovenous malformation refers to the communication between an artery and a vein. The affected skin feels warmer than the surrounding skin. It is possible to feel a "thrill" due to the high flow of blood through the arteriovenous malformation. The doctor listening with a stethoscope may hear a roar or "murmur." These are sometimes associated with other abnormalities in various vascular syndromes.
Blue rubber bleb nevus syndrome
Blue rubber bleb nevus syndrome or Bean syndrome is a rare form of venous malformation in which there are lesions in the skin and gastrointestinal tract. There is often a family history, with autosomal dominant inheritance, that is, the tendency to the syndrome is transmitted to half of the children.
Skin lesions present as blue or purple compressible rubbery nodules with a wrinkled surface. There may be a single injury or hundreds of injuries throughout the body. Lesions in the gastrointestinal tract (mouth to rectum) can bleed and cause anemia or rarely, sudden death. The nodules remain unchanged for life.
Surgical excision, sclerotherapy and/or To be Therapy may be indicated. However, in most cases no treatment is required.
A case history has described marked improvement after oral sirolimus (which inhibits angiogenesis) This drug is being investigated as a possible medical treatment for serious vascular malformations, but may have significant side effects.
Blue rubber blister nevus syndrome
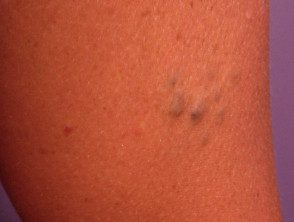
Blue rubber bleb nevus
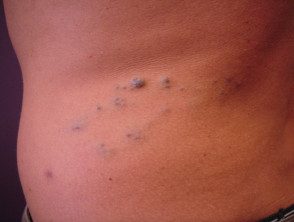
Blue rubber bleb nevus
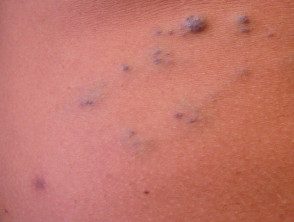
Blue rubber bleb nevus
maffucci syndrome
Maffucci syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that affects both men and women. It is characterized by cartilage growths (enchondromas), bone deformities and venous malformations. The disease is present at birth or develops during childhood.
Venous malformations stand out as soft blue nodules on the arms and legs or elsewhere. Enchondromas are often found in the fingers, toes, or the ends of long bones. Sometimes they result in fractures. Cancer (chondrosarcoma) can arise within enchondromas in approximately 30% of adult patients.
What research should be done?
Venous malformations are usually diagnosed clinically. However, a ultrasound The scan is often done to find out the extent of the abnormality. Characteristically, a compressible tubular venous malformation shows blood vessels. In some cases, fresh or older calcified blood clots (thrombosis) can be detected.
Ultrasound evaluation of arteriovenous malformations also shows evidence of blood shunting between the affected artery and vein with turbulent blood flow.
In more complicated cases it may be necessary to perform Magnetic resonance imaging (Magnetic resonance) or angiography to help plan treatment.
Treatment of venous malformations.
Treatment of venous malformations is very difficult and often involves complex surgery and/or ultrasound-guided sclerotherapy. Vascular lasers may be helpful in some cases.
Extensive malformations require careful evaluation, often by a team of specialists that may include a pediatric dermatologist, pediatrician, radiologist, plastic surgeon and/or vascular surgeon.
General care may include pain relief and compression therapy.

