What is a cyst?
A cyst is a benign, round, dome-shaped encapsulated injury containing fluid or semi-fluid material. It can be firm or fluctuating and you often gave the overlying skin. There are several types of cysts. The most common are described here.
What is a pseudocyst?
Cysts that are not surrounded by a capsule are better known as pseudocysts. These commonly arise in acne.
Who has cysts?
Cysts are very common and affect at least 20% in adults. They can be present at birth or appear later in life. They arise in all races. Most types of cysts are more common in men than women.
What Causes Cysts?
The cause of many cysts is unknown.
- Epidermoid cysts are due to proliferation of epidermal cells within dermis. Its origin is the follicular infundibulum. Multiple epidermoid cysts may indicate Gardner syndrome. The common term sebaceous cyst, it's a misnomer.
- An epidermal inclusion cyst is a response to injury. The skin folds to form a sac that is lined by healthy epidermal cells that continue to multiply, mature, and form curb.
- The origin of a tricilemmal cyst is hair root sheath Heredity is autosomal dominant (the affected gene is within the short arm of chromosome 3) or sporadic.
- The origin of steatocystoma is the sebaceous duct within the hair. follicle. Multiple steatocystoma is sometimes an inherited autosomal dominant disorder due to mutations located to the keratin 17 (K17) gene, when it may be associated with pachyonychia congenital Most often, steatocysts are sporadic, when these mutations are not present.
- The origin of the eruptive. hair The cyst is the follicular infundibulum. It can be inherited as a autosomal dominant disorder due to mutations in the keratin gene.
- A dermoid cyst is a hamartoma, a development error.
- The origin of a ganglion cyst is degeneration of the mucosa connective tissue of a joint.
- Occlusion pilosebaceous units (hair follicles) or eccrine sweat ducts lead to an accumulation of secretions, which can present as milia.
- Occlusion of the orifice of a mucous gland can lead to a fluid-filled cyst in a mucous membrane (lip, vulva, vagina)
- A milium is a pseudocyst due to the inability to release keratin from a attached structure. The origin of primary milium is the infundibulum of the hairy follicle at the level of the sebaceous gland and is a miniature version of an epidermoid cyst. The source of secondary milium is a retention cyst within a hairy hair follicle, sebaceous duct, sweat duct, or epidermis.
- Pseudocysts in acne are formed by occlusion of the follicle by keratin and tallow.
What are the clinical features of cysts?
Epidermoid cyst
- Epidermoid cysts occur on the face, neck, trunk, or anywhere there is little hair.
- Most epidermoid cysts arise in adult life.
- They are more than twice as common in men as in women.
- They appear as one or more flesh-colored to yellowish, adherent, firm, round. nodules of variable size.
- A central pore or punctum may be present.
- The keratinous content is soft, cheesy, and smelly.
- Scrotal and labial cysts are frequently multiple and can calcify.
An epidermoid cyst is also called a follicular infundibular cyst, epidermal cyst, keratin cyst.
Epidermoid cyst
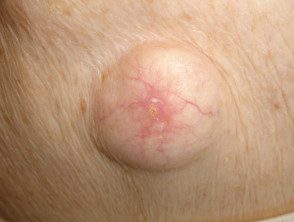
Gardner syndrome
See more images of epidermoid cysts.
Tricilemmal cyst
- The 90% of tricilemmal cysts occurs on the scalp; otherwise, face, neck, trunk and extremities.
- Most tricilemmal cysts arise in middle age.
- In 70% of cases, the tricilemmal cysts are multiple.
- They appear as firm, adherent, round or oval nodules.
- There is no punctum.
- The keratinous content is firm, white, and easily enucleated.
A tricilemic cyst is also called a pillar cyst.
Tricilemmal cyst
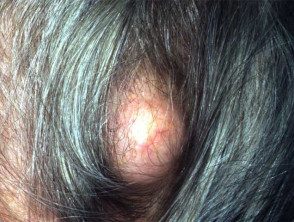
Pillar cyst
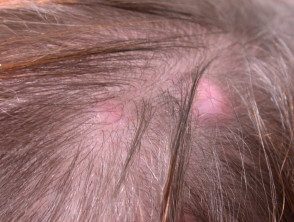
Pillar cysts
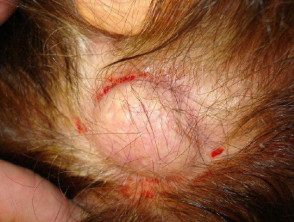
Pillar cyst
See more images of epidermoid cysts.
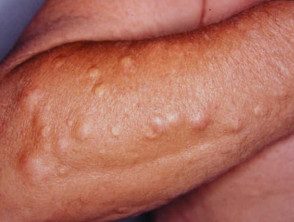
Steatocystoma
- A solitary steatocystoma is known as a simple steatocystoma.
- Most often, there are multiple lesions (multiple steatocystoma) on the chest, upper arms, armpits, neck and scrotum or vulva.
- Cysts appear in the late teens and early 20s due to the effect of androgens and persist for a lifetime.
- They are of free movement, soft pulp to yellow color. papules 3–30 mm in diameter.
- There is no central punctum.
- The content of the cyst is predominantly sebum.
Multiplex steatocystoma
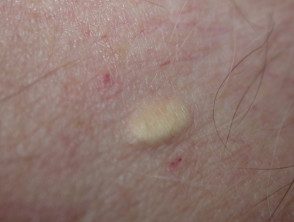
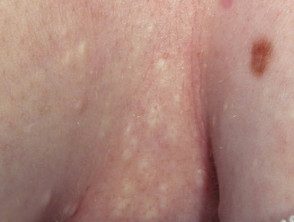
Multiplex steatocystoma
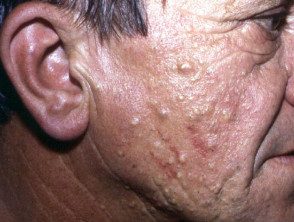
Multiplex steatocystoma
Eruptive hairy cysts
- Eruptive downy hair cysts are present in childhood if family, and then if it is sporadic.
- They are seen in association with multiple steatocystoma.
- Multiple 2–3 mm papules develop over the sternum.
- Cysts contain hairs.
Dermoid cyst
- A cutaneous The dermoid cyst can include skin, skin structures, and sometimes teeth, cartilage, and bones.
- Most dermoid cysts are found on the face, neck, and scalp; often around the eyelid, forehead and forehead.
- It's a thin wall tumor ranging from soft to hard in consistency.
- The cyst forms at birth, but the patient may not present until an adult.
Dermoid cysts
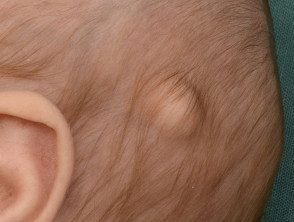
Dermoid cyst
Dermoid cyst
Dermoid cyst
Ganglion cyst
- A ganglion cyst most often involves the scapholunate joint of dorsal doll.
- These arise in young and middle-aged adults.
- They are three times more common in women than in men.
- The cyst is a firm unilocular or multilocular swelling 2–4 cm in diameter that transilluminates.
- The content of the cyst is mainly hyaluronic acid, a sticky substance with a golden color.
Ganglion cyst
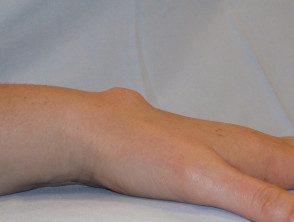
Ganglion cyst
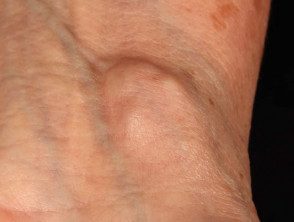
Ganglion cyst
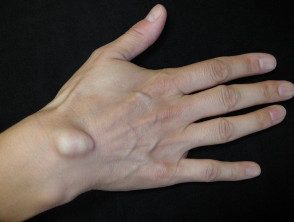
Ganglion cyst
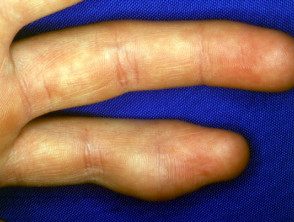
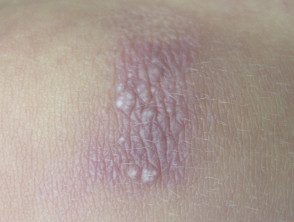
Digital myxoid pseudocyst
-
Mucous / myxoid pseudocysts arise in older adults in the distal phalanx
- Arise from distal interphalangeal joint, associated with osteoarthritis.
- They often present as a longitudinal depression in the nail due to compression at the proximal matrix.
Myxoid pseudocyst
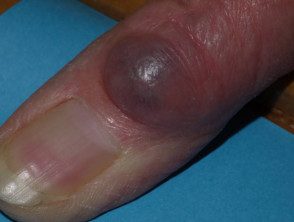
Digital myxoid cyst
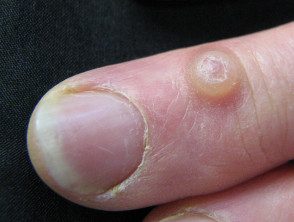
Myxoid cyst
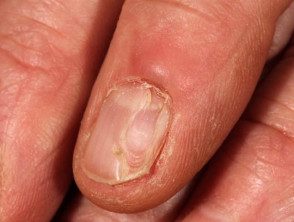
Digital myxoid cyst
See more images of digital myxoid pseudocysts.
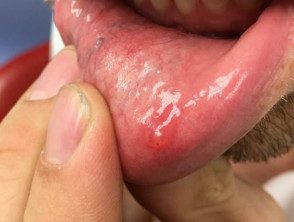
Lip mucous / myxoid cyst
- A cyst on the lip may be due to salivary duct occlusion
- They are also called mucocoele.
- It is smooth to firm, 5–15 mm in diameter, semi-translucent nodule.
Lip mucocele
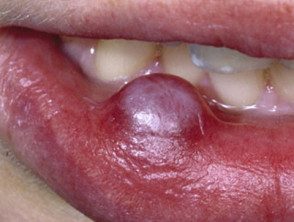
Mucocele of the lip
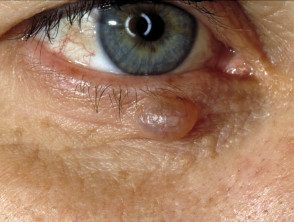
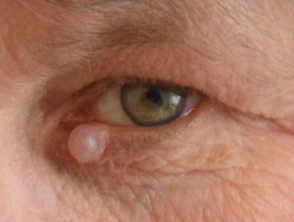
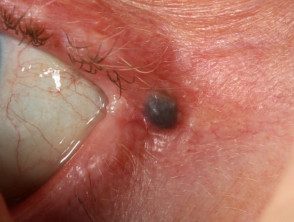
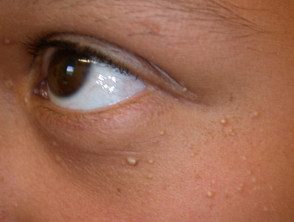
Hydrocystoma
- Hydrocystoma is a translucent, jelly-like cyst that arises on an eyelid.
- It is also known as cystadenoma, Moll's gland cyst, and sweat cyst.
- The common solitary translucent eyelid cyst is an apocrine hydrocystoma.
- Multiple cysts on the lower eyelid are eccrine hydrocystomas.
- Link to apocrine hydrocystoma - pathology.
Hydrocystoma of the eyelid
More images of hydrocystoma of the eyelid.
Milium / milia
-
Milia are 1–2 mm dome-shaped superficial white papules containing keratin
- Primary milia arise in neonates (50%), adolescents and adults; they are rarely familiar and sometimes eruptive.
- Primary milia occur on the eyelids, cheeks, nose, mucous membrane (Epstein's pearls) and palate (Bohn's nodules) in babies; and eyelids, cheeks and nose of older children and adults.
- Transverse Primary milia are sometimes seen through the nasal sulcus or around the areola.
- In milia in license plate, multiple milia arise in a erythematous plaque on the face, chin or ears.
- Secondary miliae arise at the epidermal repair site after blisters or lesions, in epidermolysis bullosa, bullous pemphigoid, late cutaneous porphyria, thermal burn and after dermabrasion.
- Secondary milia are reported as an adverse effect of current steroids, 5-fluorouracil cream, vemurafenib and dovitinib.
Milia
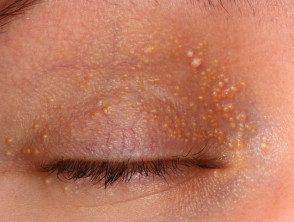
Milia eyelid
See more images of milia.
Vulvar mucous cyst
- A vulvar mucous cyst is due to occlusion of the Bartholin or Skene duct.
- It presents as a mild inflammation in the introitus of the vagina: a later the swelling is a Bartholin cyst and a periurethral swelling is a Skene cyst.
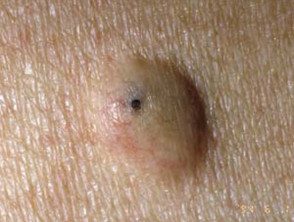
Comedo and acne pseudocyst
- Comedones they are pseudocysts formed by occlusion of the follicle by keratin and sebum.
- Open comedo (blackhead) and closed comedo (whitehead) are small, shallow papules typical of acne vulgaris.
-
Sun comedones appear on sun-damaged skin and are associated with smoking.
- Large non-inflamed pseudocysts accompany inflammatory nodules in nodulocystic acne and hidradenitis suppurativa.
Comedones
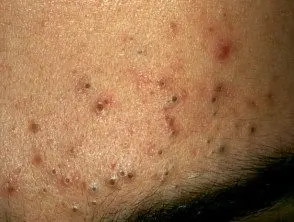
Open comedones
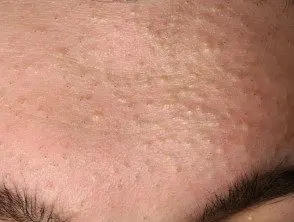
Closed comedones
Atrial pseudocyst
- Follow the pseudocyst of the auricle (outer ear) trauma.
Atrial pseudocyst
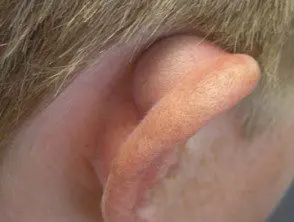
Atrial pseudocyst
Cyst Complications.
Rupture of a cyst
- The contents of the cyst can penetrate the capsular wall and irritate the surrounding skin.
- The tender area, sign inflammation extends beyond the encapsulated cyst.
- Sterile pus may be discharged.
Secondary infection
- An infrequently ruptured cyst can become secondarily infected with Staphylococcus aureus, forming a boil (boil).
Pressure effect
- A dermoid cyst can cause pressure on the underlying bone tissue.
- A ganglion cyst can cause joint instability, weakness, limitation of movement, and can compress a nerve.
- A digital mucous cyst can put pressure on the proximal matrix and cause a malformation of the nail.
Malignancy
- Cutaneous cysts and pseudocysts are notproliferative benign lesions
- Nodulocystic basal cell carcinoma it is a common skin Cancer presenting as a rounded nodule and may be initially mistaken for a cyst, but a constant increase, destruction of the epidermis with ulceration and bleeding occurs eventually.
- A evil one Proliferative tricillémic cyst is a misnomer. It is an extremely rare tumor.
How are cysts diagnosed?
Cysts have typical clinical features. When a cyst is removed surgically, it must undergo a histological exam. The type of lining of the cyst wall and the contents of the cyst help to pathologist Sort it.
-
Epidermoid cysts are lined with stratification. scaly epithelium which contains a granular layer. The content of rolled keratin is observed within the cyst. An inflammatory response may be present in cysts that have ruptured.
-
Tricilemmal cysts have a palisade outer layer without a granular layer. The contents are eosinophilic Hair keratin. Older cysts may exhibit calcification. the proliferating The variety is considered a tumor.
- Steatocystoma has a folded cyst wall with prominent lobes of the sebaceous glands.
- A dermoid cyst contains fully mature elements of the skin, such as fat, hair, sebaceous glands, eccrine glandsand on a 20% apocrine glands.
- The lining of the wall of a ganglion cyst or digital mucous cyst is collagen and fibrocytes. Contains hyaline material.
-
Hydrocystoma has a thin wall of eosinophilic bilaminar cells.
What is the treatment for cysts?
Asymptomatic Epidermoid cysts do not need treatment. In most cases, an attempt to remove only the contents of a cyst is followed by reappearance. If desired, the cysts can be completely removed. Recurrence is not uncommon andexcision can be a surgical challenge
Inflamed cysts are sometimes treated with:
- Incision and drainage
-
Intralesional injection with triamcinolone
- Oral antibiotics
- Delayed excision biopsy
How can cysts be prevented?
Unknown.
What's the outlook for cysts?
Cysts generally persist unless they are surgically removed.
