What is achromatic? nevus?
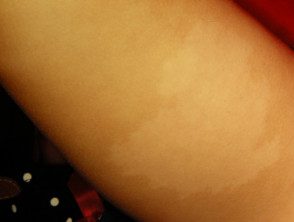
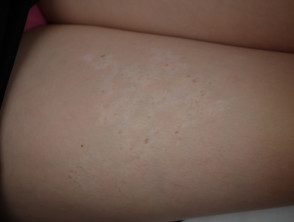
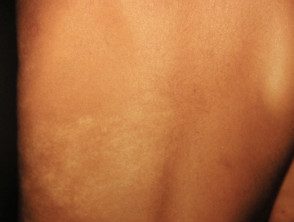
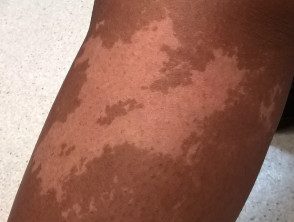
Achromatic nevus is a rare birthmark (nevus) characterized by a well defined pale patch. This is usually several inches in diameter, with a ragged but well-defined edge. The shape and size vary. Often smaller hypopigmented macules popping up around the edges, resembles a paint splatter. [1]
Achromatic nevus (American spelling nevus) is also called nevus depigmentosum and notpigmented nevus. The name is not entirely correct, since the hypomelanotic The patches of an achromatic nevus are not completely white, unlike the areas of depigmentation in vitiligo, What are they amelanoticand completely lacking melanin. Achromic naevi are generally solitary, in contrast to tuberous sclerosis, where multiple pale patches occur and are called ash spots.
Achromatic nevus is usually seen at birth or in early childhood, although lesions may not be apparent until mid-childhood in those with light-colored skin. Nevi remain stable over time. Achromatic nevus most commonly arises on the trunk, but it can also appear on the extremities and elsewhere. [4]
Achromatic nevus Achromatic nevus Achromatic nevus Achromatic nevus Achromatic nevus Achromatic nevusAchromatic nevus


What is the cause of the achromatic nevus?
Achromatic nevus is a form of cutaneous mosaicism is caused by an altered clone of melanocytes (pigment cells) with a decreased ability to produce melanin (brown pigment). It can be caused by a reduced number of melanocytes, a reduced production of melanin, or the inability of the melanocytes in the affected area to transfer melanosomes (containing melanin granules) to keratinocytes (skin cells). [2,3]
What are the variants of the achromatic nevus?
- Isolated achromatic nevus
- Segmental Achromatic nevus, also called segmental depigmentation disorder, has middle line demarcation and ill defined side borders The hypopigmented form of “segmental pigmentation disorder"
- Linear or “systematized”, the achromatic nevus has cutaneous findings that overlap with the hypomelanosis of Ito.
Occasionally, the achromatic nevus is associated with other neurocutaneous Colocalized disorders lentigines have been reported and are seen in figure 3 (top right) above. They can represent a reverse mutation. The ash-leaf macules seen in tuberous sclerosis are oval-shaped hypopigmented macules and resemble achromatic nevi, but usually present as multiple lesions.
How is the achromatic nevus diagnosed?
Coupe identified the diagnostic criteria for achromatic nevus in 1976: [4]
- The pale skin patch is present at birth or early in life.
- It stays in the same place for life.
- There is no alteration in texture or change in sensation in the lesions.
- There is no dark border around the affected skin.
In Wooden lamp On examination, the achromatic nevus appears whitish, compared to the chalk-white accentuation seen in vitiligo. [5]
What is the treatment for achromatic nevus?
Treatment of nevus achromatic is often unnecessary. Cosmetic camouflage can be helpful. Some of the options that have been used to attempt repigmentation include: excimer To be, phototherapy (PUVA) and skin graft. [5]
