What is bufexamac?
Bufexamac is a current anti-non-steroidalinflammatory drug (NSAID) It is generally combined with a topic anesthetic and an antiseptic agent.
Bufexamac is a recognized cause of contact allergy. dermatitis at the application site, and may also cause a extended polymorphic cutaneous eruption.
What is bufexamac used for?
Bufexamac preparations have traditionally been used to treat insect bites, stings, minor cuts, abrasions, sunburns, thermal and inflammatory burns. skin disease (such as dermatitis) [1,2]. However, there is little evidence to support its effectiveness [3]. It has also been previously manufactured as suppository for hemorrhoids (piles).
In which countries is bufexamac found?
Due to its adverse effects and establishment as a contact. allergenbufexamac is no Available in the following countries as of August 2018 [1,4]:
- New Zealand
- Japan
- European Union (including the United Kingdom)
- U.S
- Canada.
Bufexamac is still available on the counter in other countries. In Australia, it is available as a topical preparation at 5% in combination with lidocaine hydrochloride at 1% (also called lignocaine) hydrochloride monohydrate and chlorhexidine gluconate at 0.1% (2018).
What are the reactions to bufexamac?
Bufexamac has been established as a cause of allergic contact dermatitis. [4]. It can also result in [1.5–11]:
- Urticaria
- Pruritus
- Edema
- Burning
- Peeling
- Erythema multiform reaction
- Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis
- Pruritus pigmented skin disease
- Symmetrical drug related intertriginous and flexural rash (SDRIFE).
How is a allergy to bufexamac diagnosed?
A adverse reaction bufexamac is diagnosed by taking a careful history of the patient, examining the eruptionand patch tests.
A allergic reaction to bufexamac may appear similar to the condition for which bufexamac was being used, so reactions to bufexamac may not be reported.
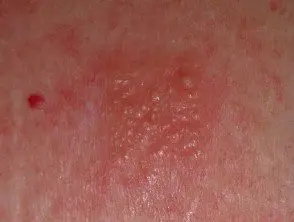
A positive patch test
How is an adverse reaction to bufexamac treated?
The use of bufexamac should be discontinued and should be avoided in the long term.
Any resulting dermatitis is treated with topical corticosteroids and emollients.
