What is it nevus simplex?
Naevus simplex is a common, benign capillary vascular malformation. It occurs at birth as pink or red. patch and is most often seen on the nape, eyelid, or glabella [1,2].
Naevus simplex is also called:
- Salmon patch
- Stork bite (when it's on the nape)
- Angel's kiss (when on glabella and eyelids)
- Naevus flammeus simplex.
Naevus simplex - the brand of the stork
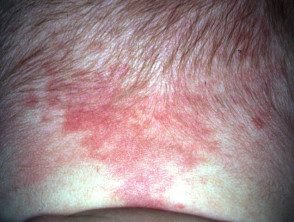
Naevus simplex
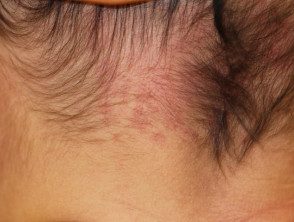
Naevus simplex
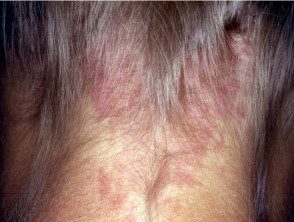
Naevus simplex adult
Who gets naevus simplex?
Naevus simplex affects babies of all races; It occurs in about 40% in Caucasian babies and less often in dark-skinned babies. [1.3]. It affects boys and girls equally [4].
What causes naevus simplex?
Naevus simplex is the result of a delay in the maturation of skin cells during embryonic development, after the migration and fusion of cells in the skin's nervous system (neuroectoderm). This results in the characteristic dilation of the dermal capillaries that defines the naevus simplex skin patch. Regulation reduced by autonomic nerves it may be a contributing factor in cases of naevus simplex [2,3].
What are the clinical features of naevus simplex?
Naevus simplex is present at birth as single or multiple, flat, pink or red patches, usually occurring with an indistinct, irregular border and pallor in compression [1,2]. Naevus simplex turns redder with crying, fever, holding your breath, straining, vigorous physical activity, and changes in room temperature. [1,2,5]. They tend to become less prominent as the child grows.
Skin lesions usually appear on middle line [4] and can be bilateral and symmetrical in presentation [6]. They are most commonly found on the nape of the neck, eyelids, and glabella, but can also affect the forehead, scalp, nose, lips, and back. [1,2]. Naevus simplex is neither painful nor itchy [7].
The term "naevus simplex complex" has been proposed to extended injuries that occur beyond common sites [2].
Associations of diseases with naevus simplex
Middle line lumbosacral The nevus simplex is sometimes called a "butterfly mark" and is occasionally seen in a baby with spinal dysraphism. Imaging studies looking for spinal dysraphism (abnormal neural tube fusion) may be done if there are other local skin changes, such as excess hair increase (located hypertrichosis), a dermis breast or hole, a lipoma, or a deviant gluteus cleft, or many similar injuries elsewhere. Babies with a simple nevus in the lumbosacral midline often also have other similar lesions that appear elsewhere [2,4].
Naevus simplex is occasionally seen in a baby with another condition, such as:
- Beckwith - Wiedemann syndrome [2]
- Macrocephalycapillary malformation syndrome [2]
- Odontodysplasia [2]
- Nova syndrome [2]
- Roberts syndrome [2]
- Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome [1].
It is unclear whether there is a true association of naevus simplex with these syndromes. [1,4].
How is naevus simplex diagnosed?
Naevus simplex can be diagnosed by its clinical appearance and generally no further testing is required [7].
Which is the differential diagnosis for naevus simplex?
Naevus simplex is sometimes confused with naevus flammeus (port wine stain) or infantile proliferative hemangioma (strawberry nevus) because these vascular lesions are also seen in infants.
Naevus flammeus
Naevus flammeus is a capillary vascular malformation found in 0.3% in newborns. [1.6]. Lesions appear as pink, red, or purple spots and can be localized, extensive, or multiple. [1.6]. Unlike naevus simplex, naevus flammeus tends to be unilateral, often persistent, darkening and thickening with age [1,6].
Infantile proliferative hemangioma
Infantile proliferative hemangioma is a vascular tumor. tumor found in 1.1–2.6% of newborns, and occurs in 10% of newborns before 1 year of age. It affects girls more often than men. The hemangioma begins as a pink patch and then enlarges. It is most commonly found on a baby's head and neck, but can also arise elsewhere on the body. Infantile proliferative hemangioma usually resolves after childhood, but may leave a residual mark [1,6].
Vascular lesions in infants.
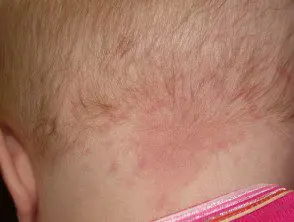
Naevus simplex

Naevus flammeus
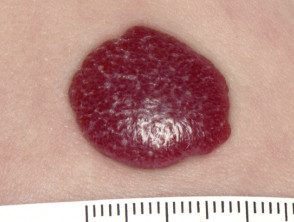
Infantile proliferative hemangioma
What is the treatment and result for naevus simplex?
At most places in the body, naevus simplex fades and disappears within the first 1 to 2 years of life. [two]. A injury in the nape it fades more slowly and incompletely, and has a 50% chance of persisting indefinitely [1,5]. Since this site is often covered in hair, it may not be a cosmetic problem.
Pulsed dye To be Therapy could be considered to lighten the color of a persistent lesion [6].
[gallerydata-ids = ”36856: Naevussimplex (1); 36851: Naevussimplex (2); 36855: Naevussimplex (3); 36853: Naevussimplex-one year later [gallerydata-ids =” 36856: Naevussimplex (1); 36851 ); 36855: Naevussimplex (3); 36853: Naevussimplex — ayearlater [1]; 36852: Naevus simplex - 2 months later [2]; 36854: Naevus simplex - 20 months later [3] ”data-copyright-ids =” 36856 :; 36851 :; 36855 :; 36853 :; 36852 :; 36854: ”> Resolution of naevus simplex over time