Ad
Skin cancer
Application to facilitate skin self-examination and early detection. read more.
What is a melanocytic nevus?
A melanocytic nevus (Nevus in American spelling) is a mole, a common skin injury composed of nevus or specialized cells melanocytes. There are several types of melanocytic. naevi (nevi)
What is a atypical melanocytic nevus?
An atypical melanocytic nevus is a mole with unusual features.
- "Atypical melanocytic nevus" is often shortened to "atypical nevus."
- The oldest names for atypical melanocytic nevus include Clark naevus and mole BK.
- Some people prefer to use the term dysplastic nevus when referring to an atypical nevus, but strictly speaking the dysplastic nevus is a histological Description of a particular type of melanocytic nevus.
What does an atypical nevus look like?
The term atypical nevus is sometimes used to refer to any funny-looking mole, and sometimes to refer to a suspected melanocytic lesion evil one melanoma (a cancerous mole).
A definition of an atypical nevus is a mole with at least 3 of the following characteristics.
- Size> 5mm diameter
- Poorly defined or blurred edges
- Irregular margin resulting in an unusual shape
- Different shades of color (mainly pink, tan, brown, black)
- Flat and bumpy components.
Atypical nevi
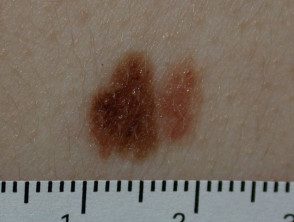
Atypical nevi
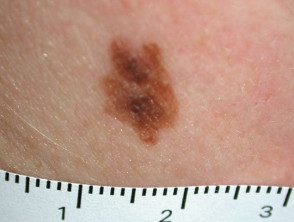
Atypical nevi
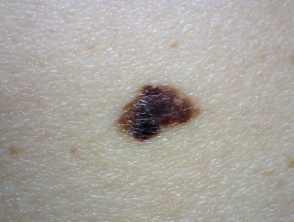
Atypical nevi
See more images of atypical nevi ...
Who has atypical nevi?
Atypical nevi may occur sporadically or may be family (inherited).
Sporadic atypical nevi
Sporadic atypical nevi primarily affect light-skinned individuals with light colors. hair and freckles (phototype 1 or 2). They are more numerous if they have been frequently exposed to the sun.
Atypical nevi can develop at any time, but most of them develop within the first 15 years of life. Typically, people with sporadic atypical nevi have one to ten moles over 6mm in diameter.
Family atypical nevi
Atypical nevi that run in families can be part of the FAMM syndrome. FAMM is short for Familial Atypical Mole and Melanoma. People with FAMM syndrome have the following:
- One or more first or second degree relatives diagnosed with malignant melanoma at an early age (<40 años);
- A large number of nevi (often more than 50), some of which are atypical;
- Nevi that are dysplastic in histopathology.
FAMM syndrome was previously known as dysplastic nevus syndrome.
People with FAMM syndrome can have several hundred atypical nevi.
Atypical nevi
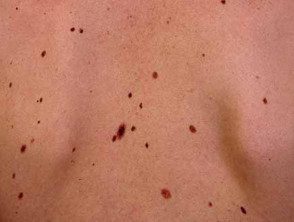
Atypical nevi
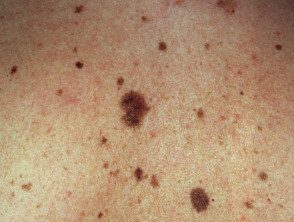
Atypical nevi
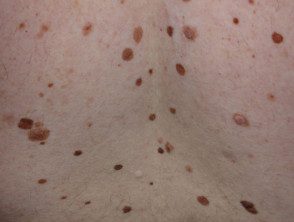
Atypical nevi
What is a dysplastic nevus?
The term dysplastic nevus is best used for a nevus with a microscopic appearance. Only a minority of clinically atypical nevi meet the microscopic criteria for dysplastic nevi. Many histologically Dysplastic nevi are clinically banale (eg, small in size and uniform in color and structure).
Histological dysplasia It can be mild, moderate, or severe. Different pathological criteria of a dysplastic nevus are listed here.
- The dysplastic nevus can be a junctional nevus (when the melanocytes are at the epidermodermal junction) or a compound nevus (when the melanocytes are at the epidermodermal junction and within the dermis)
- The nevus cells form a row along the dermoepidermal junction (this is reported as lentiginous proliferation), with or without nevus cells in nests (also called theques).
- These themes are often irregular in size and shape and can be "bridged" or joined.
- Cells can be spindle-shaped (elongated) or epithelioid (broad, similar epidermal keratinocytes)
- There may be cytology atypia (cells that are smaller or larger than usual).
- There may be fibrosis or scars in the dermis.
- Inflammatory cells can infiltrate the injury
- Associated blood vessels it can be increased in number or enlarged.
Melanoma can arise within a dysplastic nevus, within a normal non-dysplastic melanocytic nevi, or more often on normal-appearing skin.
What is the importance of atypical nevi?
People with 5 or more clinically atypical nevi have a higher risk of developing melanoma than the general population; The relative risk is reported to be six times greater than that of people without atypical nevi. People with FAMM syndrome have an extremely high risk of developing melanoma.
Melanocytic nevi are harmless (benign) and does not need to be removed. However, it is not always easy, even for an experienced dermatologist to know if an injury is a nevus or a melanoma, especially if there are atypical characteristics. Dermoscopy on trained hands can help. In case of doubt, a suspicious or changing atypical nevus should be removed by excision biopsy. It is best to avoid a partial biopsy, as the test may lose a small focus of melanoma. A pathologist It will generally make the correct diagnosis, although deeper levels and / or a second opinion are sometimes required.
People diagnosed with atypical nevi should be taught how to self-examine the skin for new skin lesions and changes in existing moles that may indicate the development of melanoma. People with numerous moles should visit their GP or dermatologist regularly for a thorough skin check.
Maintaining photographic records of melanocytic nevi (often with dermoscopic images) is often helpful; the digital archive at a photographic skin surveillance clinic is suitable for people with many moles or atypical nevi. Close-up photos with dermoscopic views should be repeated from time to time, so that the change can be detected early and determine its significance.
Careful sun protection is recommended for everyone, but it is especially important for people with many nevi or atypical nevi. Avoid excessive exposure to the sun and sunburn, dress and wear an SPF50 + sunscreen when you are outdoors in the middle of the day or for long periods of time.

