What is chrome? allergy?
Chromium allergy occurs with allergic contact dermatitis. It is due to a delay hypersensitivity reaction to chromium salts (chromates), particularly Cr(III) and Cr(VI).
Chromium salts are used as an ingredient in the manufacture of many other products such as cement, mortar, leather, paints and anticorrosives.
Although most people associate “chrome” with the bright, shiny, durable finish of chrome metal products, contact with them rarely causes a chrome allergy. Allergic contact dermatitis due to contact with a metal object is usually caused by nickel.
Chrome allergy
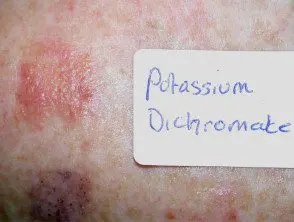
Positive patch test for potassium dichromate
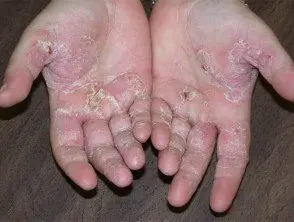
Chronic hand dermatitis in a patient allergic to chromium
Where are chromium salts found?
Most exposure to chromium salts is through the workplace, primarily from cement and mortar used in the construction industry. There are many other sources of chromates.
Home / personal sources of chromium salts
Examples include:
- Chrome-tanned leather goods, including shoes, gloves and other wearable items and accessories
- Yellow or green cosmetics
- Disinfecting and bleaching agents
- Safety match heads off and no light
- Green felt fabric used to cover pool and card tables
- Anti-rust primer and in yellow or green paint.
- Yellow-green tattoo ink
- radiator coolants
- Dental or orthopedic implants
Working sources of chromium salts.
Allergic cement dermatitis is usually due to dichromates found in cement and is highest among workers who handle wet cement. Please note that cement also causes irritating contact dermatitis.
- Primers in the automotive industry.
- Metallurgists and welders of chromium steel alloys
- Diesel locomotive radiator fluids, chromates used to prevent oxidation or radiators and pipes
- Plaster-like mixtures used in building repairs contain chromates.
- Dyemakers, colormakers, paintmakers, painters
- Engraving solutions
- pulp and paper industry
- artificial florists
- Photographic workers
- Pottery workers
- Carpenters
- Explosives workers
What are the reactions to chromium salts?
Reactions to contact with chromium salts include:
- Allergic contact dermatitis
- Irritant contact dermatitis
- Air contact dermatitis
- Prurigo pigment
- Systemic contact dermatitis due to oral chromium picolinate as a supplement
- Ulceration of the skin and drilling of the nose pulp
The insertion of intracoronary stents, hip and knee replacements, and other chromium-containing implants sometimes fail. These procedures may be associated with several skin problems, including eczema, vasculitis and urticaria. It is unknown if this is the result of a allergic reaction to chrome but this has been suspected in some cases.
Chrome ulcers and perforation of the nasal septum
- Chromium ulcers and nasal septal perforation are most commonly seen in cases of industrial exposure and can occur without chromate allergy.
- Chrome ulcers or chrome holes are usually scabby, painless lesions that reveal a 2-5 mm pit. ulcer covered with exudate.
- Ulcers occur most frequently on exposed parts of the body, primarily the hands, forearms, and feet. They also easily develop at the site of insect bites and stings, sores, or other injuries.
- Initially, ulceration of the nasal septum may be painless, but with continued exposure, the necrotizing The effect of chromates on underlying tissues can become painful and cause permanent scarring and disfigurement.
- The reaction still occurs in workers exposed to strong chromate solutions in electroplating, tanning manufacturers, and chromium producers.
Cement dermatitis
Cement dermatitis is more predominant in construction workers, but can occur in artists, DIY builders, or other people who are exposed to cement through work or a hobby. Dichromates in cement are the cause of allergic contact dermatitis reactions. Primary Irritant reactions of cement dermatitis include dryness and fissure skin damage caused by the drying (hygroscopic) properties of cement and skin lesions or ulcers caused by mechanical irritation due to rough silica particles in the cement. People can develop cement dermatitis after working for many years without any problems.
Am I allergic to chromium salts?
Chromium allergy is diagnosed from medical history and by performing special allergy tests, called patch tests, using a solution of potassium dichromate.
Characteristics of a positive patch test for potassium dichromate ion
- Patch Test Site Itches Instead of Burning
- The reaction is papulovesicular
- The reaction may spread beyond the boundaries of the original patch testing site.
- The reaction persists for at least three days.
Chromium dermatitis can persist in people even after they change occupations and are no longer exposed to chromates. Approximately two-thirds of people sensitive to chromates will remain allergic even when tested several years later.
What is the treatment for chromium allergy?
Avoidance is the only long-term management strategy for chromate allergy. Chromate dermatitis can become a chronic debilitating problem, so early diagnosis, followed by measures taken to minimize exposure or cease all contact with chromates is key to the management plan. Delaware-sensitization or hardening to chromates should not be relied upon.
Once dermatitis appears, the treatment is as for any acute dermatitis/eczema, with current corticosteroids, topical calcineurin inhibitors, emollients and treatment of any secondary bacterial infection (Staphylococcus aureus) Treatments for persistent or severe chromate allergy include phototherapy and immunomodulatory treatments such as azathioprine, cyclosporine, and methotrexate.
When it cannot be avoided, various methods have been used to try to minimize exposure.
Methods to minimize exposure to chromate.
- Wear protective clothing and employ non-contact techniques.
- The addition of other chemicals to cement or mortar neutralizes the chromate content; They are usually iron sulfate or a combination of barium hydrate, nitrate and chloride with lead acetate.
- Avoid leather footwear and other leather items in contact with the skin.
- Application of a barrier. cream made from ascorbic acid (vitamin C) and EDTA (a chemical that binds metals).
- Ascorbic acid impregnation in respirator filters improves protection against inhalation of chromate powder, particularly useful in chromate-sensitive printing and lithography workers.
- The use of disposable hand towels by workers in the chromate industry prevents cross contamination.
- Thoroughly wash all clothing contaminated with chromates.
Some people should also be advised to avoid certain foods high in chromium, such as tomatoes, broccoli, lettuce, and turnips.
What should I do to avoid a chromium allergy?
In the workplace, try to avoid exposure to chromates. However, this may not be feasible, so use measures to minimize exposure as described above. Identify potential sources of exposure using Material Safety Data Sheets; These are required for all chemicals and substances that may come into contact within the workplace.
Outside of the workplace, the best way to avoid a chromium allergy is to be aware of possible sources of chromates. Wearing thick socks and reducing foot perspiration can help reduce chromate-induced shoe dermatitis. If possible, avoid leather or choose leather items that have been vegetable tanned.
Use only cosmetics that you know do not contain chromates. Avoid direct contact with matches and do not keep matches in clothing pockets. Thoroughly wash all clothing contaminated with chromates.
If you must use products containing chromates, wear appropriate gloves or other protective clothing to avoid contact with skin. You dermatologist may have more specific advice, especially if you are very sensitive to chromates.
Alternative names for chrome
Chrome is known by several other names. These include:
- Chromate
- Chrome
- chromium salt
- Potassium dichromate
- chromium sulfate
- Chromite
Avoid all this. At work, ask for a material safety data sheet to help identify alternatives that are safe, thus avoiding contact with material containing chromates.
More information
CAS number: 7778-50-9
Formula: Cr2K20 07 7 (the hexavalent form of chromium)
Cross reactions:
- Cobalt
- Nickel
- Trivalent chromium compounds
Sensitizer
The main sensitizers are dichromates.
Patch test:
0.5% potassium dichromate in Vaseline
Sources of exposure to chromium and chromium salts.
- Anticorrosives
- Antioxidant coatings
- Antioxidant primer paints.
- mortal remains
- artificial flowers
- The batteries
- Bleachers
- Boiler linings
- Ceramics
- Cigarettes
- Cement
- Cooling oils
- Cosmetics (mascara/eye shadow)
- Cutting oils
- Degreasing solvent
- Detergents and bleaches
- Dyes (textile)
- Enamel
- Engraving solutions
- Explosives
- Fabrics
- foundry sand
- furniture polishers
- Queues
- Green cloth for cards, billiards, pool tables
- Drogas homeopáticas
- ink
- Artículos de cuero (guantes, zapatos, sombreros, billeteras, bolsos, ropa)
- Cintas magneticas
- Partidos (seguridad)
- Aleaciones de metales
- Probadores de leche
- Mortero
- Newspaper
- Impresión offset
- Aceite de metalurgia
- Pernos o tornillos ortopédicos
- Marcapasos
- Pintar
- Papel (papel de fotocopia)
- Photography
- Pulimentos y ceras (zapatos, piso, etc.)
- Sellos
- Cal viva
- Materiales refractarios
- Rubber gloves
- Lustra zapatos
- Zapatos
- Solvente
- Sutura intestinal quirúrgica (crómica)
- Tinte de tatuaje
- Proof reagent (laboratorio)
- Textile dyes
- pantallas de televisión
- Soldadura
- Wood preservatives
