What is allergic contact? dermatitis?
Allergic contact dermatitis is a form of dermatitis /eczema caused by a allergic reaction to a material called allergen, in contact with the skin. The allergen is harmless to people who are not allergic to it. Allergic contact dermatitis is also called contact. allergy.
Who gets allergic contact dermatitis?
Allergic contact dermatitis is common in the general population and in specific employment groups.
- It is more common in women than men, mainly due to nickel allergy and, recently, to the acrylate allergy associated with nail cosmetics.
- Many young children are also allergic to nickel.
- Contact allergy to current Antibiotics are common in patients over the age of 70.
- Allergic contact dermatitis is especially common in metalworkers, hairdressers, beauticians, healthcare workers, cleaners, painters, and florists.
What causes allergic contact dermatitis?
Allergic contact dermatitis is type 4 or late. hypersensitivity reaction and occurs 48–72 hours after exposure to the allergen. The mechanism involves CD4 + T-lymphocytes, who recognize a antigen on the surface of the skin, releasing cytokines that activate the immune system and cause dermatitis. Note:
- Contact allergy occurs predominantly from an allergen on the skin rather than from internal sources or food.
- Only a small number of people react to the specific allergen, which is harmless to those who are not allergic to it.
- They may have been in contact with the allergen for years without causing dermatitis.
- Contact with small amounts of an allergen can induce dermatitis.
- Patients with impaired skin barrier function are more prone to allergic contact dermatitis, for example, patients with leg ulcers, perianal dermatitis or chronic irritating contact dermatitis.
- Patients with atopic dermatitis associated with defective filaggrin (a structural protein in the stratum corneum) have a high risk of also developing allergic contact dermatitis.
What are the clinical features of allergic contact dermatitis?
Allergic contact dermatitis arises a few hours after contact with the responsible material. It is established for a few days as long as the skin is no longer in contact with the allergen.
Allergic contact dermatitis is generally limited to the site of contact with the allergen, but can spread outside of the contact area or become generalized.
- Transmission from the fingers can cause dermatitis of the eyelids and genitals.
- Dermatitis is unlikely to be due to a specific allergen if the skin area that is most in contact with that allergen is not affected.
- The affected skin may be red and itchy, swollen and blistered, or dry and bumpy.
Some typical examples of allergic contact dermatitis include:
- Eczema on the skin in contact with jewelry, due to contact nickel allergy
- Reactions to fragrances in perfumes and household items.
- Eczema under adhesive plaster, due to contact allergy to rosin
-
Swelling and blisters of the face and neck in reaction to permanent hair dye, due to allergy to paraphenylenediamine
- Hand dermatitis caused by rubber accelerator chemicals used in the manufacture of rubber gloves.
- Itchy red face from contact with methylisothiazolinone, a preservative in hair products and wet wipes
- Dermatitis on the tips of the fingers due to acrylates used in hair extensions and nail cosmetics.
- Reactions after dental implants containing acrylates
-
Located blisters at the site of topical medications how antibiotics
- Swelling and blistering at exposed sites (eg, face and hands) due to contact with plants such as poison ivy or, in New Zealand, the Japanese wax tree Toxicodendron succedaneum
There is a very long list of materials that have caused contact allergy in a small number of people.
Allergic contact dermatitis
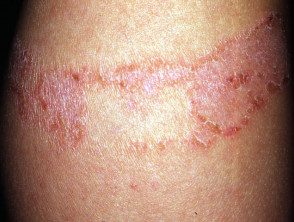
Adhesive plaster reaction
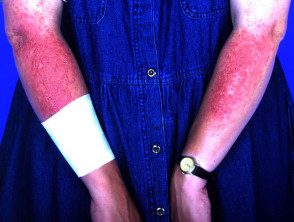
Sunscreen reaction
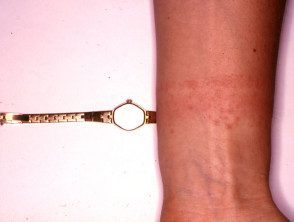
Watch the reaction of the strap
See more images of allergic contact dermatitis.
- Facial dermatitis images
- Hand dermatitis images
- Limb dermatitis images
- Trunk dermatitis images
- Patch imaging test results
Which is the differential diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis?
Allergic contact dermatitis should be distinguished from:
-
Irritant contact dermatitis, which is due to irritation or repetitive Skin lesions. Irritants They include water, soaps, detergents, solvents, acids, alkalis, and friction. Irritant contact dermatitis can affect anyone, as long as they have had enough exposure to the irritant, but people with atopic dermatitis are particularly sensitive. Most cases of dermatitis on the hands are due to contact with irritants. Irritant contact dermatitis can occur immediately after a single injury or develop slowly after repeated exposure to an irritant.
- Other forms of dermatitis, which can simulate allergic contact dermatitis.
-
Contact urticaria, in which a eruption appears within minutes of exposure and fades within minutes to hours. The allergic reaction to latex is the best-known example of allergic contact urticaria.
-
Fungal infections; ringworm of the body may present as unilateral eruption.
What are the complications of allergic contact dermatitis?
Allergic contact dermatitis begins as a localized reaction to an allergen in contact with the skin, but serious reactions can generalize due to self-eczematization and can lead to erythroderma.
Ingestion of a contact allergen can rarely lead to the baboon syndrome or generalized systemic contact dermatitis.
Photoallergy
Sometimes a contact allergy arises only after the skin has been exposed to ultraviolet light. The rash is limited to areas exposed to the sun even though the allergen may have been in contact with covered areas. This is called photocontact dermatitis.
Examples of photoallergy include:
- Dermatitis due to a sunscreen chemical, which affects the upper part but not below the surface of the arm.
- Dermatitis of the face, neck, arms and hands due to antibacterial soap.
How is allergic contact dermatitis diagnosed?
Sometimes it is easy to recognize a contact allergy and no specific testing is needed. Having a very good history, including information about the work environment, hobbies, products in use at home and work, and sun exposure will increase the chances of finding a diagnosis. The rash usually (but not always) goes away completely if the allergen is no longer in contact with the skin, but reappears even with slight contact with it again.
The open application test is used to confirm contact allergy to a cosmetic, such as a moisturizer. The suspected product is applied several times a day for several days to a small area of sensitive skin. The internal appearance of the upper arm is adequate. Contact allergy is likely if dermatitis develops in the treated area.
Dermatologists will perform patch tests on patients with suspected contact allergy, particularly if the reaction is severe, recurrent or chronic Tests can identify the specific allergen causing the rash.
Yeast skin scrapings for microscopy and culture can exclude fungi infection.
The dimethylgloxime test is available for a "spot test" if a product contains nickel.
What is the treatment for allergic contact dermatitis?
It is important to recognize how you are in contact with the responsible substance so that, whenever possible, you can avoid it.
- Find out exactly what you're allergic to by having full patch tests.
- Identify where the allergen is located and read the labels of all products before use.
- Carefully study your environment to locate the allergen. Note: Many chemicals have multiple names, and cross-reactions to similar chemicals with different names are common.
- Wear appropriate gloves to protect your hands from touching reactive materials, and remove gloves appropriately. Some chemicals will penetrate certain gloves; seek the advice of a security expert.
- You ask dermatologist help.
Active dermatitis is usually treated with the following:
- Emollient creams
- Topical steroids
- Topical or oral antibiotics for secondary infection.
-
Oral steroids, generally short courses, for severe cases
-
Phototherapy or photochemotherapy.
-
Azathioprine, cyclosporine, or another immunosuppressive agent.
-
Tacrolimus ointment and pimecrolimus cream they are immunomodulatory calcineurin inhibitors and may be useful for allergic contact dermatitis.
What is the result of allergic contact dermatitis?
Contact allergy often persists throughout life, so it is essential to identify the allergen and avoid touching it. Dermatitis may reappear on re-exposure to the allergen.
- Some Allergens they are more difficult to avoid than others, as airborne allergens are a particular problem (eg, epoxy resin, composite pollen).
- The longer a person suffers from severe allergic contact dermatitis, the longer it will take to disappear after the diagnosis is made and the cause is detected.
- Dermatitis can disappear by avoiding contact with the allergen, but sometimes persists indefinitely, for example, allergy to chromate.
Forecast it depends on patient education and compliance to avoid allergens and proper skin care.
