What is folliculitis?
Folliculitis is inflammation of the hair follicle because infection, chemical irritation or physical injury. Bacterial Folliculitis is the most common form of folliculitis.
What causes bacterial folliculitis?
Bacterial folliculitis is usually due to Staphylococcus aureus. Less frequently, coagulasenegative and gram-negative staphylococci organisms They are responsible, including anaerobes. Spa pool folliculitis is caused by Pseudomonas.
Who gets bacterial folliculitis?
Bacterial folliculitis affects children and adults, with adolescents and young adult men being infected more frequently. This predominant Worldwide.
The following factors predispose to bacterial folliculitis:
- Maceration and occlusion (clothing, dressings, ointments)
- Frequent shaving, waxing or other forms of hair removal.
- Friction for tight clothing
- Atopic dermatitis
- Acne or other follicular skin disorder
- Use of current corticosteroids
- Previous long-term use of antibiotics
- Anemia, obesity, diabetes, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) / AIDS, viral hepatitis, Cancer and another chronic disease
- Bathing in an improperly cleaned Jacuzzi or pool.
What are the clinical characteristics of bacterial folliculitis?
Bacterial folliculitis can be superficial or affect the entire hair follicle (a boil). It can arise in any part of the body, but it is most often diagnosed in the scalp, the beard area, armpit, buttocks and extremities. Systemic Symptoms are rare. Different types of bacterial folliculitis are described below.
Superficial folliculitis
Superficial staphylococcal folliculitis presents with one or more follicles pustules. They can cause itching or mild pain. Superficial folliculitis heals without scarring.
A stye or stye is a bacterial folliculitis that affects an eyelash.
Furunculosis / boils
Furunculosis or boils present as one or more painful, hot, firm or fluctuating, Red nodules or walled abscesses (collections of pus). An anthrax is the name used when a focus of infection involves several follicles and it has multiple draining breasts. Recovery leaves a scar.
Gram-negative folliculitis
Gram-negative folliculitis develops in people who use long-term antibiotics for acne. Infection with gram-negative organisms causes pustules at acne sites on the face, neck, and upper trunk.
Folliculitis in a hot tub
Folliculitis in the hot tub or spa pool presents with pain papules and pustules on the trunk a few hours after soaking in hot water, mainly in places covered by bathing suits. May be accompanied by mild systemic symptoms including fever. Without treatment, it settles in about 10 days without scarring.
Bacterial folliculitis
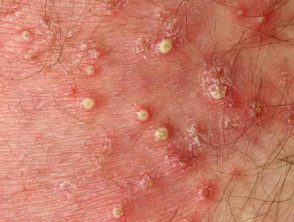
Superficial bacterial folliculitis
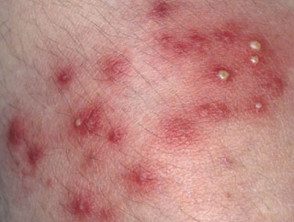
Superficial bacterial folliculitis
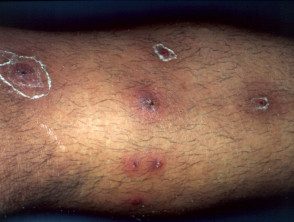
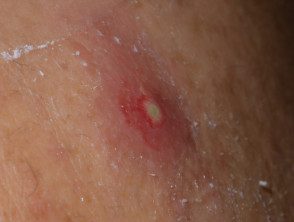
Bacterial folliculitis complications.
Soft fabric infection
Bacterial folliculitis can cause cellulite and lymphangitis; subsequent bacteremia could result in osteomyelitis, septic arthritis or pneumonia
How is bacterial folliculitis diagnosed?
Bacterial folliculitis is usually diagnosed clinically, but can be confirmed with bacterial swabs sent for microscopy, culture and sensitivity.
Blood count can reveal neutrophils leukocytosis when folliculitis is extended.
Skin biopsy It is rarely necessary. Histology dense sample neutrophilic infiltrate at subcutaneous Reaction of tissues and foreign bodies around the hair shaft.
How can folliculitis be prevented?
- Keep the skin clean and, if dry, well hydrated.
- Minimize shaving and waxing. When shaving, use a new blade each time and hydrate the skin afterward.
- Do not wear tight clothing.
- Ensure proper sterilization of the hot tubs.
- In case of repeated episodes of staphylococcal folliculitis, apply mupirocin ointment to the nostrils to remove S. aureus carrier state.
What is the treatment for bacterial folliculitis?
- Warm compresses to relieve itching and pain.
- Analgesics and anti-inflammatories to relieve pain.
-
Antiseptic cleaners (eg, Hydrogen peroxide, chlorhexidine, triclosan)
- Incision and drainage of fluctuating lesions and abscesses
- Topical antibiotics such as erythromycin, clindamycin, mupirocin, and fusidic acid. To reduce bacterial resistance, these should be applied for courses of no more than one week.
- Oral or intravenous antibiotics for more extensive or serious infections.
- Photodynamic therapy
- Repeated To be hair removal
