What is it amelanotic melanoma?
Amelanotic melanoma is a form of melanoma in which the evil one cells produce little or nothing pigment.
What are the clinical features of amelanotic melanoma?
Amelanotic melanomas they are classically described as skin-colored. A significant proportion of melanomas are red or pink. Typical early lesions present as asymmetric macules which may be uniformly pink or red and may have a slight light tan, brown, or gray pigmentation on the periphery Borders can be well or poorly defined. Use of the The 3 Rs (red, raised, recent change) can help detect amelanotic melanoma.
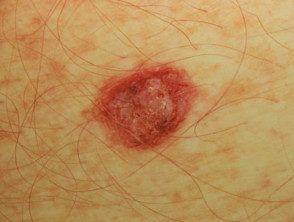
Amelanotic melanoma
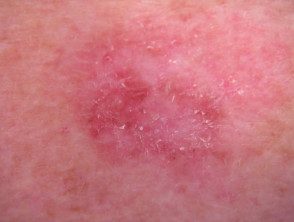
Amelanotic melanoma
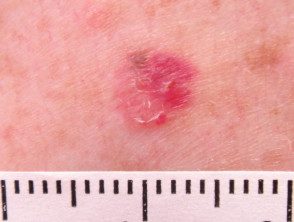
Amelanotic melanoma
What are the dermoscopic features of amelanotic melanoma?
Dermoscopic features of amelanotic melanoma may include:
- Irregular pigmentation / pigment traces (if any are present)
- Irregular dots or blood cells (in pigmented areas)
- Polymorphous vascular pattern, especially if there are irregular dotted vessels, or acombination of points and linear Irregular vessels (the most common dermoscopic finding). Helical vessels are strongly specific for melanoma.
- Multiple shades of pink.
- Milky red areas or lumps
- Lattice depigmentation
- Unstructured white areas
- White lines in polarized dermoscopy.
Vessel analysis using the 5 + 2 List [1].
Vessel morphology it must be carefully evaluated if the lesions lack pigmentation. In the 5 +2 list below, the presence of a certain type of vessel is requested; If the answer is "no", continue to the next question.
- Branched serpentine vessels (arborization) (basal cell carcinoma)?
- Crown glasses (sebaceous hyperplasia)?
- Coma glasses (dermal nevus)?
- Nonspecific vessels (Kaposi sarcoma, regressive lesions)?
- Pointed or fork glasses?
- Absence of white halos?
- Presence of traces of melanin?
If question number 5 is answered in the affirmative (that is, if there are pointed glasses or loops), assess the absence of white halos and presence of traces of melanin. If so, the suspicion of melanoma is raised. Traces of brownish melanin, which may not be clinically visible, occur focally within the injury Support the diagnosis of melanoma or Spitz nevus. It can be very difficult to discriminate between amelanotic melanoma and Spitz nevus by dermoscopy. Lesions with pointed or loop-shaped vessels without a white halo should be considered suspicious and removed [1].
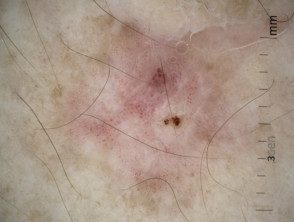
Dermoscopy of amelanotic melanoma.
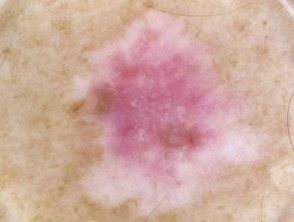
Multiple shades of pink.
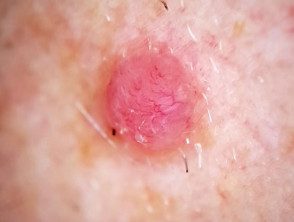
Irregular linear vessels
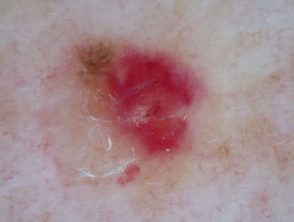
Pigment remnants
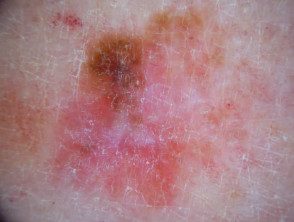
Milky pink areas
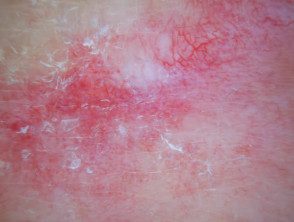
Unstructured white area, irregular linear vessels
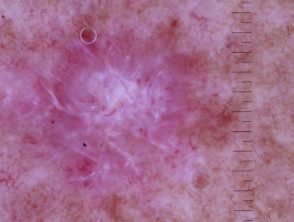
White lines, polymorphic vessels.
Which is the differential diagnosis of amelanotic melanoma?
Other non-pigmented tumors include:
- Basal cell carcinoma
- Spitz naevus
- Seborrheic keratosis
- Actinic keratosis
- Pyogenic granuloma
- Dermatofibroma
- Keratoacanthoma
- Intraepidermal scaly cell carcinoma
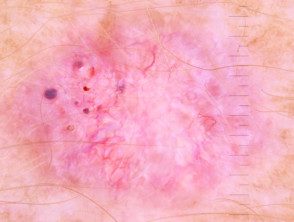
Basal cell carcinoma
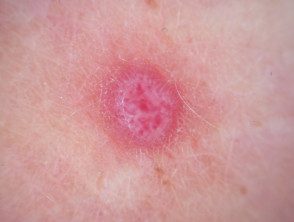
Spitz naevus
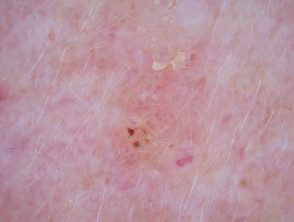
Seborrheic keratosis
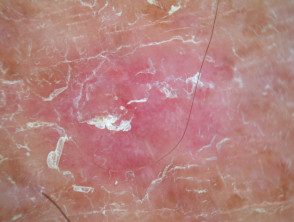
Actinic keratosis
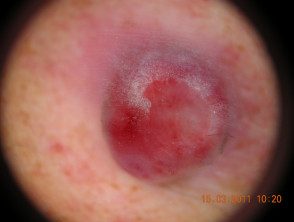
Pyogenic granuloma
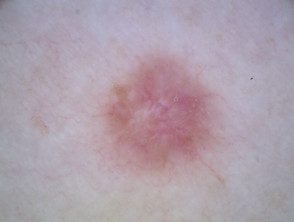
Dermatofibroma
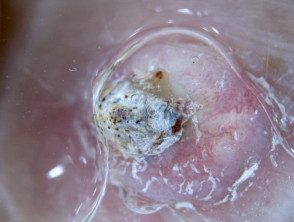
Keratoacanthoma
Intraepidermal carcinoma
Which is the histological explanation of amelanotic melanoma?
Histopathologically, an amelanotic melanoma is usually made up of highly malignant epithelioid cells. These cells show pleomorphism, mitotic activity, enlargement, large nucleoli, and lack of maturation as cells descend to the dermis.
