What is fibromatosis?
Fibromatosis is a condition where the fibrous growth of dermal and subcutaneous connective tissue develop tumors called fibroids. These fibroids are generally benign (not cancerous).
What is the classification of fibromatosis?
There seem to be many different ways to classify fibromatosis. A classification system used is based on age (i.e. youth vs. adult fibromatosis) and location (i.e. superficial vs. deep fibromatosis).
| Youth | Adult |
|---|---|
|
Superficial fibromatosis (fascial)
|
Deep fibromatosis (musculoaponeurotic)
|
See also elastofibroma. pathology.
What are the characteristics of fibromatosis?
The following table lists the distinctive features between deep and superficial fibromatosis.
| Superficial fibromatosis | Deep fibromatosis |
|---|---|
|
|
While most fibromatosis are benign tumors and are not metastasis (they spread to other parts of the body), desmoid tumors although they do not metastasize like evil one cancers can be locally aggressive. They can grow rapidly in large tumors that can obstruct vital structures such as major blood vessels, nerves and organs.
Fibromatosis
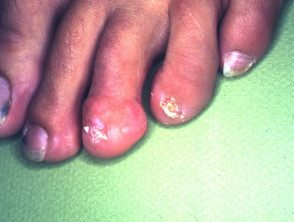
Children's digital fibroma
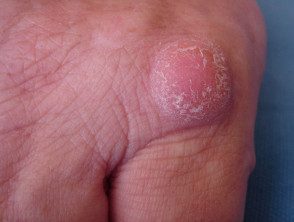
Knuckles
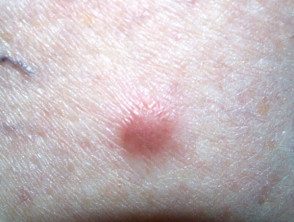
Dermatofibroma
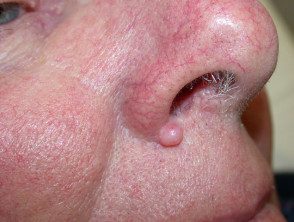
Fibrous papule
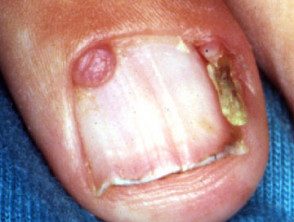
Periungual fibroma
What causes fibromatosis?
The cause of fibromatosis remains unclear. In some types of fibromatosis, such as desmoid tumors, it is believed that the condition may be related to trauma, hormonal factors, or having a genetic association. Superficial fibromatosis such as palmar, plantar, and penile fibromatosis have sometimes been linked to certain diseases such as diabetes, liver disease, and hypertension.
What is the treatment for fibromatosis?
The management of fibromatosis depends on the individual disease. For more information on the different types of fibromatosis, select from the list below.
-
Generalized congenital fibromatosis (childhood myofibromatosis)
- Aponeurotic fibroma
- Childhood digital fibromatosis
- Aggressive childhood fibromatosis
- Fibromatosis colli
- Lenticular dermatofibrosis (Buschke-Ollendorf syndrome)
- Palmar (Dupuytren's disease) and plantar fibromatosis (Ledderhose's disease)
- Fibromatosis of the penis (Peyronie's disease)
- Knuckles
- Pachydermodactyly
- Dermatofibroma
- Nodular fasciitis
- Elastofibroma
- Fibrous papule of the nose or face
- Desmoid tumors (aggressive fibromatosis)
