What is heat urticaria?
Heat urticaria is a rare type of physical illness or chronic inducible urticaria. Also called contact heat hives and located Heat urticaria.
Heat urticaria occurs after direct contact of a warm stimulus with the skin. The onset of hives is usually rapid (in minutes) and the hives resolve within 1 to 2 hours. [one]. It can also cause angioedema and systemic symptoms
Urticarial scars in acute spontaneous urticaria.
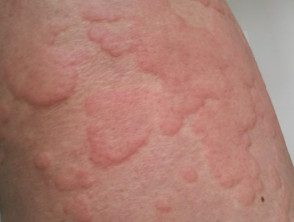
urticarial scars
Who gets hives due to heat?
Heat urticaria is very rare, with few reported cases, so epidemiology is unknown. the the inheritance was autosomal dominant in orA family with delayed heat urticaria [2]. Most of the patients reported have been women between 20 and 45 years old, with family cases that appear during childhood [3].
Chronic inducible urticaria, in general, has an estimate predominance of 0.5% and female predominance of 74% [4]. People with heat urticaria can develop another type of inducible urticaria, such as cold urticaria or dermographism. [1,4].
What causes heat urticaria?
Examples of stimuli that can cause heat urticaria may include:
- Dip a limb in warm water
- Cooking on a gas stove
- Hot air (eg, hair dryer) or sun exposure.
- Close contact with a heater or hot water bottle
- Hot food or drink. [3].
The exact Pathogenesis Heat urticaria is unknown. The heat stimulus is activated. mast cells resident on the skin to release proinflammatory mediators, mainly histamine. This causes small vessels in the skin to dilate, leading to a localized area of swelling, erythemaand healing [4].
Unlike cholinergic urticaria, heat urticaria does not involve activation of the cholinergic glands (sweat) and is independent of total body temperature. [5].
What are the clinical characteristics of heat urticaria?
The clinical characteristics of heat urticaria are generally limited to the area affected by thermal stimulation. There are three clinical subtypes of heat urticaria. [3].
Immediate localized heat urticaria
Immediate localized heat urticaria is the most common type and presents as large, well-circumscribed, which produces itching cure [3].
- Scars generally appear within 10 minutes of contact with the hot stimulus on the skin or a mucous membrane surface.
- They are confined to the contact site.
- Cures resolve in 1 to 3 hours.
-
Angioedema can occur.
- Half of the patients report systemic symptoms such as weakness, fainting, headache, nausea and diarrhea.
Righ now generalized heat urticaria
Some patients with heat urticaria develop widespread scarring if exposed to a general heat environment. [3].
- Heat stimuli can include bathing, hot air, and sun exposure.
- Cutaneous Lesions are limited to areas in contact with the thermal stimulus.
Delayed heat urticaria
Delayed heat urticaria presents as scars that cause itching or a burning sensation. [3].
- There may be a family history of late heat urticaria.
- The onset of healing is delayed between 0.5 and 2 hours after contact with the hot stimulus.
- Scars can persist for up to 24 hours.
-
Angioedema does not occur [3].
How is heat urticaria diagnosed?
Heat urticaria is generally diagnosed by the clinical features of a localized area of hives after the application and removal of a heat stimulus to the skin. [6].
The diagnosis is confirmed by provocation tests. A warm stimulus (a test tube with water> 44 ° or a heated cylinder) is applied to the inner forearm [6]. Hives typically develop within minutes after the warm stimulus has been removed. The test can be repeated using different temperatures to determine heat sensitivity and to monitor response to treatment.
Which is the differential diagnosis for heat urticaria?
Heat urticaria should be differentiated of cholinergic urticaria (generalized heat urticaria) in the sense that it is located in the skin in contact with the thermal stimulus and does not imply activation of the sweat glands systemically [5].
Hives is common symptom and it can come from many rushing or unknown causes, as described below.
-
Spontaneous chronic urticaria appears without a known precipitating cause, is not associated with a thermal stimulus, and is typically extended.
-
Cholinergic urticaria results from an increase in core body temperature and leads to sweating, causing urticaria. Cholinergic urticaria usually causes occasional scarring with pronounced redness on the trunk and extremities. In severe cases, it can cause wheezing and anaphylaxis.
-
Aquagenic urticaria is very rare. Curing follows direct skin contact with water, regardless of temperature.
- Other forms of chronic inducible urticaria are dermographism; Cold urticaria, delayed pressure, sun, contact, induced by exercise and vibration. These are classified according to the stimulus that causes the development of urticaria and are confirmed by provocation tests.
What is the treatment for heat urticaria?
It is important to identify and avoid triggers for heat hives.
Antihistamines tend to be less effective for heat urticaria than for other forms of urticaria [1].
The first-line treatment is a non-sedating second-generation H1 antihistamine, such as cetirizine or loratadine, 10 mg daily. [5]. If symptoms persist, the dose increases, up to 4 times the standard dose per day. [5]. This is at least somewhat effective for approximately 60% of patients with heat urticaria [3].
Possible additional options may include:
- H2 antihistamines, such as ranitidine [3]
- Nonsteroidal anti-steroidsinflammatory medications, such as indomethacin or ketotifen [3]
-
Omalizumab (an anti-IgE medicine) [3]
- Desensitization therapy with daily hot baths, which runs the risk of inducing systemic disease. anaphylactoid reaction [1].
What is the result of heat urticaria?
Chronic inducible urticaria generally has a long duration, with lower rates of remission at 1 year compared to chronic spontaneous urticaria [5]. The impact on quality of life can be significant.
