What skin changes occur due to cold?
Acrocyanosis
Acrocyanosis is the name given to cold peripheries mottled with cyanosis (blue discoloration) or erythema (reddened skin). Predisposes to chilblains.
Chilblains (pernio)
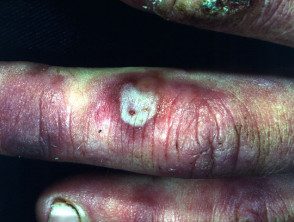
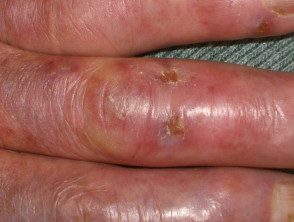
Chilblains arise due to a located cold injury to exposed areas (most often, fingers and toes, ears). They present with erythema, cyanosis, edemablisters and ulceration. Lesions usually heal within several weeks, provided there is no further significant cold exposure. Severe pernio may be the presentation sign of connective tissue illness, especially systemic lupus erythematosus (sable lupus) or systemic sclerosis. However, they are also an occupational hazard for dairy farmers, fishermen and other outdoor workers.
Severe cold injuries can damage small bones in the digits, which leads to microgeodic disease, swelling and sometimes bone fracture.
Preventing chilblains requires keeping fingers and ears warm and dry. A vasodilator medication such as oral nifedipine may be helpful.
Chilblains
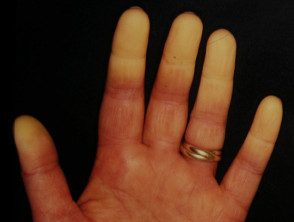
Raynaud's phenomenon
The term Raynaud's disease refers to primary Raynaud's phenomenon. Secondary Raynaud's phenomenon is associated with many underlying diseases, especially systemic sclerosis.
Characteristically, painful attacks follow exposure of the fingers to cold. They turn white, then, in turn, cyanize and erythematous before returning to a normal color.
Raynaud's phenomenon
Raynaud's phenomenon
Raynaud's phenomenon
Freezing
Frostbite is due to severe cold injuries (subzero temperatures). The first signs are pallor and numbness
Treat areas exposed to severe cold by rapid rewarming in a 40° water bath (no further risk of frostbite). Late aftermath include pain, numbness, feeling cold, hyperhidrosisdystrophic nail, fibrosis, osteoporosis and cold intolerance.
Cryoglobulinemia
Cryoglobulinemia is a condition in which proteins circulate in the bloodstream that can solidify in cold conditions. Cold precipitable proteins are deposited in cold areas (ears, toes, fingers). Cryoglobulinemia can present as livedo reticular or superficial heart attack or cutaneous vasculitis.
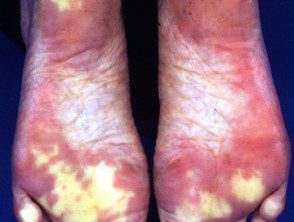
Livedo reticularis
Livedo reticularis
Cold urticaria
Cold hives and family Cold urticaria are rare types of chronic inducible hives that arise during rewarming after exposure to cold. The most common acquired variety usually affects children and young adults.
Weals It can affect any site, most frequently on the face and in exposed places. Scars persist for up to two hours (or longer, in familial cold urticaria). Cold hives can cause anaphylactoid symptoms, for example when swimming in cold water.
Ice-induced hives
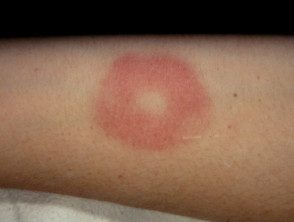
Ice-induced hives
What skin changes occur due to heat?
Erythema ab igne
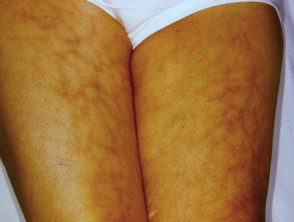
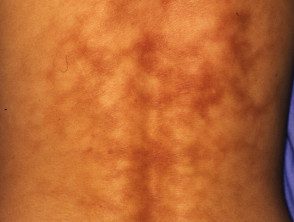
Erythema abigne is due to local heat, such as a hot water bottle or being near a fire. It presents as erythema on a vascular distribution and is often followed by post-inflammatory pigmentation. No treatment is effective, but appearance improves over time.
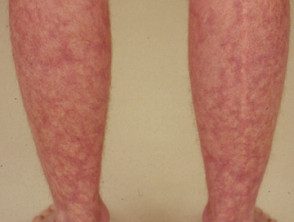
Erythema ab igne
Erythema ab igne
Erythema ab igne
Erythromelalgia
Erythromelalgia causes burning when the feet or hands are hot. The affected areas are erythematous or cyanotic. Some cases are associated with polycythemia, thrombocythemia or lupus erythematosus. In these secondary cases, symptoms may respond to low doses of aspirin.
Heat urticaria
Heat urticaria is a local healing reaction to heat and is rare.
Cholinergic urticaria
Cholinergic urticaria is a kind of Chronic inducible urticaria caused by heat, emotional stress and exercise. The mechanism is uncertain, as healing can occur without sweating. It usually presents with numerous pruritus Scars of 2–3 mm surrounded by a red flare, which persist for 15–30 minutes and are at least sometimes associated with exercise. Treatment may include oral antihistamines, phototherapy, propranolol, or scopolamine with variables effectiveness.
Cholinergic urticaria
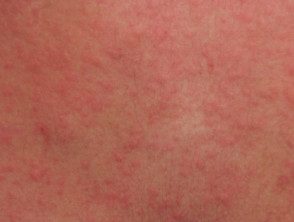
Cholinergic urticaria
Hyperhidrosis
Excessive eccrine discharge or hyperhidrosis can be generalized or localized (most often in hands, feet, armpits and face). Most cases occur in adolescence or young adulthood and appear to be due to idiopathic hypothalamic stimuli Hyperhidrosis is rarely due to systemic disorders such as hyperthyroidism or hypothalamic disease when it is more likely to occur later in adult life.
Hyperhidrosis is aggravated by thermal, emotional or gustatory stimuli can result in bromhidrosis and work difficulties. All patients should use medical grade antiperspirant lotions, which contain aluminum salts. Other treatments include iontophoresis, oral propantheline, propranolol, intradermal botulinum toxin, axillary liposuction or excision of the affected skin, or in severe cases, sympathectomy.
Hyperhidrosis
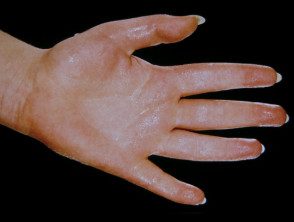
Palmar hyperhidrosis
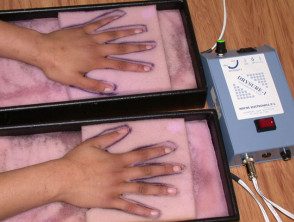
Iontopheresis
Miliaria
Miliaria refers to sweat eruption (prickly heat) due to clogged and perhaps localized sweat glands hyperproliferation of specific diner microorganisms such as strains of Staphylococcus epidermidis. It comes withfollicular superficial papules, vesicles or pustules They arise mainly on the trunk. Treatment requires cooling; calamine lotion can be calming
Miliaria
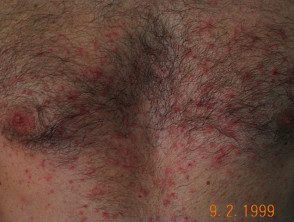
Miliaria rubra
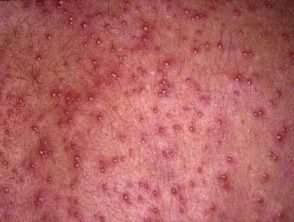
Pustular miliaria
