What is iontophoresis?
Iontophoresis is a procedure in which an electrical current passes through the skin soaked in running water (not distilled water), normal saline (0.9%), or a solution Containing an anticholinergic medication, which allows ionized (charged) particles to cross the normal skin barrier. Reduces sweating and improves the administration of drugs and macromolecules within and through the skin. It is safe, effective and economical.
Iontophoresis for palmoplantar hyperhidrosis
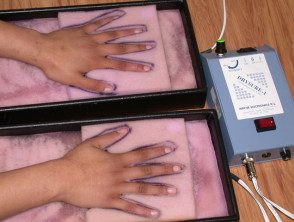
Iontophoresis for palmar hyperhidrosis
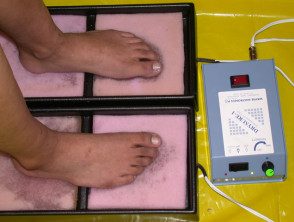
Iontophoresis for plantar hyperhidrosis
What is iontophoresis used for?
The main use of iontophoresis is to treat focal areas of excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis), particularly on the palms or soles of the feet. Tap water iontophoresis is less effective in the armpit.
Limited robust data are available; Some studies suggested that up to 80-85% of patients with palm Hyperhidrosis notices a subjective improvement of its symptoms in 2 to 4 weeks. A study of iontophoresis with running water showed an improvement of 33% in the soles and 37.5% in the armpits after 14 days, they increased to 78% and 75% respectively for 20 days.
Iontophoresis has also been used successfully to administer medications to the skin to:
- Reduce sweating further by using an anticholinergic agent such as glycopyrronium or botulinum. toxin TO.
-
Anesthetize an area of the skin with lignocaine.
- Treat mushrooms infection of the nail plate (onychomycosis).
- Eradicate infection due to micro-resistantorganisms using silver ions
- Treat bursitis or tendinitis with antiinflammatory drugs
How does iontophoresis work in hyperhidrosis?
The mechanism of action of iontophoresis in reducing sweating is not fully understood. Sweat forms in response to an electrical gradient produced by sympathetic nerve activity in the sweat gland cells. There are several theories on how a change in the electrical gradient reduces sweat production.
- The ions produced by iontophoresis can physically block the sweat ducts in the stratum corneum.
- External electric current can interrupt normal transmission of the sympathetic nerve.
- the pH drops in the sweat gland due to an accumulation of hydrogen ions.
Iontophoresis for hyperhidrosis is usually carried out under running tap water; however, an electrolytic solution of sodium chloride or an anticholinergic agent (glycopyrronium bromide) can be added if the water alone is not effective.
Procedure / what to expect
Both battery powered direct current (DC) and mains powered alternating current (DC) devices are available. Individual machines vary, and the instructions provided by the manufacturer must be followed carefully.
For palmar hyperhidrosis, each hand is placed in a tray of water containing indifferent, active electrodes. It is recommended that petroleum jelly be applied to the skin in the waterline and to small cuts or wounds to avoid discomfort and located inflammation. The device is turned on so that the current passes through the water between the electrodes. The initial current should be very low and then adjusted according to tolerance.
Initially, the treatment is carried out for 20-30 minutes every 1-3 days until the desired effect is achieved, and then it is reduced to once a week to maintain the result. It is up to the patient to find which treatment regimen works best to maintain results.
Side effects and risks of iontophoresis.
Iontophoresis is generally a safe procedure. It is important to avoid direct contact with the electrodes during treatment, as it can cause a slight electric shock.
Most people experience a pins and needles or burning sensation. Adverse effects may include:
- Redness of treated skin
- Small blisters (vesicles) or pompholyx
- Dry and cracked skin or dermatitis.
Although these side effects of iontophoresis are expected to resolve in a few days, emollientsMoisturizers should be applied several times a day to reduce symptoms. Current Corticosteroids can be applied.
If used, anticholinergic medications such as glycopyrronium can be absorbed by the body and produce systemic side effects like dizziness, dry eyes and dry mouth.
Contraindications to iontophoresis
Iontophoresis must not be used by:
- A patient who is epileptic or has a history of seizures.
- A patient with a heart condition or a pacemaker.
- A patient with a metal implant.
- A pregnant woman
Patients should delay treatment if they have a recent wound, a skin graft, or scar in the area that requires treatment, since iontophoresis can be painful and the treatment less effective.
