What is a lax beetle?
Lax beetles are common insects found throughout the world, belonging to the family Oedemeridae [1–3]. The beetles are 6–20 mm long, soft and thin. The body is light brown with darker brown/black stripes or spots on the plate-like structure on the back. [1,2].
Lax beetles are also called false blister beetles because male beetles produce cantharidin, which is also found in true blister beetles of the family Meloidae, to which they are closely related [1,3,4]. Meloidae beetles are not found in New Zealand. Cantharidin extracted from the beetle Cantharis vesicatoria It is sometimes used to treat viral warts and molluscum contagiosum. “Kantharis” means “blister fly” in Greek [5].
Common names for the lax beetle include the striped lax beetle, spotted lax beetle, false blister beetle, and pollen-feeding beetle.
lax beetles

Lax beetle

Skin lax beetle

Lax beetle
See more images of lax beetles.
Where are lax beetles found?
In New Zealand, most lax beetles are native with several adventitious species, meaning they could have been introduced from other countries by humans [3]. The beetles are found on the North and South Islands of New Zealand, Stewart Island and the Chatham Islands [2,3].
The beetles and young larvae are found in driftwood or rotting wood just above high tide in coastal areas and in inland vegetation. Adults are found under the bark of dead tree trunks and on tree branches. They feed on pollen and nectar from flowers or vegetation. On summer nights, adult beetles are attracted to bright, artificial white lights. [1–3].
Who gets blisters from the lax beetle?
Anyone can get blisters if the beetle is crushed, brushed, or pressed against the skin when gardening or during outdoor activities. Sometimes called “morning blisters,” they occur hours after contact with the beetle. [1,5,6].
Lax beetle blisters
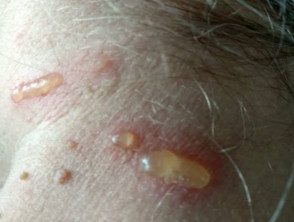
Day 0: Beetle blisters 8 hours after contact
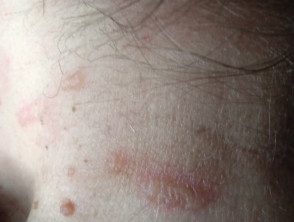
Day 1: Beetle blisters drying
What causes lax beetle? skin disease?
By crushing the beetle on the skin, or by accidentally pressing or brushing against the skin, the beetle releases a fluid called hemolymph from the leg joints. The liquid contains cantharidin or cantharid, which is intended to deter predators from eating the beetle eggs and is irritating to human skin. [1,3,7]. The male beetle passes the blister fluid to the female beetle during mating [5].
Beetles do not bite or sting [8].
What are the clinical characteristics of lax beetle dermatosis?
Blister beetle dermatosis is characterized by superficial blisters.
- The face, neck, and chest are commonly affected.
- Taut blisters filled with clear fluid develop 24–48 hours after contact with blister beetle hemolymph.
- Single or multiple vesicles, bullas, or multiple blisters appear in a line or track where the beetle has been in contact with the skin.
- There may be mild itching and minimal surroundings. erythema, but the blisters are not painful.
- “Kissing or mirror image” lesions can be seen when a blister comes into contact with adjacent skin when bending the arms or legs [1,5,9].
What are the complications of beetle lax dermatosis?
There are no complications from blister beetle dermatosis, which heals in a few days without leaving scars. [6,9].
How is lax beetle dermatosis diagnosed?
Lax beetle dermatosis is diagnosed by clinical appearance and history of contact, or probable contact, with a lax beetle.
- Swabs can be taken to exclude bullous impetigo, herpes simplex or Herpes zoster.
- In recurrent cases, patch Tests can be performed to exclude a contact allergy.
Which is the differential diagnosis for blister beetle dermatosis?
Other blistering conditions that may need to be considered include:
- Friction ampoules
-
allergic or irritating Contact dermatitis
-
Phytophotodermatitis (a reaction to contact with certain plants)
- Blistering impetigo
-
Herpes simplex or herpes zoster [10].
What is the treatment for blister beetle dermatosis?
Blister beetle dermatosis can be prevented by avoiding contact with the beetle.
- Screens will help keep them outdoors.
- Avoid touching the beetle.
- If a beetle lands on your skin, blow it off instead of brushing or squishing it.
If blisters occur:
- Wash the skin with soap and water or clean with acetone or alcohol to dissolve and dilute the cantharidin.
- Cover the area until the blister is absorbed to reduce the spread of cantharidin-containing fluid.
- Symptomatic current Treatment may include application of a mild topical steroid [1,7,8].
What is the result of lax beetle dermatosis?
Loose beetle blisters heal in 4–7 days without ulceration, infectionor scars [6,9].
