What is it neurofibromatosis?
Neurofibromatosis (NF) is a genetic bone-affecting disorder Soft fabric, skin and nervous system. The clinical manifestations increase over time.
At least 8 different clinics phenotypes of NF have been identified. It is classified into 2 different types:
- Neurofibromatosis 1 (NF1)
- Neurofibromatosis 2 (NF2).
Neurofibromatosis 1
NF1 occurs in about 1 in 3,000 births. It is also known as von Recklinghausen's disease. It is characterized by the presence of:
- 6 or more coffee with milk macules - light brown flat birthmarks
- Freckles in the folds of the skin.
- Lisch nodules in the iris of the eye
- Multiple neurofibromas - tumors hanging from the skin
Neurofibromatosis 2
NF2 occurs in about 1 in 50,000 births. Also known as bilateral acoustic neurofibromatosis or central neurofibromatosis. It is characterized by multiple tumors and injuries to the brain and spine. cable.
Lonely neurofibroma it is not associated with NF1 or NF2.
What causes neurofibromatosis?
NF1 and NF2 occur as a result of defects in different genes.
- NF1 is caused by a mutation in neurofibromin gene located in the pericentromeric region of chromosome 17)
- NF2 is caused by a mutation on chromosome 22.
The mutated gene can be inherited from a parent who has NF by autosomal dominant transmission, or it may be a founder gene due to spontaneous mutation. A parent with NF has a 50% chance of passing the gene on to each of their children.
Genetics of neurofibromatosis 1 and 2 *
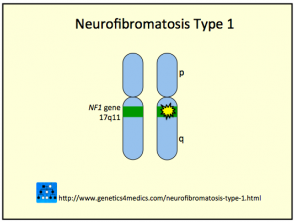
Neurofibromatosis Type 1
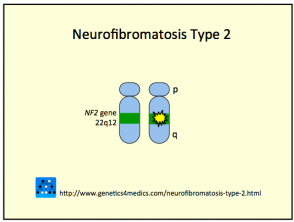
Type 2 neurofibromatosis
* Image courtesy of Genetics 4 Medics
What are the signs and symptoms of neurofibromatosis?
The extent and severity of NF manifestations vary greatly from person to person and vary within the same family.
Neurofibromatosis 1
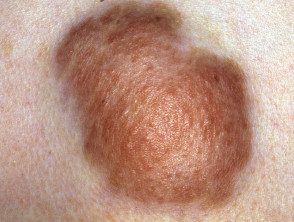
Café-au-lait macules
Café au lait macules are light, oval or irregularly shaped, light brown patches over 0.5 cm in diameter. They can be present at birth and increase in number during the first years of life.
Although isolated café au lait macules can be found in many people without NF, people with more than 5 of them have a good chance of also having NF1, particularly if they appear on the skin within the first 5 years of life.
More than 5 café au lait macules are found in 1.8% in newborns, 25-40% in children, and 14% in adults with NF1.
Freckles
Freckles in the armpits also known as Crowe sign and it is characteristic of neurofibromatosis type 1. Freckles appear during puberty, after the development of café au lait macules and before neurofibromas. They may also appear in other skin folds, such as the groin.
Neurofibromatosis
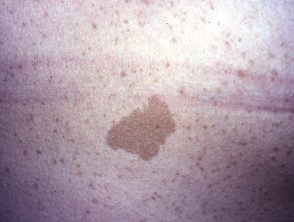
Café-au-lait mark
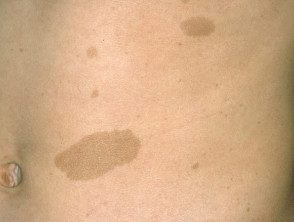
Café-au-lait mark
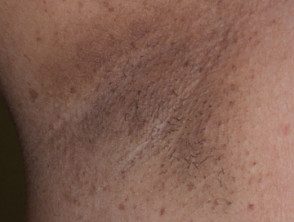
Freckles in the armpit
Lisch nodules
Lisch nodules are small tumors in the iris of the eye. After puberty, Lisch's nodules are present in the 97-100% of NF1 patients. Clinically, they don't cause any problems, but they do help confirm the diagnosis.
Neurofibromas
Neurofibromas are made up of Schwann cells, fibroblasts, mast cellsand vascular components, and can develop at any point along a nerve. They are three types: cutaneous, subcutaneousand plexiform. Cutaneous and subcutaneous neurofibromas are not specific for neurofibromatosis, but plexiform neurofibromas are only seen in NF1.
-
Skin neurofibromas are circumscribedShallow, smooth nodules such as brown, pink, or skin-colored buttons with a smooth or firm consistency. They may have pathognomonic buttonhole invagination when pressed with a finger. They do not have evil one potential.
- Subcutaneous neurofibromas are similar to cutaneous neurofibromas, except that they are of deeper origin. Can cause located pain or tenderness
- Plexiform neurofibromas present as bag-like masses within the skin. Nodular Plexiform neurofibromas involve the dorsal nerve roots and diffuse plexiform neurofibromas are invader tumors that can affect all layers of skin, muscle, bone and blood vessels.
Neurofibromatosis
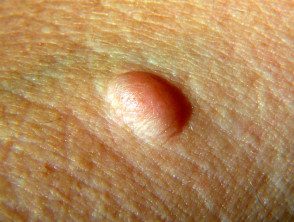
Neurofibroma
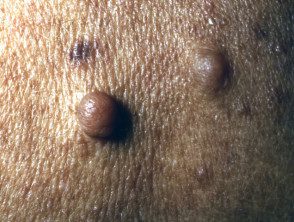
Neurofibromas
Plexiform neurofibroma
See more images of neurofibromatosis ...
Other NFI Features
The severity of skin involvement in NF1 is not an indicator of the extent of the disease, as internal manifestations are common and often more severe. Problems in other parts of the body include:
- Malformation of the long bones (below the knee and elbow) and the curvature of the spine (scoliosis)
- Short stature and growth hormone deficiency
- Learning difficulties (speech problems) and behavior problems (25–40% have learning disabilities, 5–10% may have mental retardation)
- Tumors of the optic nerve; these can cause visual loss
- High blood pressure and other blood problems.
- Tumors in the spine and brain; these increase the risk of epilepsy
- Tumors or lesions in the gastrointestinal tract that can cause bleeding or obstruction.
- Hearing defects.
Although most tumors are benign (non-cancerous), it is estimated that a person with NF1 has a 3 to 15% increased risk of developing cancerous tumors.
Neurofibromatosis 2
NF2 does not have as many external signs as NF1. It is characterized by multiple tumors and injuries to the brain and spinal cord. First symptom is generally hearing loss due to tumor growing in one or both auditory nerves. Often this is not evident until the late teens or early twenties.
Tumors in NF2 are usually benign. But the benign enlargement of the tumor in the brain and spinal cord can interfere with vital functions.
Follow-up for patients with neurofibromatosis
The main role for follow-up is to monitor tumor development and intervene when necessary.
- Healthy children with NF should be followed and examined every 6-12 months by a pediatrician.
- Those with eye symptoms and signs should be evaluated and monitored by a ophthalmologist.
- Hearing defects must be evaluated and controlled by an otolaryngologist (ENT).
- A neurologist may need to examine the patient with any neurological symptoms and signs such as clumsiness, numbness, or weakness.
Images with ultrasound scans, Connecticut scans and Magnetic resonance it can be arranged to determine the site of any suspicious tumors.
What treatment is available?
There is no cure for NF.
Neurofibromas that become large and painful can be cut to reduce the risk of malignancy and Other Complications Facial deformity can be mitigated by cosmetic (plastic) surgery.
Genetic counseling and education about NF is important. A concern that should not be overlooked is the risk of isolation or loneliness in people with NF. People with NF are often eager for future complications, and sometimes disfiguring injuries can lead to withdrawal from society.
Managed molecular Therapies hold promise for the future treatment of neurofibromatosis.
