What are calcineurin inhibitors?
Calcineurin inhibitors are drugs that work by inhibiting calcium.dependent protein phosphatase calcineurin, a enzyme which results in the activation of T lymphocytes through the positive regulation of interleukin-2 and related cytokinesand leads to immunosuppression [1].
- Oral calcineurin inhibitors are cyclosporine and tacrolimus.
- Current Calcineurin inhibitors are tacrolimus (available as 0.03% or 0.1% ointment) and pimecrolimus (1% cream) [2,3].
What are topical calcineurin inhibitors used for?
Calcineurin inhibitors tacrolimus and pimecrolimus are indicated for the treatment of atopic dermatitis.
They are commonly used off-label in dermatology for:
-
Facial, flexuraland genital psoriasis
- Seborrheic dermatitis
- Chronic hand dermatitis
- Contact dermatitis
- Vitiligo
- Morph
- Lichen sclerosus
- Cutaneous lupus erythematosus
-
Oral and erosive vulvar lichen planus [2,4].
Topical calcineurin inhibitors are free of many adverse effects of topical corticosteroids, such as skin striae. atrophy, glaucoma, bounce shoots and systemic absorption, or the potential for hypothalamic suppression of the pituitary-adrenal axis (HPA).
Indications for topical calcineurin inhibitors.
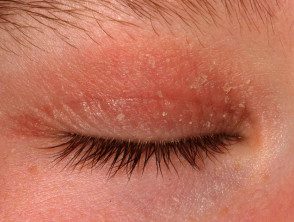
Atopic dermatitis of the eyelid.
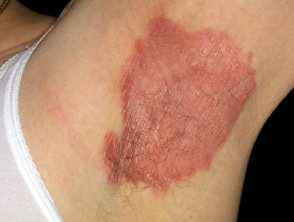
Armpit psoriasis.
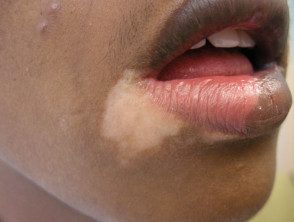
Vitiligo that affects the lips and perioral skin.
What are oral calcineurin inhibitors used for?
Oral calcineurin inhibitors are commonly used for immunosuppression after solid Organ transplant. Occasionally, cyclosporine and tacrolimus can also be used to treat diseases mediated by the immune system, such as psoriasis and atopic dermatitis; however, its use is mainly restricted to patients who have not responded to conventional therapy. [3].
What are the skin side effects of topical calcineurin inhibitors?
The most commonly reported side effect of topical calcineurin inhibitors is local skin irritation (burning, pruritusand erythema) on the application site. However, this is usually transient and decreases over time (usually within a month).
Other adverse effects may include:
- Allergic contact dermatitis
- Folliculitis
- Reactivation of infection (herpes simplex and viral warts)
- Improvement of facial redness after alcohol. ingestion
-
Rosacea type dermatitis
- Facial acne
- Molluscum contagiosum
-
Tinea incognito.
There is no evidence to support the theoretical concern that topical calcineurin inhibitors may increase the risk of malignancy, as basal cell carcinomacutaneous scaly cell carcinoma melanoma and cutaneous lymphoma. The information reporting this risk is based on data from animal studies, case reports in a small number of patients, and knowledge of how these drugs work [2,4,5].
Indications for topical calcineurin inhibitors.

Atopic dermatitis of the eyelid.

Armpit psoriasis.

Vitiligo that affects the lips and perioral skin.
What are the skin side effects of oral calcineurin inhibitors?
Los efectos adversos de tacrolimus y ciclosporina son generalmente similares. Éstas incluyen:
- Gingival hyperplasia
- Hypertrichosis (this is more common with cyclosporine)
-
Drug induced alopecia (higher doses of tacrolimus and cyclosporine are associated with an increased risk of hair lost)
- Drug induced itching
- Drug induced acne
-
Redness
- Generalized hyperhidrosis
- An increased risk of squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. [1.3].
Adverse effects of oral calcineurin inhibitors.
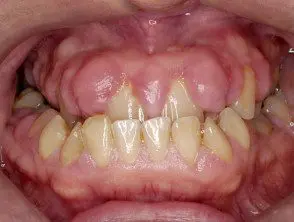
Gum hypertrophy due to cyclosporine
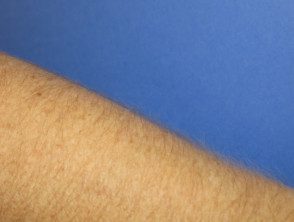
Cyclosporine hypertrichosis
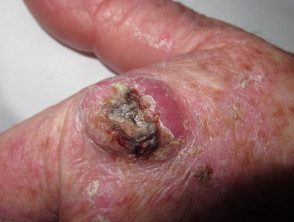
A moderately well-differentiated, histologically confirmed squamous cell carcinoma of the dorsal hand
What are the non-cutaneous side effects of calcineurin inhibitors?
Calcineurin inhibitors can cause several side effects in addition to the effect on the skin.
Oral calcineurin inhibitors
Oral calcineurin inhibitors can cause the following side effects:
- Nephrotoxicity (the most common adverse effect)
- Hypertension
- Neurotoxicity (tremors, severe headache, visual abnormalities, seizures, encephalopathy, and coma)
- Metabolic abnormalities (glucose intolerance, hyperlipidemia, hyperuricemia, hyperkalemia, hypomagnesemia, liver dysfunction with jaundice)
- Infectionsbacterial, viral and fungal)
- Increased risk of malignancy (benign and evil one lymphoproliferative disorders)
- Gastrointestinal side effects (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal discomfort) [1,3].
Topical calcineurin inhibitors.
Topically applied calcineurin inhibitors do not cause significant suppression of the immune system as less than 0.1% is absorbed from the applied dose. Big epidemiological Studies have not found that topical calcineurin inhibitors are correlated with an increased risk of lymphoma or other malignancies [6].
