What is redness?
Redness occurs because the blood vessels In the skin they dilate. When the redness is caused by the activity of the nerves to the blood vessels, is accompanied by sweating. Agents that act directly on blood vessels cause dry redness.
Redness
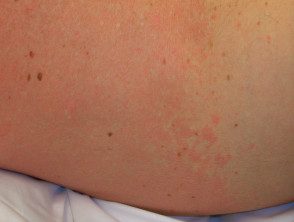
Nicotinic acid-induced redness
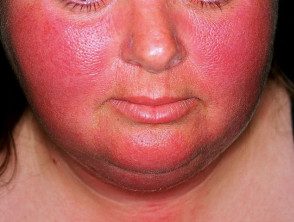
Unexplained redness
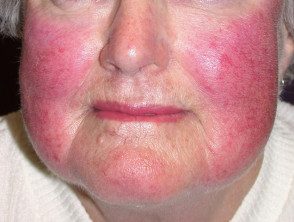
Rosacea causing redness
Causes of redness
The causes of redness can be considered under the following headings.
- Alcohol
- Food Additives
- Eating
- Neurological problems
- Drugs
- Other causes of redness
Alcohol-related redness
- There is an increased susceptibility to alcohol-related redness in Asians, who have a defect enzyme (acetaldehyde dehydrogenase) leading to accumulation of acetaldehyde.
- Tyramine or histamine in fermented alcoholic beverages (beer, sherry, wine) it can cause redness.
- Occupational "degreaser" discharge occurs in workers who drink beer after exposure to industrial solvents, such as trichlorethylene vapor, N, N-dimethylformamide, and N-butyraldoxime.
Some drugs cause redness when the patient drinks alcohol. These include:
- Disulfiram
- Chlorpropamide
- Calcium carbamide (urea)
- Phentolamine
- Metronidazole
- Cephalosporin antibiotics
Alcohol can also cause redness while consuming mushrooms, and in patients with the rare tumorcarcinoid
Washing related to food additives
Redness related to food additives is rare.
- MSG (monosodium glutamate) (E621 and 622) in large doses can cause "Chinese restaurant syndrome“.
- Sodium nitrite (and nitrates) (E249, 250,251,252) in cured meats, sausages, bacon, salami, ham, can cause headaches and flushing in some people.
- Sulfites (potassium metabisulfite) (E224), found in beer, cider, wine, desserts, fried and frozen vegetables, fruit juices, frozen prawns and shrimp, and dairy products can cause wheezing and flushing.
Note: E numbers are now on most food made in New Zealand. However, fermented beverages, delicatessen and restaurant food do not have to indicate additive content.
Flushing associated with eating
Redness associated with eating is very common.
- Hot foods, drinks, or spicy foods can cause flushing in normal people.
- Auriculotemporal syndrome refers to one-sided redness, warmth, and sweating after parotid gland injury or surgery.
- Gustatory flushing affects both sides of the face and is associated with excessive salivation, tear production, and runny nose with no history of parotid gland injury. This can be reproduced by chewing on a chili pepper and holding it in your mouth for 5 minutes.
- Dumping syndrome is the association of facial flushing with a racing heart, sweating, dizziness, weakness, and an upset stomach. Symptoms start after gastric surgery and are triggered after a meal or ingestion hot or strong drinks glucose. The syndrome worsens after menopause.
Neurological redness
Neurological redness occurs in association with the following conditions.
- Simple blush due to embarrassment or anxiety
- Brain tumors
- Spinal cable injuries
- Orthostatics hypotension
- Migraines
- Parkinson's disease
Blush
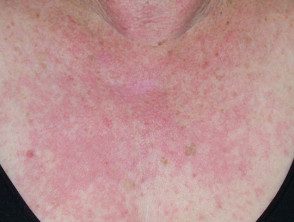
Medications that can cause redness
In susceptible individuals, medications that can cause redness include:
- All vasodilators
- All calcium channel blockers.
- Nicotinic acid (discharge can be blocked with aspirin or indomethacin)
- Morphine
- Amyl nitrite and butyl nitrite
- Cholinergic drugs
- Bromocriptine
- Thyroid releasing hormone
- Tamoxifen
- Cyproterone Acetate
- Systemic steroids
-
Cyclosporine
Other causes of redness
Rosacea It is the most common skin condition that is associated with a tendency to redden easily. Other causes are listed below.
- Drinking Kava
-
Scombroid fish poisoning results of bacteria acting on refrigerated incorrectly mackerel, tuna and bonito fish. Histamine is formed in the meat of fish. Combined with a toxin known as saurine, can, when ingested, Produces:
- spicy taste
- Diarrhea
- burning mouth
- urticaria
- blush
- headache
- disease
- vomiting
- obstacle.
Note: cooking does not destroy the toxin and even canned tuna can cause facial flushing.
-
Carcinoid tumor with liver metastasis (high schools); redness is due to circulating serotonin
-
Pheochromocytoma (an adrenal tumor); the redness is due to circulating catecholamines (epinephrine / norepinephrine)
- Systemic mastocytosis; the redness is due to circulating histamine and is associated with low blood pressure (fainting) and breathing difficulties (bronchospasm)
Redness treatment
Treatment for redness depends on the underlying cause.
