What is rosin and where is it found?
Rosin, also known as rosin, is the sap or sticky substance that comes from pine and fir trees. Its adherence lends itself to be used in a wide range of products. The following table shows just a few of the many rosin-containing products that we can come into contact with, whether at home or at work.
| Home / Recreational Fountains | Job sources |
|
|
What are the reactions to rosin? allergy?
Reactions to rosin contact in an allergic individual include acute allergic contact dermatitis and shortness of breath. In allergic contact dermatitis, dermatitis tends to occur 1-3 days after contact with rosin, although reactions may occasionally occur within 24 hours or even more than a week after exposure. Dermatitis tends to be limited to the site of contact with rosin (for example, hands and forearms after transporting pinewood, although the face may also be involved). Initially, the skin becomes red and inflamed and usually itchy. As the reaction progresses, it can blister and itch even more intensely. If exposure continues, dermatitis may eventually become chronic with thickened and lichenified skin.
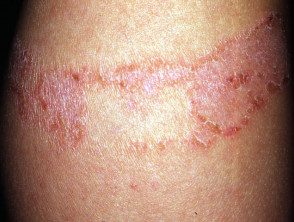
Plaster rash
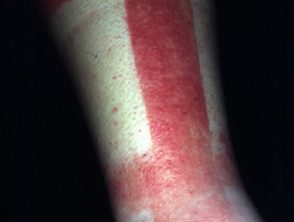
Contact dermatitis
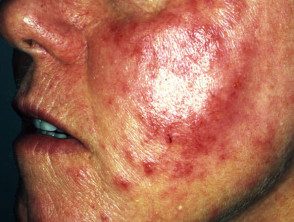
Contact dermatitis
Am I allergic to rosin?
Rosin allergy is diagnosed from the medical history and by conducting special allergy tests, which are called patch tests
If you want to perform an automatic rosin test on a product, you can test a small area of your skin using the repeated open application test (ROAT). However, many chemicals are very irritating, you must be very careful. Discuss this with your dermatologist First. Apply a very small amount of the product in question to a small area of the skin, such as the curve of your arm twice a day for seven days. If, after applying the product for 7 consecutive days, there has been no reaction, it is unlikely that you are allergic to the product. However, you can still develop an irritating or intolerant reaction to the product.
Rosin Allergy Treatment
Avoidance is the only long-term allergy treatment. There is no mechanism to desensitize rosin. Once the dermatitis appears on the skin, the treatment is as for any acute dermatitis /eczema, with topical corticosteroids, emollientsand treatment of any secondary bacterial infection (Staphylococcus aureus)
What should I do to avoid allergy to rosin?
The best way to avoid an allergy to rosin is to know the products that contain rosin. Look for the ingredient list on product labels or on the packaging of all the substances you come in contact with, not just the ones you think you might be reacting with. If necessary, contact the manufacturer of the product or cosmetic. Avoid products that don't list all the ingredients.
If you must use products containing rosin, wear gloves or other protective clothing to avoid contact with your skin. Your dermatologist may have more specific advice, especially if you are very sensitive to rosin.
Alternative names for rosin
Rosin is also known by several other names. These include:
- Rosin
- Rosin
- Resin terebinthinae
- High oil
- Abietic acid
- Methyl Abetate Alcohol
- Abietic alcohol
- Abietyl alcohol
Avoid all this. At work, request a material safety data sheet to help identify alternatives that are safe, thus avoiding contact with material containing rosin.
More information
CAS number: 8050-09-7
Cross reactions:
- Balsam of Peru
- Dihydroabyethyl alcohol
- Wood tars
- Pine resin
- Fir resin
- Turpentine oil
Appearance:
Yellow resin. 90% for resin acids (mainly abietic acid), 10% for neutral matter
Sensitizer:
The main sensitizers are abietic acid and abitol.
Patch test:
20% in Vaseline
| Sources of exposure to rosin | ||
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
