What is crusted scabies?
Crusted scabies, or Norwegian scabies as it was formally known, is a highly contagious hyperinfestation with Sarcoptes scabiei var hominis. It is a presentation of scabies in immunocompromised patients It can also result from a misdiagnosis such as psoriasis or seborrheic dermatitis and treatment of these disorders.
People with crusted scabies are estimated to have up to 4,000 Mites per gram of skin. Patients are often infected with more than 1 million mites. Compare this to most scabies patients, who are infected with around 10-20 mites.
Who gets scabby scabies?
Scabies is transmitted from another individual who is infested by scabies mites. Crusted scabies can arise in people who do not achieve a normal immune response to mites.
Worldwide, crusted scabies is more predominant in remote Aboriginal communities in northern Australia.
Risk factors for crusted scabies include:
- Increase in age
- Dementia
- Down syndrome
- Human immunodeficiency virus infection (HIV)
- Leprosy
- Lymphoma
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
- Long-term use of corticosteroids or immunosuppressants
- Institutional housing – prisons and nursing homes (institutional scabies)
What causes crusted scabies?
The exact reason why crusted scabies arises is unknown. It is associated with elevation eosinophils, IgE and IgG. the dermis is infiltrated with lymphocytes and eosinophils. There is a higher proportion of CD8 + lymphocytes compared to normal.
What are the clinical characteristics of crusted scabies?
Crusted scabies begins as ill-defined red spots that later become thick scaly plates between the fingers, under the nail, or diffusely on palms and soles. Other common areas include elbows and knees. Mites can also accumulate in the nail beds, causing the nail plates to split.
Scabies with scab
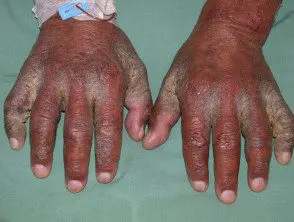
Scabies with scab
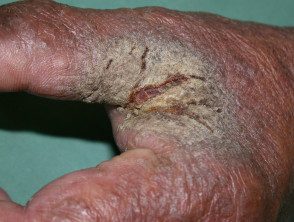
Scabies with scab
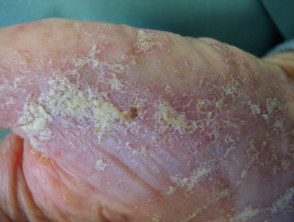
Crusted mange burrows 10
Itching in crusted scabies may be minimal or absent. This may be due to the immune compromised nature of the individual. The following may contribute to reducing scratching:
- Physical limitation
- Neuropsychiatric disorders.
- Osteoarticular deformities
- Muscular atrophy
- waste of cutaneous sensation
What are the complications of crusted scabies?
Complications of crusted scabies include:
- Infestation from numerous contacts, including family and staff members
- Secondary bacterial infection
How is crusted scabies diagnosed?
Scabies is easily diagnosed clinically and confirmed by identification of mites or eggs dermoscopically or microscopic burrow examination. Confocal reflectance microscopy It has also been used to examine burrows, mites, eggs and Pinch faeces. Fur biopsy is rarely necessary and will show characteristic scabies pathology.
What is the treatment for crusted scabies?
A dermatologist or an infectious disease physician must be involved in the care of the patient and their contacts. Treatment of crusted scabies should be done in a hospital or residential setting, with the patient in a private room. Healthcare personnel should take contact precautions and wear full personal protective equipment, including shoes and hair covers.
Treatment consists of oral ivermectin and current insecticides. The following classification system designed at the Royal Darwin Hospital can be used to determine management.
A: Distribution
- Wrists, web spaces, feet or <10% del área total de superficie corporal (TBSA)
- Above forearms, legs, buttocks, trunk (TBSA 10–30%)
- Above the scalp more or > 30% TBSA
YEAH. Crust/shedding
- Light bark (<5 mm de profundidad Cortex), minimal skin shedding
- Moderate crusts (5–10 mm), moderate peeling
- Severe (> 10 mm), profuse skin shedding
C. Past episodes
- I never had it before
- 1–3 previous hospitalizations for crusted or scabies depigmentation elbows, knees
- ≥ 4 prior hospitalizations for crusted scabies or depigmentation as above plus legs/back or residual skin thickening/ichthyosis
D. skin condition
- No cracks or pyoderma/impetigo
- Multiple pustules and/or superficial sores and cracks
- Deep cracks in the skin with bleeding, extended purulent exudates
Grade 1: total score 4–6
Grade 2: total score 7–9
Grade 3: total score 10–12
The dose of ivermectin is 200 μg/kg for adults and children over 14 kg, rounded to the nearest 3 mg and taken after a high-fat meal to aid absorption.
- Grade 1: 3 doses – days 0, 1.7
- Grade 2: 5 doses – days 0, 1, 7, 8, 14
- Grade 3: 7 doses – days 0, 1, 7, 8, 14, 21, 28
A topical scabicide is applied every other day for the first week, and then twice a week until healed.
- Permethrin 5% cream or benzyl benzoate emulsion at 25% for patients > 6 months of age
- Crotamiton 10% for babies under 6 months.
- Sometimes additional 5% tea tree oil or sulfur ointment
Keratolytic The creams are used on scaly plaques on alternate days to the scabicide. First, soften the crusts in warm water. Then apply any of:
-
Salicylic acid 5% to 10% in sorbolene cream
-
Lactic acid 5% plus urea 10% in sorbolene cream.
The treating dermatologist or infectious disease physician should carefully re-examine the patient to decide when to discontinue treatment.
A combination regimen for the treatment of crusted scabies developed by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Control (CDC) recommends:
- 5% topical permethrin or 5% topical benzoyl benzoate applied daily for seven days, then twice a week until cured
AND
- Oral ivermectin (200 mcg/kg/dose) administered on days 1, 2, 8, 9 and 15 (add days 22, 29 if infestation is severe).
Treatment of family members
Family members should also be screened for crusted scabies and treated accordingly. Regardless of the test results, all family members should be treated with a topical scabicide and should repeat the treatment in one week.
The environment
Mites can survive up to 72 hours away from a human host. Living areas should be thoroughly cleaned, as crusted plaques usually fall off. Bedding and mattresses should also be cleaned.
- Washing with water (with or without detergent) removes most mites. Water temperature has no effect on the number of dead mites.
- If items cannot be washed, they should be kept sealed in plastic bags for at least 4 days.
- Sunlight is also effective in killing mites.
What is the outcome of crusted scabies?
Treatment will cure crusted scabies. However, patients with crusted scabies, due to their immune status and living conditions, are at risk of reinfestation. Education and regular monitoring are essential.
Mortality is significantly higher in elderly patients with crusted scabies compared to patients with regular scabies. Disease-related mortality is attributed to septicemia.
