What is it telangiectasia?
Telangiectasia is a condition in which there are small visible linear Red blood vessels (broken capillaries) These are also called telangiectasias. The small visible blue blood vessels (spider veins) are called venulectasis why venules They are involved.
Telangiectasia
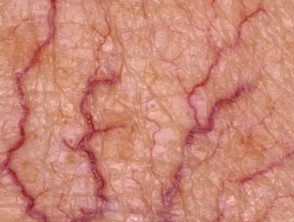
Telangiectasia
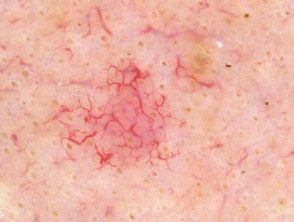
Telangiectasia
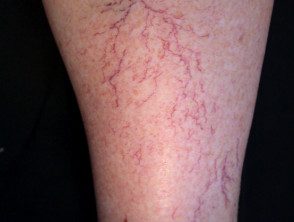
Telangiectasia
Which is the differential diagnosis of telangiectasia?
Telangiectasias must be distinguished from others vascular conditions, including blood vessel tumors like infantile hemangiomas and angiomas arising in adults; Y capillary or venous vascular malformations
The large red blood vessels are arteries and the large blue blood vessels are veins. The arteries can become enlarged due to the formation of aneurysms. The enlarged veins due to the destruction of your valve system are known as varicose veins.
Classification of telangiectasia
Inherited conditions
- Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia
- Benign hereditary telangiectasia
- Generalized essential telangiectasia
- Unilateral nevoid telangiectasia
- Angioma serpiginous
- Rothmund Thompson syndrome
- Ataxia-telangiectasia
-
Bloom syndrome (congenital telangiectatic erythema)
- Cockayne syndrome
- Skin marmorata telangiectatica congenita
- Focal dermal hypoplasia (Goltz syndrome)
- Kindler's syndrome
Note that telangiectasia can be seen as a normal feature of facial skin in some families.
Hereditary telangiectasia
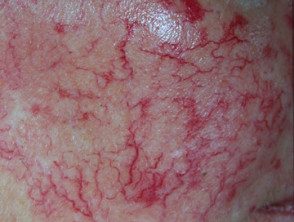
Familial telangiectasia
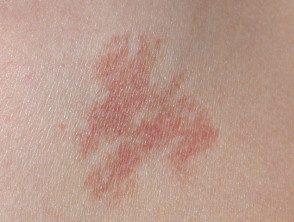
Benign hereditary telangiectasia
Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia
Acquired telangiectasia
- Rosacea
-
Sun damaged and aged skin, especially in those who smoke
-
Spider telangiectasias (also called spider nevus or spider angioma)
- Poikiloderma from Civatte (sun damage affecting the sides of the neck)
- The pregnancy
-
Liver disease, particularly when associated with alcohol or viruses. infection
- Cushing's syndrome
- Systemic sclerosis especially CRST syndrome (which forms telangiectatic mats)
- Cutaneous lupus erythematosus
- Mixed connective tissue disease
- Dermatomyositis
-
Mastocytosis, specifically the variant, eruptive telangiectasia macularis perstans
- Carcinoid syndrome
- Necrobiosis lipoidica
- Male genitalia dysesthesia
Telangiectasia due to disease
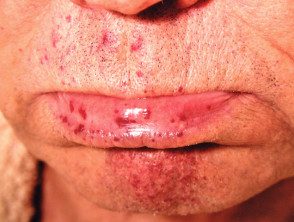
CRST syndrome
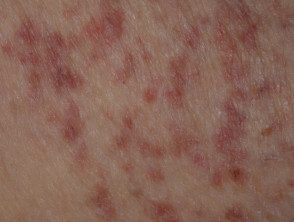
Telangiectasia in mastocytosis
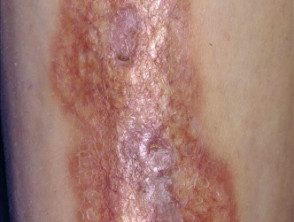
Lipoid necrobiosis
Telangiectasia can follow a skin lesion. For example:
- Scars, including hypertrophic and keloid scars
- Livedoid vasculopathy and atrophie blanche
- Radiation damage
-
Erythema ab igne.
Telangiectasia after injury.
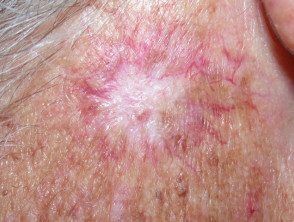
Radiation site
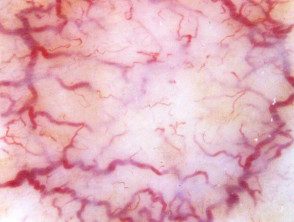
Radiation site
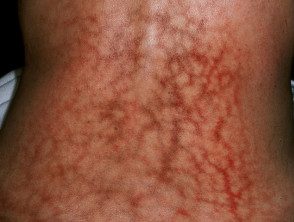
Erythema ab igne
Some tumors are characterized by telangiectasia, such as:
- Sebaceous hyperplasia
- Basal cell carcinoma
- Merkel cell carcinoma
- Kaposi sarcoma
-
Cutaneous T cell lymphoma (CTCL), particularly variant of poikiloderma vasculare
- Intravascular B cell lymphoma.
Telangiectasia in skin tumors.
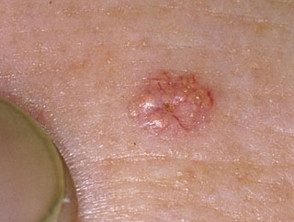
Sebaceous hyperplasia
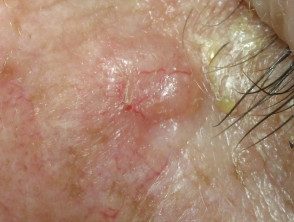
Basal cell carcinoma
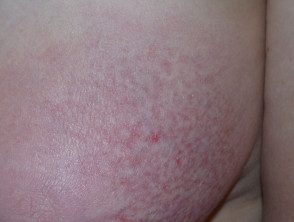
CTCL
Certain medications can lead to telangiectasia.
- Vasodilators, especially calcium channel blockers; sites exposed to the sun are mainly affected
- Long-term systemic corticosteroids.
- Long-term current corticosteroids including steroidal rosacea
- Intralesional Triamcinolone Injections
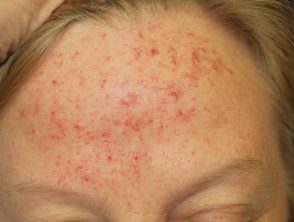
Telangiectasia related to topical steroid use
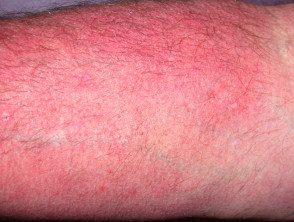
Telangiectasia due to topical steroids
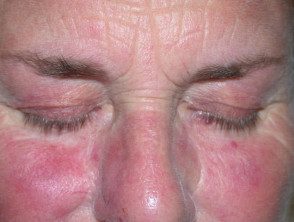
Steroid-induced telangiectasia
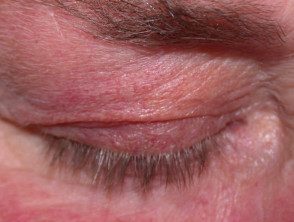
Steroid-induced telangiectasia
What is the treatment for telangiectasia?
Telangiectasias are generally harmless. Treatment may be sought for bleeding or unsightly appearance. Facial red vein treatment methods include:
- Electrosurgery
-
Intense Pulsed Light (IPL)
- Vascular To be treatment
-
Sclerotherapy
