What is it vesicular hand dermatitis?
Vesicular dermatitis of the hand is a form of hand. eczema characterized by vesicles or bullas (blisters) A similar condition can affect the feet (vesicular dermatitis of the foot).
This form of eczema is also called vesicular endogenous eczema, dyshidrotic eczema and pompholyx; cheiropompholyx affects the hands and pedopompholyx affects the feet.
Vesicular hand/foot dermatitis
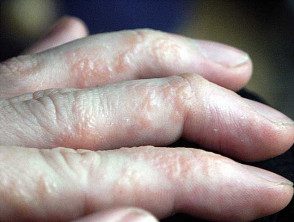
Pompholyx
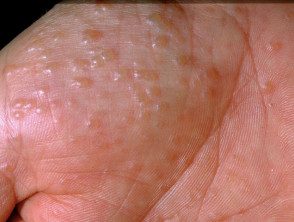
See more images of vesicular hand/foot dermatitis.
Who gets vesicular hand/foot dermatitis?
Vesicular hand/foot dermatitis most often affects young adults.
- It is more common in women than in men.
- Many of them report palmoplantar hyperhidrosis.
- There is a personal or family history of atopic eczema in 50%.
What causes vesicular hand/foot dermatitis?
Vesicular hand/foot dermatitis is multifactorial. In many cases, it appears to be related to sweating, as rashes often occur during hot weather, damp conditions or after an emotional disturbance. Other contributing factors include:
- Genetics
-
Contact with irritants such as water, detergents, solvents and friction
- association with contact allergy to nickel and others Allergens
- Inflammatory dermatophyte infections (ringworm) (when known as dermatophytes)
- Adverse reaction to drugs more often immunoglobulin therapy.
What are the clinical features of vesicular hand/foot dermatitis?
Vesicular hand/foot dermatitis presents as recurrent Deep blister cultures on the palms and soles. They cause intense itching or a burning sensation. The blisters peel off and the skin appears red, dry and sore. fissures (cracks)
When it involves the distal finger adjacent or proximal to the nail fold, can result in paronychia (swelling of the nail fold) and nails dystrophy with irregular bites and crests.
What are the complications of vesicular hand/foot dermatitis?
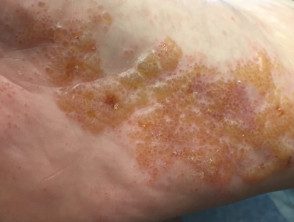
Secondary bacterial infection with Staphylococcus aureus me Streptococcus pyogenes is common in vesicular hand/foot dermatitis and results in pain, swelling, and pustules on the hands and/or feet.
Infected vesicular dermatitis of the hand
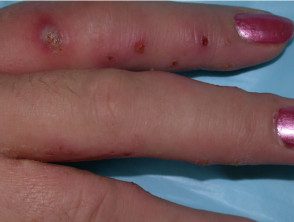
Pustules
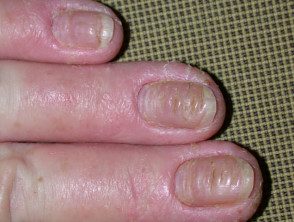
chronic paronychia
How is vesicular hand/foot dermatitis diagnosed?
The clinical presentation of vesicular hand/foot dermatitis is typical.
- If you suspect a fungal infection (tinea pedis), skin scrapings should be taken for mycology.
- Patch the test is indicated in chronic or atypical cases.
-
Skin biopsy It is rarely necessary. Sample spongy eczema.
What is the treatment for vesicular hand/foot dermatitis?
Vesicular hand/foot dermatitis is difficult to treat. Current therapy is relatively ineffective due to the thick horny layer skin of palms and soles.
General measures
- Wet dressings to dry blisters, using diluted potassium permanganate, aluminum acetate, or acetic acid
- cold compresses
- Pain relieving emollient lotions and creams
- Powerful antiperspirants applied to palms and soles at night
- Protective gloves should be worn when doing wet or dirty work.
- Well-fitting footwear, with 2 pairs of socks to absorb sweat and reduce friction.
Contact with irritants such as water, detergents and solvents should be avoided as much as possible and protective gloves should be worn to prevent irritating contact dermatitis.
- Note that cream cleaners are not antimicrobial; Soap and water or a disinfectant is needed to wash your hands in order to destroy pathogens such as the SARS-CoV-2 virus responsible for COVID-19.
People with vesicular hand dermatitis who are allergic to nickel should try to avoid touching nickel items.
Prescription drugs
- Ultra-strong topical corticosteroid creams applied to new blisters below occlusionand ointments applied during the dry inflamed phase.
- short courses of systemic Corticosteroids, usually prednisone or prednisolone, are prescribed for flare-ups.
- Oral antistaphylococcal antibiotics are prescribed for secondary bacterial infection.
- Topical and oral antifungal agents are prescribed for confirmed dermatophytic infection.
- In patients with hyperhidrosis, it may be worth trying an anticholinergic agent such as propantheline or oxybutynin.
- In severe cases, immunomodulatory drugs are indicated. These include methotrexate, mycophenolate mofetil, azathioprine, and cyclosporine.
- When available, alitretinoin is used for chronic resistant disease.
Other options
- Superficial radiotherapy
-
Botulinum toxin injections (to prevent sweating)
-
Phototherapy and photochemotherapy (PUVA) therapy
What is the prognosis for vesicular hand/foot dermatitis?
Vesicular hand/foot dermatitis usually subsides gradually and resolves spontaneously. It may recur in hot weather or after a period of stress, and in some patients it is recalcitrant.
