What is epoxy resin?
Epoxy resin is a chemical that is part of an epoxy resin system. Epoxy resin systems are widely used in industry due to their strong adhesive properties, chemical resistance, and toughness. Common two-part epoxy resin systems contain epoxy resin, catalysts / curing agents, and diluents and / or other additives. Any of these chemicals alone can cause irritating and / or allergic contact dermatitis. Cured epoxy resin (the fully hardened combination of epoxy resin system chemicals) should not be irritating or sensitizing.
| Epoxy resin system component | Characteristics |
| Epoxy resin (uncured) |
|
| Catalysts / curing agents |
|
| Diluents / additives |
|
Where is epoxy resin found?
Most people associate epoxy resin with glues and adhesives. Epoxy glues like Araldite® are often used by DIYers and hobbyists. These glues generally come in two parts, the hardener and the resin. When mixed, it is claimed that the resulting compound can bond almost anything. The following table shows other uses for epoxy resin.
| Uses of epoxy resin. |
|
|
|
|
What are the reactions to epoxy resin? allergy?
Typical allergic contact dermatitis reactions can occur in people who are allergic to epoxy resin or other components of an epoxy resin system. Uncured epoxy resin, hardener, and thinner are potent irritants and potent sensitizers. Skin contact with the hardening agent can cause severe burns. They can also cause a severe allergic contact dermatitis characterized by redness, swelling, and itching. The skin should be washed with soap and water if any contact occurs. Additionally, hardeners and thinners are more volatile than resin and can cause allergic reactions by breathing the fumes.
Cured epoxy resins are rarely a problem, but measurable amounts of uncured have been found reagents it can remain in the “cured” resin after 1 week.
Epoxy resin dermatitis
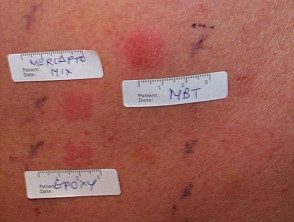
Patch tests
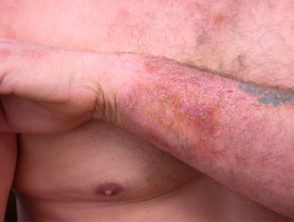
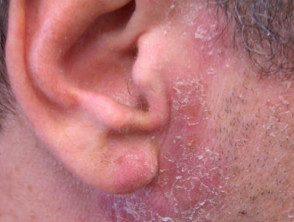
Am I allergic to epoxy resin?
An allergy to epoxy resin is diagnosed from your medical history and by performing special allergy tests, called patch tests
Standard patch tests with test epoxy resin material to 1% in acetone or petroleum jelly will generally find that people's 75% are allergic to epoxy, although not all epoxy resins have the same chemical structure. The standard test does not test hardener, but most people allergic to hardeners are also allergic to resin. Therefore, the detection of epoxy allergy is done using the epoxy resin.
Possibilities of developing a allergic reaction increase with the amount and concentration of exposure to the epoxy resin. There is a small risk of causing an allergy to develop from the patch test, so testing should only be done in people at risk.
Treatment of contact dermatitis due to exposure to epoxy resin
If you are diagnosed with an allergy to epoxy resin, avoid exposure to products that contain epoxy; otherwise, take steps to reduce potential exposure.
Washing the area immediately with soap and water should treat accidental exposure to glue or paints. Sometimes solvents (acetone, alcohol, or methyl ethyl ketone) can be used to reduce exposure. However, the routine use of these chemicals is not recommended as they tend to dry out and irritate the skin.
Dermatitis can be treated like any other acute dermatitis/eczema, with current corticosteroids emollients, antibiotics for any secondary bacterial infection (Staphylococcus aureus), etc.
What should I do to avoid an allergy to epoxy resin?
When using epoxy glues at home, avoid touching the glue and breathing in the fumes.
In the workplace, try to avoid exposure to epoxy resins, however this may not be feasible. Identify potential sources of exposure using the Material Safety Data Sheets; These are required for all chemicals and substances that you may come into contact with in the workplace. To reduce exposure, wear special gloves (nitrile rubber or nitrile butatoluene gloves) to protect hands. Rubber gloves do not help, as the resin penetrates through the glove in 30 seconds. Neoprene vinyl and rubber are not fully protective.
Allergy is more likely to fluid (low molecular weight) epoxy resin systems used in paints and coating materials than those used primarily for structural bonding, which have a higher molecular weight.
If you are very sensitive to epoxy resin, be aware of products that may contain it. In addition to obvious sources such as glues and two-part paints, be careful around items like vinyl or plastic bags, gloves, and jewelry.
Alert your doctor or dentist to the fact that you are allergic to epoxy resin. your dermatologist You may have more specific tips, especially if you are very sensitive to epoxy resin.
Alternative names for epoxy resin
Epoxy resin is also known by various other names. These include:
- Bisphenol A [2,2-bis (4-hydroxyphenyl) propane] (diphenylpropane)
- Diglycidyl ether
- Epichlorohydrin (1-chloro-2,3-epoxypropane) (8-chloropropylene oxide)
- 4,4′-isopropylidenediphenol-epichlorohydrin
Avoid all this. At work, request a material safety data sheet to help identify potential sources of exposure.
More information
Sensitizer uncured epoxy resin
Patch test:
1% epoxy resin in acetone or petroleum jelly
| Sources of exposure to epoxy resin | |
|---|---|
|
|

