What is ethylenediamine and where can it be found?
Ethylenediamine is a powerful sensitizer used in current medications, particularly antibiotic / steroid creams for their chemical stabilizing properties. It has been commonly found that people who show a positive patch The test reaction to ethylenediamine has used Kenacomb®, Kenacort® or Mycolog Cream®), a popular broad-spectrum antifungal / steroid cream, or one of its generic preparations. Although ethylenediamine has now been removed from Mycolog Cream®, there may be generic preparations or other similar formulations that may still contain allergen. Ethylenediamine is not used in ointment Preparations and rarely found in cosmetics and toiletries.
Ethylenediamine is also an ingredient in aminophylline, a xanthine bronchodilator used in the treatment of asthma and other respiratory problems. Other medications where ethylenediamine or its derivatives are found include some antihistamine and anti-nausea agents.
Industrial exposure to ethylenediamine is also possible through contact with products such as:
-
epoxy resin catalysts in glues, adhesives, paints
- refrigerant oils
- rubber latex stabilizer
- albumin or casein solvent
- fungicides and insecticides
- textile lubricants
- color developers
- antifreeze solutions
- electroplating solutions
- nail polish remover
- animal feed supplements
What are the reactions to ethylenediamine? allergy?
In ethylene diamine allergic individuals, contact with ethylene diamine from topical medications produces classic allergic contact. dermatitis reactions Usually the eruption is a worsening of an original eczematous condition that was being treated with a cream containing ethylenediamine. Damaged skin is sensitized more easily than normal intact skin.
Very often, people sensitive to ethylenediamine are also allergic to other components of the preparation. Neomycin is commonly associated and is also a powerful sensitizer that can exacerbate the problem.
Systemic administration either through inhalation or the oral use of preparations containing ethylenediamine has caused exacerbations of generalized eczematous rashes (systemic contact dermatitis).
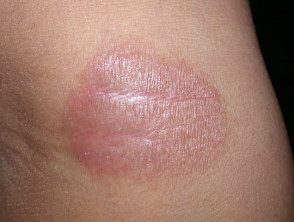
Ethylenediamine contact dermatitis
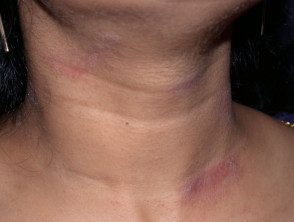
Ethylenediamine contact dermatitis
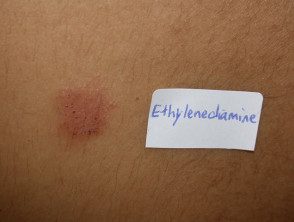
Ethylenediamine contact dermatitis
Am I allergic to ethylenediamine?
Ethylenediamine allergy is diagnosed by performing special allergy tests, that is, patch tests. A concentration of ethylenediamine at 1% in petrolatum is the recommended concentration used for patch testing. This is usually about five times the concentration found in commercial preparations, but it is necessary because the patch test with the actual commercial preparation often produces a false negative patch test response.
Ethylenediamine allergy treatment
Confirmation of ethylene diamine allergy requires rapid removal of the causative agent and then management as for any acute dermatitis/eczema; This may include treatment with topical corticosteroids and emollients.
What should I do to avoid an allergy to ethylenediamine?
Alert your doctor or dentist to the fact that you are allergic to ethylenediamine. Carefully read the labels on all products for potential sensitizers. Avoid products that contain ethylenediamine or other related substances to which it may react. Since many antihistamines and anti-nausea products are already available on the counter, you must inform your pharmacist if you are sensitive to ethylenediamine. They will be able to provide you with suitable alternative products. Ethylenediamine allergy can make you sensitive to other related compounds. As a precaution, you should avoid using products that contain any of these substances.
In the workplace, try to avoid exposure to ethylenediamine, however this may not be practical. Identify possible sources of exposure using the Material Safety Data Sheets; These are necessary for all chemicals and substances that can come into contact within the workplace. To reduce exposure, wear protective clothing such as gloves, aprons, and masks.
your dermatologist You may have more specific advice, especially if you are very sensitive to ethylenediamine.
Alternative names for ethylenediamine
- Ethylenediamine dihydrochloride
- 1,2-Ethanediamine dihydrochloride
- 1,2-diaminoethane dihydrochloride
- Chloretamine
More information
Formula: C2H10Cl2north2
CAS number: 333-18-6
Cross reactions:
- Aminophylline
- Tripelennamine
- Phenothiazine (eg, Promethazine)
- Piperazines (eg Cyclizine, Cetirizine, Meclizine)
Appearance: colorless liquid
Sensitizer: ethylenediamine
Patch test: 1% of ethylenediamine in petrolatum


