What is it alopecia areata?
The term alopecia means hair lost. In alopecia areata, one or more round, bald patches appear suddenly, most often on the scalp. Alopecia areata is also called autoimmune alopecia, which can also cause diffuse alopecia.
Alopecia areata
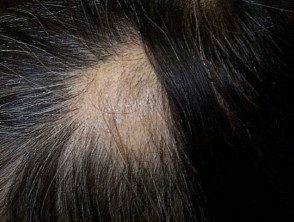
Alopecia areata
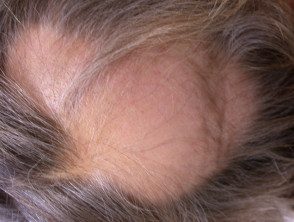
Alopecia areata
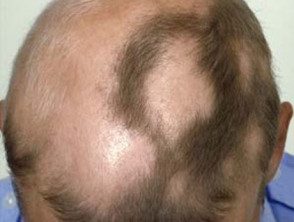
Alopecia areata
See more images of alopecia areata.
Who gets Alopecia Areata?
Alopecia areata can affect men and women at any age. It begins in childhood at about 50%, and before age 40 at 80%. The lifetime risk is from 1 to 2% and is independent of ethnicity.
- There is a family history of alopecia areata and / or other autoimmune diseases in 10-25% of the patients.
- At least 8 susceptibility genes have been detected
- Alopecia areata patients have higher than expected rates of thyroid disease, vitiligo, and atopic eczema.
- There is an increase predominance in patients with chromosomal disorders like Down syndrome.
- It is possibly drug-induced when it arises in patients on biological drugs.
What causes alopecia areata?
Alopecia areata is classified as an autoimmune disorder. It is histologically characterized by T cells around the hair follicles. These 2D-positive group N8 CDG (+) NK T cells (NKG2D (+)) release proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines that reject hair The exact mechanism is not yet understood.
The start o reappearance Hair loss is sometimes triggered by:
- Viral infection
- Trauma
- Hormonal change
- Emotional / physical stressors.
What are the clinical features of alopecia areata?
Various clinical patterns of alopecia areata are described. The most serious disease is associated with early age, concurrent atopic eczema and chromosomal abnormalities.
Most patients have no symptoms and have baldness patch or thinning hair is noted incidentally, often discovered by a hairdresser. Other patients describe a burning and prickly discomfort in the affected areas, this is known as trichodynia.
Alopecia areata irregular
Alopecia areata patches can affect any hairy area, most often the scalp, eyebrows, eyelashes, and beard.
Irregular alopecia areata has three stages.
- Sudden hair loss
- Enlarged patch or bald patches
- Regrow hair
Bald areas may have a smooth, completely hairless or scattered 'exclamation mark' hair surface.
- The exclamation mark hairs are 2-3 mm long, broken or tapered, with a club-shaped root. Microscopy (also called dermoscopy or tricoscopy) shows a proximal shaft and normal gauge distal axis.
- Regrowing hairs are usually initially white or gray; They can be curled even when previously they were straight.
- It can take months and sometimes years for all hair to grow back.
- One patch may fall off while another grows back.
Total alopecia
- Affects up to 5% in patients with autoimmune hair loss
- All or almost all scalp hair is lost.
Universal alopecia
- Affects less than 1% of cases
- All or almost all hair is lost throughout the body.
Ophiasis
- A pattern of alopecia areata that affects the occipital and side scalp
- The bald area can surround the scalp.
Diffuse alopecia areata
- Sometimes called alopecia areata incognito
- It presents with sudden diffuse alopecia
- Persistent hair tends to be gray, hence descriptions of 'turning white overnight'
- Positive hair pull test
- Diffuse alopecia areata can be confused with telogen effluvium or hair loss due to medications.
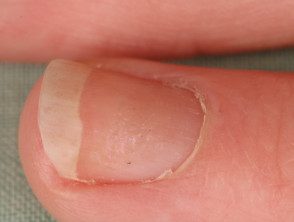
Alopecia areata nail
-
Nail disease affects 10 to 50% of people with alopecia areata.
- Regular bites and ridges are the most common findings.
- It can also cause koilonychia, trachyonychiaBeau lines, onychorrhexis, onychomadesis, onycholysis and red spots on the lunula.
Alopecia areata nails
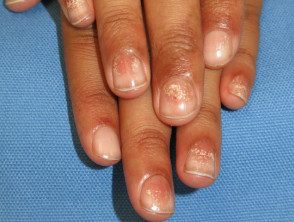
Alopecia areata nails
Alopecia areata nail

Alopecia areata nails
Alopecia areata complications
Alopecia can be temporary or persistent. More severe and persistent disease increases the chance that alopecia areata causes psychosocial consequences of your illness, such as depression and anxiety.
Patients should be evaluated for atopy, vitiligo, thyroid disease and other autoimmune conditions.
How is alopecia areata diagnosed?
Alopecia areata is diagnosed clinically. Although generally straightforward, additional tests are sometimes needed to confirm the diagnosis.
- Trichoscopy (use of a dermatoscope to examine hair and scalp)
-
Skin biopsy (histopathology)
What is the treatment for alopecia areata?
There is still no reliable cure for alopecia areata and other forms of autoimmune hair loss. Because spontaneous growth is common in alopecia areata, especially in the early stages of the disease, and research has often been of poor quality, the effectiveness of reported treatments is largely unknown. Systemic The therapy is reserved for patients with:
- Over the 20% of Scalp Hair Loss
- Rapid hair loss.
- Chronic Hair loss
- Severe distress.
Current deals
Various topical treatments used for alopecia areata are reported to result in temporary improvement in some people. Your role and effectiveness unknown Hair can fall out when stopped. These include:
- Powerful or ultra-powerful topical steroids
- Minoxidil solution or foam
-
Dithranol (anthralin) ointment
Intralesional corticosteroid injections.
Triamcinolone acetonide injections 2.5–10 mg / ml into irregular alopecia areata of the scalp, beard, or eyebrows may accelerate hair growth. Its effect is temporary. If bald patches reappear, they can be re-injected.
Systemic corticosteroids
High-dose pulse and oral intravenous steroids can cause temporary regrowth of hair. Most physicians agree that long-term systemic steroid treatment is not warranted due to the potential and actual adverse effects.
Immunotherapy
The sensitizers diphenylcyclopropenone (diphencyprone) and dinitrochlorobenzene cause a contact allergy. dermatitis in treated areas These sensitizers can be reapplied once a week to bald areas of the scalp. The resulting dermatitis is irritating and can be unpleasant. It is often accompanied by an inflamed lymph gland.
Other treatments
A combination of lipidAntiretroviral drugs simvastatin and ezetimibe (which have immunomodulatory effects) have been reported to be effective.
A single case of substantial hair growth is reported in a patient with longstanding total alopecia after dupilumab use for her. concomitant severe atopic eczema.
There are no convincing data to support the use of methotrexate, sulfasalazine, azathioprine, cyclosporine, or phototherapy.
JAK / STAT inhibitors
Several patients with severe alopecia areata have improved when treated with oral tofacitinib or oral ruxolitinib, which are Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors. It is believed that they can act by blocking interleukin (IL) -15 signaling and interferon gamma (IFNγ). Be careful with the results of clinical trials of these biological medicines.
What else should be considered for alopecia areata?
Advice
Some people with alopecia areata seek and benefit from professional advice to accept the disorder and regain self-confidence.
Camouflaged hair loss
Scalp
A hairpiece is often the best solution to disguise the presence of hair loss. These cover the entire scalp or only part of the scalp, using human or synthetic fibers tied or woven to a fabric base.
- A full wig is a cap that fits over the entire head.
- A partial wig should be cut or glued to existing hair.
- A hair integration system is a custom-made hair net that provides artificial hair where it is required, and normal hair is pulled through the net.
- Hair additions are fibers stuck to existing hair and removed after 8 weeks.
Styling products include gels, mousses, and sprays to hold hair in place and add volume. They are reapplied after washing or styling hair.
Tabs
Artificial eyelashes come in singles, demilashes and complete sets. They can be trimmed if necessary. Eyelashes can irritate the eyes and eyelids. They are attached with methacrylate glue, which can also irritate and sometimes cause allergic contact dermatitis.
The eyeliner tattoo is permanent and should be done by a professional cosmetic tattoo artist. The color eventually fades and can slightly move from the original spot. It is extremely difficult to remove the pigment, if the result is unsatisfactory.
Eyebrows
Artificial eyebrows are made from natural or synthetic human hair in a net that is glued in place.
An eyebrow pencil is available in a variety of colors made of inorganic pigments.
The tattoo can also be performed to disguise the loss of the eyebrows, but it tends to seem unnatural due to the shine of the hairless skin.
How can alopecia areata be prevented?
We still don't know how to prevent the appearance of alopecia areata.
What is the prognosis for alopecia areata?
In many patients with a single bald patch, spontaneous growth occurs within one year. Even in the most severe cases of total alopecia and universal alopecia, recovery can occur at some future date. Research has shown:
- The 40% of patients with a single patch of hair loss regrow in 6 months.
- The 27% of patients with multiple patches of hair loss have full growth within 12 months.
- The 33% of patients with alopecia areata has chronic hair loss.
Poor forecast factors include:
- Young age at start
- Extensive disease
- The bald patches persist for more than 1 year.
- A pattern of hair loss opiasis.
- Alopecia areata of the nails.
- The onset of alopecia areata before puberty.
- Family members with alopecia areata
- Personal or family history of other autoimmune diseases.
- Down's Syndrome.
New monoclonal antibody targeted biological agents cytokine The pathways offer promise for the future treatment of alopecia areata.

