What is athlete's foot?
Athlete's foot is a term often used to describe a fungus infection (or dermatophytosis) of the foot (tinea pedis).
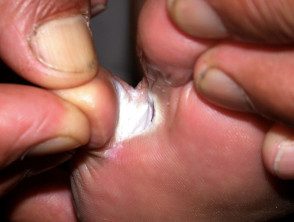
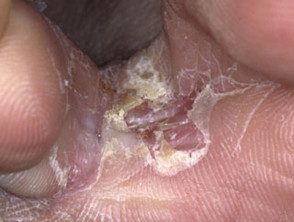
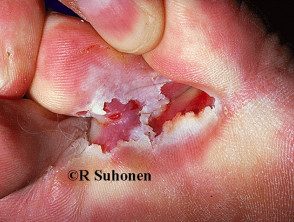
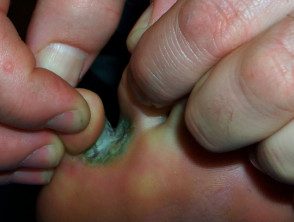
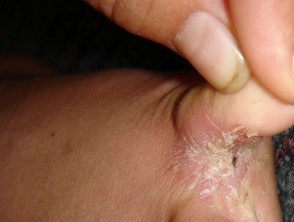
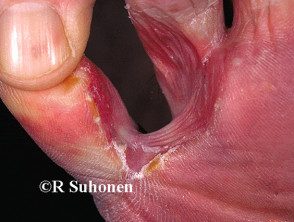
It most often produces peeling of the skin and fissure between the toes (toe clefts) the cleft between the fourth and fifth fingers is the most affected.
Fungal infection isn't the only reason for peeling and cracking between the toes, and the term athlete's foot is sometimes used to refer to any condition in which the clefts of the toes are inflamed.
Athlete's foot
Athlete's foot
Athlete's foot
Athlete's foot
What causes athlete's foot?
He athlete's foot is usually due to proliferation of dermatophyte fungi of the genera Trichophyton rubrum, Trichophyton interdigitaleand Epidermophyton floccosum.
Predisposing factors
Athlete's foot is more common in those who participate in sports because:
- Can use occlusive footwear
- they sweat a lot
- They may not dry their feet carefully after bathing
- They are exposed to fungal spores on surfaces in common areas.
What are the clinical features of athlete's foot?
Clinical features of athlete's foot may include:
- Moist, peeling skin between the toes
- White, yellow, or greenish discoloration
- Sometimes thickened skin
- Painful fissures
- Unpleasant smell.
Athlete's foot is usually mild; highly inflamed athlete's foot is usually due to a secondary bacterial infection.
How is athlete's foot diagnosed?
Diagnosis is usually clinical, as athlete's foot has a characteristic appearance. If it is resistant to treatment, investigations are done to identify a specific infection.
- Scrapings for fungi microscopy and culture
- Swabs for bacterial microscopy and culture
- Wood's examination (ultraviolet light) for coral-red fluorescence, characteristic of erythrasma
Which is the differential diagnosis of athlete's foot?
Athlete's foot is a located interdigital form of intertrigo.
In addition to ringworm of the foot, peeling and cracking between the toes can be due to:
- yeast infection (candida)
- Bacterial infection (erythrasma, pseudomonas, staphylococci, and streptococci)
- mold infection
- Soft corn (accumulation of thick skin due to repetitive trauma fingers pressing against each other)
- Injuries, for example, excessively vigorous removal of peeling skin
- A skin condition, such as psoriasis (scaly patches on the scalp, on the elbows and knees or rashes in the folds of the body), foot eczema or exfoliative keratolysis.
Non-fungal causes of athlete's foot
Pseudomonas infection
Psoriasis
Eczema
Was it the athlete's foot treatment?
Treatment for athlete's foot should begin with general measures.
- Dry carefully between the toes.
- use a powder dust to keep the affected area dry.
- Keep your fingers apart using a cotton or foam wedge.
- Wear shoes that are loose around the toes or go barefoot.
- Apply one current antifungal agent These can also control a lot of bacteria They live in the moist skin between the toes.
Whitfield ointment (3% Salicylic Acid, 6% Benzoic Acid in Vaseline) is particularly helpful as it removes the top layer of wet peeled skin (i.e. it is keratolytic), and eliminates bacteria and fungi.
Make sure that other fungal infection sites are also treated effectively.