Ad
Skin cancer
Application to facilitate skin self-examination and early detection. read more.
What is it basal cell nevus syndrome?
Basal cell nevus syndrome is a rare inherited condition characterized by:
- Early and multiple-onset basal cell carcinomas.
- Other tumors including melanoma, medulloblastoma, meningioma, breast carcinomanot Hodgkin lymphomaand ovary fibroma
Synonyms for basal cell nevus syndrome (BCNS) include basal cell carcinoma nevus syndrome (BCCNS), Gorlin-Goltz syndrome, Gorlin syndrome, and nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome. The so-called basal cell naevi they are actually small basal cell carcinomas.
Developmental abnormalities in affected people may include:
- Odontogenic cysts in the jaw
- Wide forehead
- Holes in palms and soles
- Rib abnormalities
- Falx cerebri calcified (seen on x-ray of the skull)
Basal cell nevus syndrome
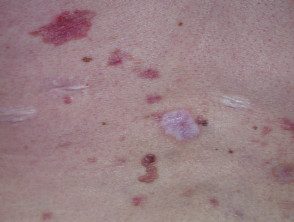
Numerous basal cell carcinomas
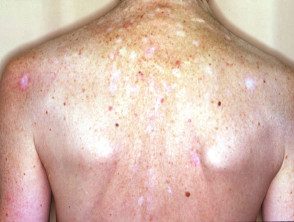
Multiple scars from cryotherapy.
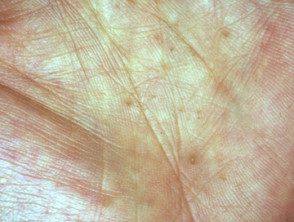
Holes Palmar
What is the cause of basal cell nevus syndrome?
Basal cell nevus syndrome is most often due to abnormal PTCH 1 (patched) gene in chromosome 9q22.3-q31. This gene normally works as a tumor suppressor, so when it doesn't work properly it can allow cancers to grow. Other cases are due to mutations at 1p34.1 (PTCH 2 gene) or 10q24.32 (SUFU gene).
Basal cell nevus syndrome is a autosomal Dominant condition which means that half of the children of an affected person also have the syndrome. It affects one in 50 to 100,000 people.
Recent research is studying how the genetics of basal cell carcinoma can lead to effective treatments in the future.
Genetics of Basal Cell Nevus Syndrome *
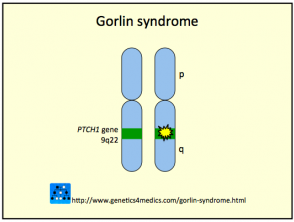
Basal cell nevus syndrome
* Image courtesy of Genetics 4 Medics
How was the diagnosis made?
A diagnosis of basal cell nevus syndrome can be made if there are 2 major criteria or 1 major and 2 minor criteria.
Main criteria
- Multiple (> 2) basal cell carcinomas at any age or a basal cell carcinoma of less than 20 years or> 10 basal cell nevi
- Histologically proven odontogenic keratocyst or polyostotic bone cyst
- Palm or plant holes (3 or more)
- Ectopic calcification: lamellar or early calcification (<20 años) del falx cerebri
- Family history of basal cell nevus syndrome.
Minor criteria
- Congenital skeletal defects: bifid rib, fused, extended or missing, or bifid, wedge, or fused vertebra
- Large head with occipitofrontal circumference> 97th percentile, with frontal protrusion
- Cardiac or ovarian fibroma (benign tumor in heart or ovary)
- Medulloblastoma (a evil one brain tumor that usually arises in young children); this is generally associated with mutations in the SUFU gene
- Lymphomesenteric cysts (abdominal cysts filled with lymph fluid)
- Congenital malformation: cleft lip and / or palate, polydactyly (additional fingers or toes), birth defect of the eye, such as waterfall, microphthalmos (small eye) or coloboma (iris tumor)
Basaloid follicular hamartoma has also been linked to a mutation in the patched gene but it's a benign tumor. There are loners and multiples hereditary variants
What is the treatment for basal cell nevus syndrome?
First sign Basal cell nevus syndrome may be the development of a medulloblastoma in a 2 to 5 year old, but fortunately this is rare. Only a few children with medulloblastoma also have basal cell nevus syndrome. If detected early enough, the tumor can be treated by surgery and chemotherapy.
Patients with basal cell nevus syndrome often require surgery to remove the cysts from the jaw at age 20. Often, it is not until they are 30 or 40 years old that basal cell carcinomas begin to appear, so the diagnosis of the syndrome is often delayed.
All patients with basal cell nevus syndrome should see a dermatologist for regular skin exams so that basal cell carcinomas can be treated when they are small. This may require surgery or one of the many other treatments available for these tumors, including cryotherapy, photodynamic therapy, fluorouracil cream and imiquimod cream. They should not be treated with irradiation, as this can lead to the development of more tumors.
Some patients may require long-term oral treatment. retinoids like isotretinoin or acitretin. Advanced basal cell carcinomas can sometimes be treated with vismodegib.
Sunscreen is vital in reducing the number of developing skin cancers, but even full protection will not prevent all basal cell carcinomas in patients with basal cell nevus syndrome.


