Ad
Skin cancer
Application to facilitate skin self-examination and early detection. read more.
What are brown spots and freckles?
Brown spots and freckles in the sunexposed skin are ephelides (the plural of ephelis) and lentigines (the plural of lentigo) The difference between an ephelis and a lentigo is that an ephelis fades during the winter months, while a lentigo persists in the absence of ultraviolet (UV) stimulation. Ephelides and lentigos can occur in the same individuals, and the risk factors for both are generally the same.
Who gets ephelides?
Ephelides are very common in fair-skinned people, especially children with redness. hair, where he MC1R gene it is believed to be the main gene involved. They are an inherited trait that sometimes also affects people with darker skin types.
What causes ephelides?
An ephelis is brown due to the pigment melanin. Melanin is made by melanocytes and disseminated in keratinocytes. The production of melanin by melanocytes decreases during the winter months and increases when the skin is exposed to UV radiation in sunlight. The color is due to the located accumulation of melanin in keratinocytes. There is no increase in melanocytes.
What are the clinical characteristics of ephelides?
Ephelides arise on an individual's midface and sometimes more widely from early childhood onward. As a person ages, this type of freckle generally becomes less noticeable. They are more prominent in summer but fade considerably or disappear in winter. An ephelis is usually less than 3 mm in diameter.
Apart from the need for sun protection, no particular treatment is necessary.
Freckles
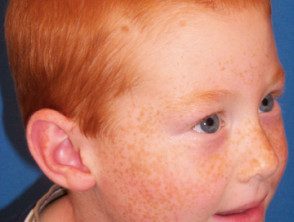
Freckles
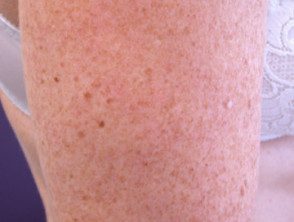
Freckles
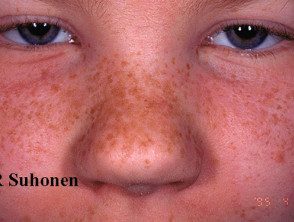
Freckles
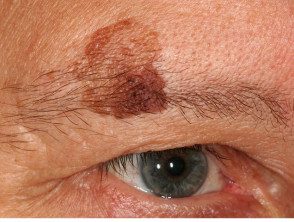
What are lentigos?
Lentigos are flat brown lesions with a clearly defined border. The most common type, solar lentigos, arise in middle age and result from sun damage. They are most often found on the face and hands, and are larger and more defined than freckles. Other types of lentigo include ink-stained lentigo and simple lentigo.
Who gets lentigos?
Lentigos are common in people with fair skin, but they also frequently arise in sun-exposed places in people who tan easily or have naturally dark skin. Lentigos are common after the age of 40, but they can also occur in younger people.
What Causes Solar Lentigos?
Solar lentigines are caused by UV radiation from sun exposure or other forms of UV radiation, such as that involved in medical treatment (for example, phototherapy) or the use of tanning beds. In biopsy, a solar lentigo has a proliferation keratinocytes, which form challenge pegs, and often there is also an increase in the number of melanocytes.
What are the clinical characteristics of solar lentigos?
Solar lentigos tend to persist for long periods and do not disappear in the winter, although they can fade. They vary in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters in diameter. The color tends to be uniform throughout the injury, with a yellowish or grayish light brown tone. The edge of the lesion is clearly defined, and an irregular edge can give it a scalloped shape. They may have a dryness or a little scaly surface.
One or more seborrheic keratosis it can arise from a solar lentigo.
It is important to distinguish a harmless but atypical solar lentigo from early evil one melanoma and its subtypes, lentigo maligna and lentiginous melanoma. Lesions that are clinical, dermoscopic, or histologically atypical must be completely removed surgically excision with pathological examination.
Lentigos
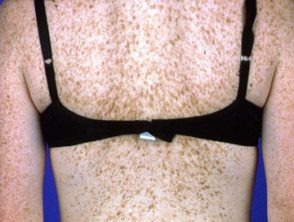
Lentigos
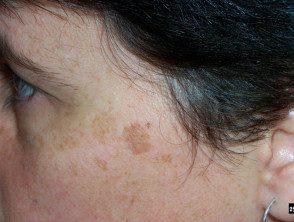
Lentigos
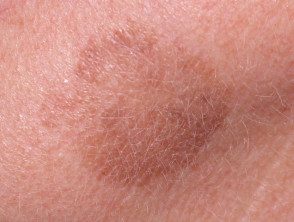
Lentigos
How are brown spots and freckles diagnosed?
Most ephelides and lentigos can be easily diagnosed clinically by a healthcare professional trained in examining the skin. If there is any doubt about whether a brown mark can be Cancer, the lesion can be monitored (with digital dermoscopic surveillance) or excised for pathological examination.
Which is the differential diagnosis for freckles and solar lentigines?
A brown mark can also be an actinic keratosis (sun damage) or a seborrheic keratosis (senile wart) in which there is proliferations keratinocytes. Actinic and seborrheic keratoses tend to be more scaly and thickened than solar lentigos. Facial pigmentation It may also be due to melasma, a chronic pigmentation disorder
Other brown brands
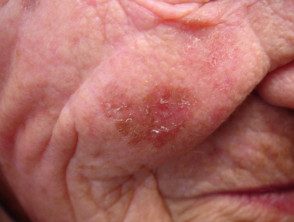
Actinic keratosis
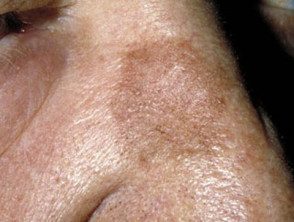
Actinic keratosis
Seborrheic keratosis
What is the treatment for brown spots and freckles?
Prevention of brown marks
Not all brown marks on the skin can be prevented. Careful sun protection will reduce the number of new solar lentigos. Staying out of the sun and wearing sunscreen clothing is much more effective than wearing sunscreen alone. Sunscreens should have a high sun protection factor (SPF 50+) and good broad spectrum coverage, and should be applied liberally and frequently.
Treatment of brown marks
Brown marks can fade with careful sun protection, such as applying a broad spectrum sunscreen daily. Regular applications of anti-aging or discoloration creams can also help.
These may contain hydroquinone or antioxidants such as:
- Alpha hydroxy acids
- Vitamin C
- Retinoids
- Cysteamine
- Resveratrol
- Vitamin E
- Tyrosinase inhibitors such as:
- Arbutin - natural hydroquinone
- Azelaic acid
- Kojic acid.
- Melanosoma inhibitors such as niacinamide (B3).
Brown marks can be removed more quickly and effectively by chemical peels, cryotherapy, or certain pigment lasers that target melanin in the skin. Multiple treatments are often necessary.
Suitable green light devices to remove epidermal pigment includes:
- Pulsed dye pulsed with flash To be
- Doubled frequency Q-Switched neodymium laser: yttrium-aluminum-garnet (Nd: YAG).
Suitable red light devices that can be used to remove epidermal pigment include:
- Q-Switched Alexandrite Laser
- Q-changed ruby laser.
Intense pulsed light has a similar effect. Carbon Dioxide and Erbium Lasers: YAG laser lasers vaporize the skin from the surface, thereby removing pigmented Injuries A fractional laser can also be effective. More recently, picosecond lasers have begun to be used to remove epidermal pigment.
The results of laser and light treatment are variable, but are sometimes very impressive with minimal risk of scarring.
With surface resurfacing techniques, there is minimal discomfort and no downtime, but multiple treatments are often necessary. Treatment occasionally worsens pigmentation by causing post-inflammatory pigmentation. Continuous and careful sun protection is essential, because the pigmentation is likely to recur next summer.
Treatment effect
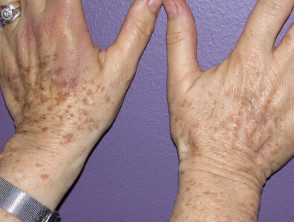
Freckles on hand before and after green laser light
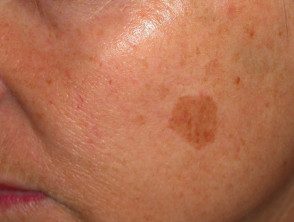
Freckles before cryotherapy
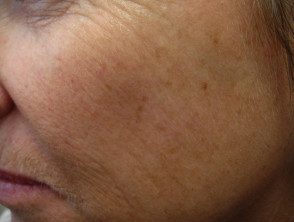
Freckles after cryotherapy


