What is contact? dermatitis?
Contact dermatitis (also called contact eczema) refers to a group of skin disorders in which the skin reaction is due to direct contact with the causative agent. The term dermatitis implies that the outer layers of the skin are affected. Can be acute (single episode) or chronic (persistent). Dermatitis almost always itches.
Contact dermatitis includes several entities.
- Chemical burns
- Irritating contact dermatitis
- Allergic contact dermatitis
-
Contact stomatitis and contact cheilitis
- Protein contact dermatitis
- Systemic contact dermatitis
Contact dermatitis is sometimes of mixed origin, particularly when it is causing hand dermatitis. Contact dermatitis is the most common cause of occupational skin disease, and is particularly common in cleansers, healthcare workers, food handlers, and catering and hairdressers. It can even occur in people who use computers (computer dermatitis).
Contact dermatitis
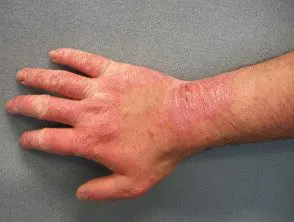
Rubber allergic contact dermatitis.
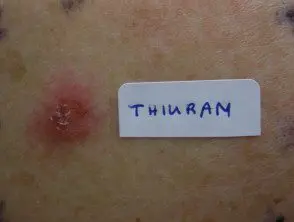
Rubber allergic contact dermatitis.
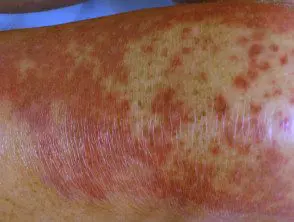
Skin contact dermatitis
What does contact dermatitis look like?
The appearance of contact dermatitis is highly variable. It can affect any area of the body and can have any shape (linear, round, polygonal, irregular). The affected skin can have any of the following characteristics.
- Redness (erythema)
- Blisters that are small (vesicles) or big (bullas)
- Swellingedema)
- Dryness or climbing
- Cracks (fissure)
- Lichenification (thickened and lined skin)
- Pigmentation increased (hyperpigmentation) or reduced (hypopigmentation)
Minor changes may include:
- Scratch marks (excoriation)
- Crust (due to exudate)
- Pustules (because bacterial infection)
How is the diagnosis of contact dermatitis made?
Contact dermatitis is usually identified after taking a careful history.
- the eruption it is eczematous (changes on the skin surface such as blisters, dryness, peeling and redness)
- The eruption has occurred in an area in contact with the suspected cause.
- The eruption has not occurred in places that are not in contact with this agent
- May or may not affect all skin areas in contact with the agent
- Contact dermatitis is usually asymmetric in distributioneg one hand more severely affected than the other
The various forms of contact dermatitis may seem similar to each other. They can be distinguished by the following characteristics.
-
Chemical burn occurs after a single exposure to a toxic agent like a strong acid or alkali. Only skin in contact with the chemical is affected.
-
Irritant dermatitis can occur after a single exposure, but more commonly follows repetitive exposure to an irritant such as friction injuries, soaps and detergents, excessive immersion in water, mild acids and alkalis, solvents. At least initially, only the skin in contact with the irritant is affected and generalized The spread of dermatitis is rare. Irritant dermatitis is more common in atopics (often people with a history of atopic eczema), sensitive skin and other conditions where the skin barrier function is compromised.
-
Allergic dermatitis generally occurs unexpectedly after allergen was previously tolerated. Then contact with minimal amounts of the allergen causes dermatitis at the exposed sites. Dermatitis can extend beyond the limits of direct contact with the allergen and can extend more widely (self-eczematization).
-
Contact stomatitis and contact cheilitis affect the inside of the mouth and lips, respectively.
- Protein contact dermatitis results from contact with food (such as meat or potatoes). Immediate contact urticaria it is followed by acute and sometimes chronic dermatitis at the same site.
- Follow systemic contact dermatitis ingestion of a substance that has previously caused allergic contact dermatitis. It results in a symmetrical skin rash, which often affects push-ups (for example, baboon syndrome), and can generalize. Systemic contact dermatitis is rare.
Patch testing is important to identify contact Allergens in any case severe or persistent contact dermatitis. An open application test may also be recommended.
How is contact dermatitis treated?
Once the causes of contact dermatitis are identified, it is important to avoid direct contact with them. But whatever the cause of dermatitis, the skin's barrier function has been impaired and more dermatitis can occur if exposed to irritants.
- Avoid soap: use a pHbalanced cleanser suitable for sensitive skin
- To treat and prevent dermatitis of the hands, wear appropriate gloves to protect against friction, detergents, dirt, plants, paints, diesel, etc.
- Dry the skin carefully after washing.
The rash can be treated with a short cycle of current corticosteroid creams. Apply emollients often while the rash is active and for a few weeks thereafter as normal skin barrier function is restored.
Severe contact dermatitis can be treated with a short cycle of systemic corticosteroids, e.g. Eg oral prednisone Occasionally, for chronic contact dermatitis, phototherapy may be tried, or immunosuppressive agents such as methotrexate, cyclosporine, or azathioprine may be prescribed.

