What is dupilumab?
Dupilumab is an innovative first-class biological agent for atopic dermatitis (eczema)
Dupilumab (Dupixent®; Sanofi, Paris, France; Regeneron, New York, USA) is fully human monoclonal antibody, which has been shown to be significant effectiveness and a favorable safety profile in moderate to severe atopic dermatitis alone and in combination with current corticosteroids
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Dupixent® as a treatment for moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in adults in March 2017 and in patients aged 12 to 17 years in March 2019. It was approved by Therapeutic Administration of Goods (TGA) in Australia in January 2018, and Medsafe classified it as a prescription drug in New Zealand in March 2018.
The Biologics License Application (BLA) for dupilumab contains data from three pivotal phase 3 clinical studies evaluating dupilumab as monotherapy and in concomitant administration with topical corticosteroids.
What is dupilumab used for?
- Dupilumab is indicated for the treatment of patients over 12 years of age with inadequately controlled moderate to severe atopic dermatitis.
- Current treatment options include moisturizers, antihistamines, topical corticosteroids, or topical calcineurin inhibitors (TCI), systemic corticosteroids, systemic calcineurin inhibitors, phototherapy, and other oral immunosuppressants.
Severe atopic dermatitis in adults.
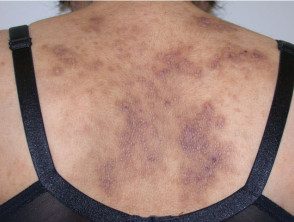
Atopic eczema
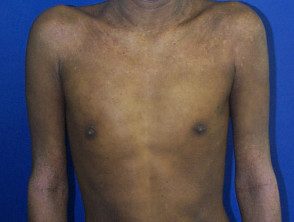
Atopic eczema
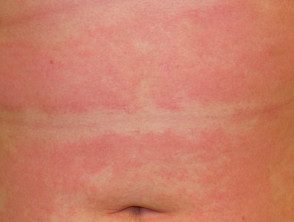
Subacute atopic dermatitis
How does dupilumab work?
- Dupilumab is believed to work by blocking the inflammation causing atopic dermatitis
- Atopic dermatitis is characterized by type 2 helper T (Th2) cell-driven inflammation,
- Dupilumab, a fully human monoclonal antibody, targets shared IL-4 receiver alpha subunit, which blocks both IL-4 and IL-13 signaling.
- IL-4 and IL-13 are key cytokines (signaling molecules which are made by cells and help control immune system and disease fighting) that are required for the initiation and maintenance of Th2 (Helper Type 2 T cell) immune response, which is believed to be a critical pathway in allergic inflammation.
Dosage and administration
- Dupilumab is given as subcutaneous injection.
- Dupilumab is intended to be a long-term treatment.
- If it is suspended for any reason, it can be restarted.
Link to key evidence from clinical trials on dupilumab.
What are the adverse effects of dupilumab?
Most common (> 5%) Adverse reactions associated with dupilumab treatment in clinical trials were:
- Injection site reactions
- Conjunctivitis up to 30%
- Dry eyes
- Allergic conjunctivitis
-
Herpes infections
-
Atopic dermatitis exacerbation
- Nasopharyngitis
- Headache
- Upper respiratory tract infection
No specific blood test is required for drug testing.
In rare cases, induction of another skin disorder, such as psoriasis, has been reported.
Conjunctivitis treatment
Mild conjunctivitis is managed with lubricating eye drops. Patients receiving dupilumab should be advised to use them from the start of treatment to prevent ocular symptoms Some patients may require other treatment.
- Topical corticosteroid drops
- Tacrolimus topical eyelid ointment
- Referral to a ophthalmologist
Dupilumab shows promise for atopic dermatitis in phase 3 studies
- Dupilumab is a fully human monoclonal antibody that inhibits the actions of both IL-4 and IL-13.
- Clinical trials of systemic dupilumab in moderate to severe atopic dermatitis have shown marked improvement in patient symptoms, including pruritus and clinically visible disease.
- Importantly, treatment with dupilumab has been correlated with changes in the molecular signature of diseased skin, with reduction of both inflammatory and proliferative markers
-
Topical corticosteroids, emollients, phototherapy, and systemic agents (such as prednisone, cyclosporine, methotrexate, or azathioprine) can be continued during treatment with dupilumab. The dose of systemic agents may need to be reduced and they may be weaned as dupilumab begins to control the dermatitis.
