What is it eosinophilic skin disease of hematological malignancy?
Eosinophilic dermatosis from hematologic or hematologic malignancy (blood Cancer) is a rare skin eruption seen in patients with underlying hematologic malignancy. First rated as overkill arthropod bites like clinic and histological Features resemble arthropod bites, with prominent eosinophilia (greater number of eosinophils)
What is a eosinophils?
An eosinophil is a type of white blood cell produced by the bone marrow. It is characterized by thick granules inside the cell cytoplasm. The functions of eosinophils include:
- Antiparasitic activity
- Bactericide exercise
- Modulation of inflammatory reply
- Participation in allergic reactions.
Who gets eosinophilic dermatosis from hematologic malignancy?
People with underlying hematologic malignancies, in particular, chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Less frequently, the condition has been documented in patients with acute myelocytic leukemia, acute lymphocytic leukemia, mantle cells lymphoma and multiple myeloma.
The skin rash can occur at the same time, before or after the diagnosis of the underlying hematologic malignancy.
What are the clinical features of eosinophilic dermatosis from hematologic malignancy?
The diagnosis of eosinophilic dermatosis of hematological neoplasia is made using the following characteristics:
- Small, dome-shaped, recurring, itchy bumps or tender bumps (papules) and packages (nodules)
- Hivesurticarial cure)
- Variable size fluid filled ampoules (vesiclesand bullas)
- Involvement of exposed and unexposed body sites.
Eosinophilic dermatosis of hematologic malignancy.
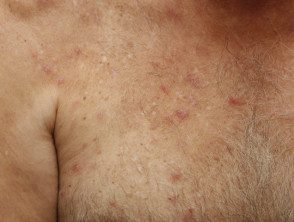
Eosinophilic dermatosis of hematologic malignancy.
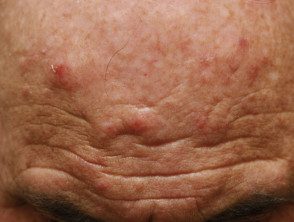
Eosinophilic dermatosis of hematologic malignancy.
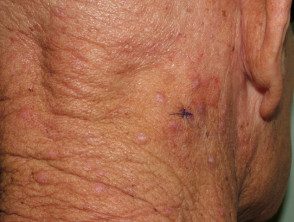
Eosinophilic dermatosis of hematologic malignancy.
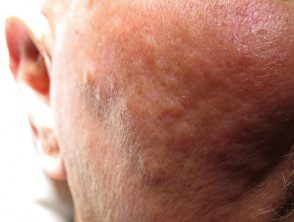
Eosinophilic dermatosis of hematologic malignancy.
What causes eosinophilic dermatosis from hematologic malignancy?
The exact cause of eosinophilic dermatosis from hematologic malignancy is poorly understood. A proposed theory is that the underlying cancer causes immunity deregulation. This leads to an imbalance in the production of cytokines (messenger proteins), with a higher production of interleukin-5 (IL-5). IL-5 recruits eosinophils into the skin.
How was the diagnosis made?
The diagnosis of eosinophilic dermatosis of hematologic malignancy is based on the following diagnostic criteria:
- Papules, nodules and / or itching. vesiculobullous eruption
- There is no discernible relationship with outdoor activity.
- In biopsyrich in eosinophils lymphohistiocytic infiltrate in shallow and deep dermis with or without flame figures (these are granules of extracellular eosinophils that cover collagen fibers in the dermis)
- Exclusion of other causes of tissue eosinophilia (such as drug reaction, insect sting reaction, eosinophilic folliculitis, and Wells syndrome)
- Pre-existing diagnosis of a hematological neoplasm or its subsequent development.
What is the treatment for hematologic malignancy eosinophilic dermatosis?
Various treatments have been used to treat eosinophilic dermatosis from hematologic malignancies, but they have been reported to be largely disappointing. They include:
- Current and systemic corticosteroids
- Phototherapy
- Antihistamines
- Dapsone
- Alpha interferon
- Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg)
- Chemotherapy.
It is not clear whether eosinophilic dermatosis from hematologic malignancy may have forecast implication. Some studies have suggested that patients with eosinophilic dermatosis of hematologic malignancy perform poorly compared to those with the same hematologic malignancy but without the skin condition.
