What is folliculitis?
Folliculitis is the name given to a group of skin conditions in which there is inflammation. hair follicles. The result is a noticeable red stain, often with a surface pustule.
Folliculitis can be superficial or deep. It can affect anywhere there is hair, including the chest, back, buttocks, arms, and legs. Acne and its variants are also types of folliculitis.
Folliculitis
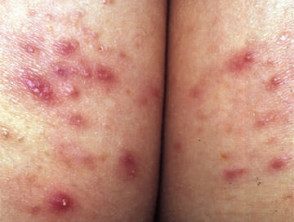
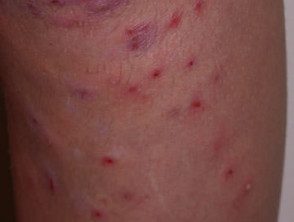
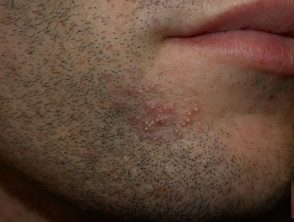
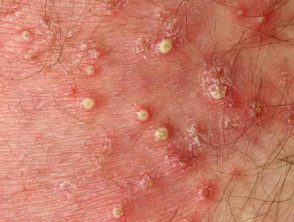
Superficial bacterial folliculitis
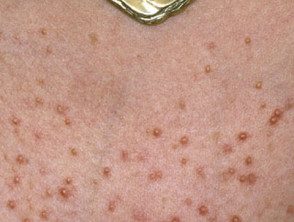
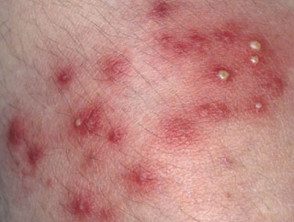
Superficial bacterial folliculitis
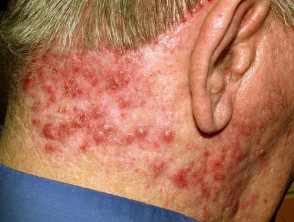
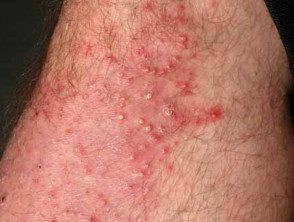
Folliculitis
See more images of folliculitis.
What Causes Folliculitis?
Folliculitis may be due to infection, occlusion (blockage), irritation and various skin diseases.
Folliculitis due to infection.
Swabs should be taken from pustules for cytology and culture at the laboratory to determine if folliculitis is due to infection.
The bacteria
Bacterial Folliculitis is commonly due to Staphylococcus aureus. If the infection involves the deep part of the follicle, results in a painful boil. Recommended treatment includes gentle hygiene, antiseptic cleanser, or creamantibiotic ointmentor oral antibiotics.
Spa pool folliculitis is due to an infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which thrives in warm waters with inadequate chlorine. Gram-negative folliculitis is a pustular facial eruption Also due to infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa or other similar organisms. When it appears, tetracycline treatment of acne is usually followed, but it is quite rare.
Yeasts
The most common yeast to cause folliculitis is Pityrosporum ovale, also known as Malassezia. Malassezia folliculitis (Pityrosporum folliculitis) is an itchy acne-like condition that usually affects the upper trunk of a young adult. Treatment includes avoiding moisturizers, stopping antibiotics, and current oral antifungal or antifungal medication for several weeks.
Candida albicans can also cause folliculitis in the skin folds (intertrigo) or the beard area. It is treated with topical or oral antifungal agents.
Mushrooms
Ringworm of the scalp (ringworm of the head) usually causes climbing and hair loss, but sometimes it results in folliculitis. In New Zealand, cat ringworm (Microsporum canis) is the most common. organism causing fungal infection of the scalp. Other fungi such as Trichophyton tonsurans are increasingly being reported. Treatment is with oral antifungal agents for several months.
Viral infections
Folliculitis can be caused by the herpes simplex virus. This tends to be sensitive and resolves without treatment in about ten days. Serious recurrent Attacks can be treated with acyclovir and others antiviral agents
He Herpes zoster (the cause of shingles) can also present as folliculitis with painful pustules and scabbed spots within a dermatome (an area of skin supplied by a single nerve). It is treated with high doses of acyclovir.
Molluscum contagiosum, common in young children, can also cause follicular umbilical papules, usually grouped in and around a fold of the body. The mollusk can cause dermatitis.
Parasitic infection
Folliculitis on the face or scalp of older people or immunosuppressed adults may be due to colonization by the hair follicle Mites (demodex). This is known as demodicosis.
The human infestation, scabies, often causes folliculitis, as well as non-follicular papules, vesicles and pustules.
Folliculitis due to irritation of hairs that grow back.
Folliculitis can arise when hair grows back after shaving, waxing, electrolysis, or waxing. The swabs taken from the pustules are sterile: there is no growth of bacteria or other organisms. In the beard area irritating Folliculitis is known as beard pseudofolliculitis.
Irritant folliculitis is also common on the lower legs of women (shaved eruption) Often very itchy. Treatment consists of stopping waxing and not starting again for about three months after the folliculitis has healed. To avoid recurring irritant folliculitis, use a gentle hair removal method, such as a woman's electric razor. Avoid soap and do a lot of shaving. gel, if you use a razor blade.
Folliculitis due to contact reactions.
Occlusion
Paraffin-based ointments, moisturizers, and plasters can cause sterile folliculitis. If you need a moisturizer, choose an oil-free product, as it is less likely to cause occlusion.
Chemical products
Coal tar, cutting oils, and other chemicals can cause irritating folliculitis. Avoid contact with the causal product.
Topical steroids
Overuse of topical steroids can lead to folliculitis. Newspaper Dermatitis is a facial folliculitis caused by topical moisturizers and steroids. Perioral dermatitis is treated with tetracycline antibiotics for about six weeks.
Immunosuppressive folliculitis
Eosinophilic Folliculitis is a specific type of folliculitis that can occur in some immunosuppressed people, such as those infected with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) or those that have Cancer.
Drug folliculitis
Folliculitis can be caused by medications, particularly corticosteroids (steroid acne), androgens (male hormones), adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH), lithium, isoniazid (INH), phenytoin, and B complex vitamins. Protein kinase inhibitors (epidermal growth factor receiver inhibitors) and targeted therapy for metastatic melanoma (vemurafenib, dabrafenib) almost always result in folliculitis.
Folliculitis due to inflammatory Skin diseases
Certain rare inflammatory skin conditions can cause permanent hair loss and scarring due to deep sterile folliculitis. These include:
- Lichen planus
- Discoid lupus erythematosus
- Folliculitis decalvans
-
Folliculitis keloidalis.
Treatment depends on the underlying condition and its severity. A skin biopsy The diagnosis often needs to be established.
Variants of acne
Acne and acne or acne-like disorders are also forms of folliculitis. These include:
- Common acne
- Noulocystic acne
- Rosacea
- Folliculitis of the scalp
-
Chloracne.
Follicular occlusion. syndrome refers to:
-
Hidradenitis suppurativa (acne inverse)
-
Acne conglobata (a severe form of nodulocystic acne)
-
Dissecting cellulitis (peripholliculitis capitis abscedens et suffodiens)
-
Pilonidal breast.
Treatment of acne variants may include topical therapy, as well as long courses of tetracycline antibiotics, isotretinoin (derived from vitamin A), and in women, antiandrogen therapy.
Buttock folliculitis
Folliculitis affecting the buttocks is quite common in both men and women.
- Acute Gluteal folliculitis is usually bacterial in origin (such as boils), resulting in red, painful papules and pustules. Clears up with antibiotics.
- Chronic Buttock folliculitis often does not cause significant symptoms, but it can be very persistent. Although antiseptics, topical acne treatments, exfoliating agents such as alpha-hydroxy acids, long courses of oral antibiotics, and isotretinoin can help buttock folliculitis, they are not always effective. Waxing is worth trying if the affected area is hairy. As hair regrowth can make it worse, permanent hair reduction by To be or intense pulsed light (IPL) is best.

