What is frontal? fibrous alopecia?
Fibrosing frontal alopecia describes hair loss and scarring in the frontal region of the scalp. It was first described in a group of Australian women in 1994. [1]. Is a located form of lichen planopilaris.
Who gets fibrosing frontal alopecia?
Frontal fibrosing alopecia generally affects postmenopausal women over the age of 50. It is rare in younger women and men.
the incidence It is reported to be increasing in fair-skinned women (possibly due to increased awareness of the condition), and is rare in women with dark skin.
What is the cause of fibrosing frontal alopecia?
The exact cause of fibrosing frontal alopecia is unknown. There is a disturbed immune response to some component of intermediate-sized scalp hair and vellus follicles. GeneticHormonal and environmental factors may be involved. Contact allergy or allergy to photocontact cosmetics, hair dye and sunscreen have been suggested as possible unconfirmed causal factors [2,3].
Fibrosing frontal alopecia is considered a variant of lichen planopilaris.
What are the clinical features of fibrosing frontal alopecia?
Frontal fibrosing alopecia is characterized by a symmetrical hair loss band on the front and side of the scalp and loss of eyebrows. The edge may appear eaten by moths, and the 'lonely' lone hairs may persist in bald areas.
The skin in the affected area generally looks normal but may be pale, shiny, or slightly scarred, with no visibility follicular openings At the edges of bald areas, a close inspection or dermoscopy shows redness and climbing around the hair follicles.
In some cases, follicular skin is colored or yellowish. papules located on the forehead and temples [4]. Some women with fibrosing frontal alopecia also have female pattern hair loss.
Trichoscopy reveals absent follicles, white spots, tubular peripheral scale and peripheral erythema. On skin that tans easily, peripheral pigmentation can be observed
Fibrosing frontal alopecia
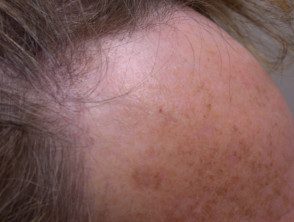
Fibrosing alopecia
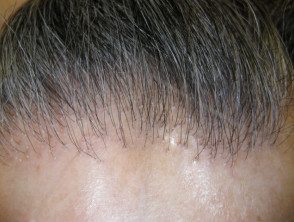
Fibrosing alopecia
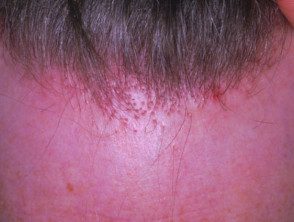
Fibrosing alopecia
How is the diagnosis of fibrosing frontal alopecia made?
The clinical features of fibrosing frontal alopecia are characteristic. A skin biopsy Laboratory examination can help make or confirm the diagnosis. The recently affected hair follicles are surrounded by a lichenoid pattern inflammation associated with scars. the histopathological The characteristics are identical to those of lichen planopilaris.
Biopsy of skin papules may show a pattern of lichenoid inflammation, fibrosing alopecia, or sebaceous gland hyperplasia.
What is the prognosis for fibrosing frontal alopecia?
Frontal fibrosing alopecia is usually slow progressive. In some patients, it stabilizes after a few years. Hair growth has been reported in some patients.
What is the treatment of fibrosing frontal alopecia?
There is no very effective treatment available for fibrosing frontal alopecia to date. A short course of oral steroids, intralesional steroid injections, anti-inflammatory Antibiotics like tetracyclines or antimalarial tablets can benefit patients who have a rapid onset of hair loss. The five alpha-reductase inhibitors, finasteride and dutasteride, have been reported to stop hair loss in some women, but have not been confirmed by controlled studies.
The use of the antidiabetic agent pioglitazone (not indicated on the label) for the treatment of frontal fibrosing alopecia has been reported to reduce the symptoms, inflammation and progression of frontal fibrosing alopecia [5] but its use has not been supported by research additional [6]. Side effects include inflammation of the ankle and weight gain.
Adalimumab, a tumor necrosis The alpha factor inhibitor (TNFα) has also been reported to be effective in some patients [8].

