What are fungal nail infections?
Mushrooms infection of the nail It is also known as onychomycosis. It is increasingly common with increasing age. It rarely affects children.
Which organisms cause onychomycosis?
Onychomycosis may be due to:
-
Dermatophytes like Trichophyton rubrum (T. rubrum), T. interdigitale (tinea unguium)
-
Yeast like Candida albicans and rarely, Candida species not albicans
-
Molds like Scopulariopsis brevicaulis and Fusarium species.
Nail fungus infections
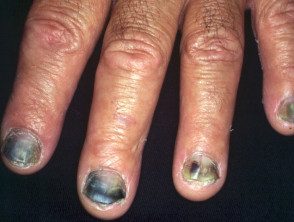
Onychomycosis
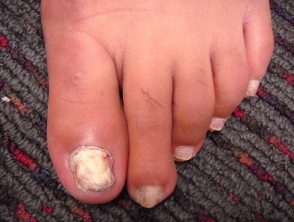
Onychomycosis
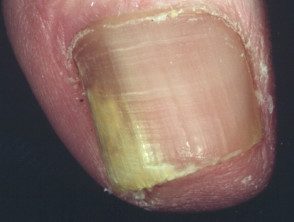
Onychomycosis
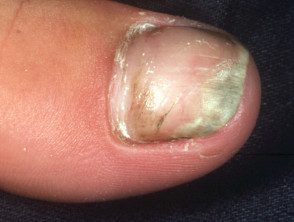
Onychomycosis
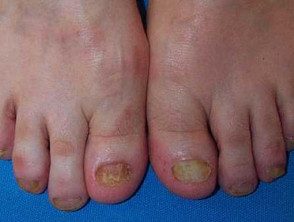
Onychomycosis
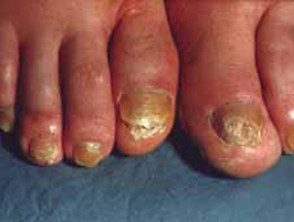
Onychomycosis
See more images of candida nail infection.
What are the clinical features of onychomycosis?
Onychomycosis can affect one or more toenails and toenails and most often involves a large toenail or a small toenail. It can come in one or more different patterns.
- Side Onychomycosis: A white or yellow opaque line appears on one side of the nail.
- Subungual hyperkeratosis – climbing occurs under the nail.
- Distal onycholysis- The end of nail lifts. The free edge often crumbles.
- Superficial white onychomycosis: Scaly white patches and holes appear on top of the nail plate.
- Proximal onychomycosis: yellow spots appear on the crescent (lunula)
- Onychoma or dermatophytoma: a thickness located area of infection on the nail plate.
- Destruction of the nail.
Tinea unguium often results from untreated tinea pedis (feet) or tinea manuum (hand). It may follow an injury to the nail or inflammatory nail disease.
Candida infection of the nail plate usually results from paronychia and it begins near the nail fold (the cuticle). The nail fold is swollen and red, lifted off the nail plate. White, yellow, green, or black marks appear on the nearby nail and spread. The nail can rise from its bed and is sensitive if pressed.
Mold infections are similar in appearance to ringworm.
Onychomycosis must be distinguished from other nail disorders.
- Bacterial infection especially Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which turns the nail black or green
- Psoriasis
- Eczema or dermatitis
- Lichen planus
- Viral warts
- Onycholysis
- Onychogryphosis (thickening and peeling of the nails under the nail), common in the elderly
How is the diagnosis of onychomycosis confirmed?
Clippings should be taken from the crumbled tissue at the end of the infected nail. The discolored surface of the nails can be scraped off. The remains can be removed from under the nail. Cuttings and scrapes are sent to a mycology laboratory for microscopy and culture.
Pretreatment can reduce the chance of the fungus growing successfully in a crop, so it is best to take the clippings before starting any treatment:
- To confirm the diagnosis: antifungal treatment will not be successful if there is another explanation for the nail condition
- Identify the person responsible. organism. Molds and yeasts may require different treatment of dermatophyte fungi
- Treatment may be required for a long period and is expensive. The partially treated infection may be impossible to prove for many months, as antifungal medications can be detected even a year later.
One one biopsy can also reveal characteristics histopathological characteristics of onychomycosis.
What is the treatment of onychomycosis?
Nail infections generally heal faster and more effectively than toenail infections.
Mild infections involving less than 50% from one or two nails may respond to current antifungal medications, but the cure usually requires an oral antifungal medication for several months.
Devices used to treat onychomycosis.
Recently, a non-pharmacological treatment has been developed to treat onychomycosis, thus avoiding the side effects and risks of oral antifungal drugs.
Lasers that emit infrared radiation are believed to kill fungi by producing heat within infected tissue. To be The treatment is reported to safely eradicate nail fungus with one to three, almost painless, sessions. Various lasers have been approved for this purpose by the FDA and other regulatory authorities. However, high-quality studies of effectiveness They are lacking, and existing studies indicate that laser treatment is less medically effective than topical or oral antifungal agents.
-
Continuous, long or short pulse lasers Nd: YAG
- Ti: modelcked sapphire laser
- Laser diode
Photodynamic Therapy with the application of 5-aminolevulinic acid or methyl aminolevulinate followed by red light exposure has also been reported to be successful in a small number of patients, whose nails were previously hardened or medically agitated using 40% urea. ointment for a week or so.
Iontophoresis and ultrasound They are being investigated as devices used to improve the administration of antifungal medications to the nail plate.

