What is it granuloma facial?
Facial granuloma is a rare noncancerous skin disorder characterized by one or more papules, plates or nodules, most often on the face.
Who gets facial granuloma?
Facial granuloma most commonly affects healthy, middle-aged white men, although it has been found in men and women of all races and ages.
What are the signs and symptoms of facial granuloma?
Patients most often present to their doctor after noticing a spot or injury on your face which then enlarges or multiplies in number over several weeks or months. These injuries are usually:
- Varied color: skin color, reddish brown, blue or purple
- Its size varies from a few millimeters to several centimeters.
- Elevated and smooth
- Characterized by prominent follicles (pores)
- Defined with an edge
- On the face, although similar lesions have been found in other parts of the body, such as the scalp, trunk and extremities, when they are known as extrafacial facial granuloma
Facial granuloma usually has no symptoms. Some patients may complain of tender, itchy or stinging lesions.
Facial granuloma
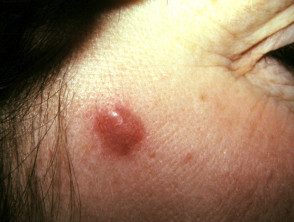
Facial granuloma
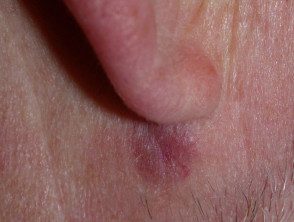
Facial granuloma
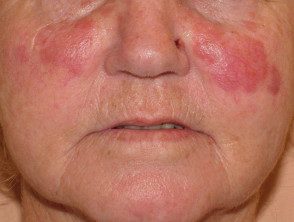
Facial granuloma
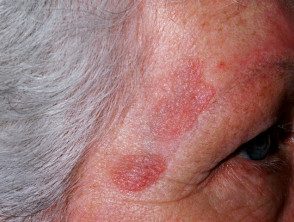
Facial granuloma
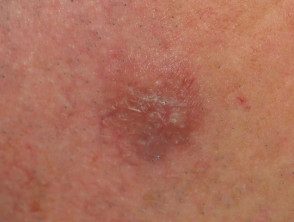
Facial granuloma
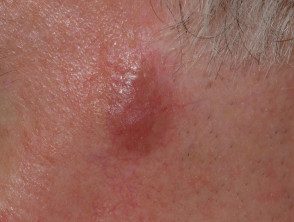
Facial granuloma
What causes facial granuloma?
It is unknown why facial granuloma occurs, but sun exposure has been implicated:
- Lesions appear most frequently in areas exposed to the sun.
- The lesions darken when exposed to the sun.
How is it diagnosed?
The diagnosis is confirmed by the skin. biopsy and it is often necessary to rule out other skin diseases that have a similar appearance. Facial granuloma is characterized by inflammatory cells in the dermis even eosinophils (allergy cells) and vasculitis (acrimonious blood vessels)
Differential diagnosis
Skin conditions that may appear similar to facial granuloma include:
- erythema elevatum diutinum
- sarcoidosis
- cutaneous lupus erythematosus
- polymorphous light eruption
- Jessner lymphocytic infiltration
- lymphocytoma skin
- mycosis fungoides
-
insect bite reaction
-
Fixed drug rash.
Treatment of facial granuloma
Facial granuloma is a chronic condition with exacerbations and referrals. Spontaneous resolution rarely occurs. The disease appears to have no relation to internal disease and treatment is primarily to improve appearance. Various medical and surgical therapies have been used, but none have been consistently successful. Facial granuloma also has a tendency to recur after treatment.
Medical therapies used with variable results include:
- Current steroids
- Corticosteroid injections
- Dapsone
-
Antimalarial tablets (hydroxychloroquine)
- Dapsone
- Topical psoralen UV-A (PUVA)
- Radiotherapy
Surgical therapy can also be used. Results are variable and may leave scars.
- Surgical excision
- Dermabrasion
- Carbon dioxide To be
- Electrosurgery
- Cryotherapy
- 585nm pulsed dye laser
