Why is hand care necessary?
Good hygiene practices and prevention of the cross.infection are essential for health workers working in hospitals, clinics, rest centers and private residences. Hand care is necessary because healthcare workers are prone to hands. dermatitis mainly due to contact with irritants during frequent hand washing or cleaning with harsh disinfectants and detergents. Wearing surgical gloves can also cause dermatitis in some people.
Exposure to irritants in the home or during recreation can exacerbate the problem. Chemicals, extreme temperatures and humidity, mechanical injuries (e.g., rough surfaces and friction), plants, paints, some foods and Ultraviolet radiation It can damage the skin.
The skin barrier can be affected by:
- Short and infrequent exposure to strong irritants, and
- Regular repetitive exposure to less harmful irritants.
The disruption of the cutaneous barrier manifests as frank eczema or irritating contact dermatitis. The damaged skin is then susceptible to secondary bacterial infection and development of allergies (allergic contact dermatitis), as well as itching, pain, and less flexibility.
Dermatitis is more likely in people with pre-existing sensitive skin or who have atopic dermatitis at other sites.
Dermatitis of the hand
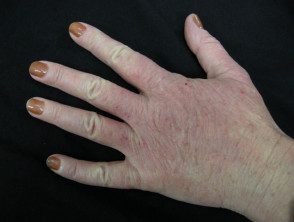
Dermatitis of the hand
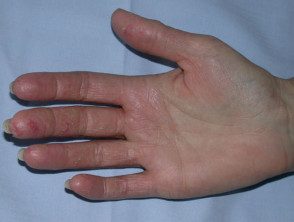
Dermatitis of the hand
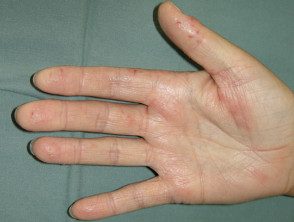
Dermatitis of the hand
Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes are the common causes of a bacterial infection. Hand dermatitis and wet work too predispose to yeast infection, usually presenting as paronychia infected by Candida albicans or as intertrigo between the toes, and can be confused with tinea manuum (a type of fungal infection).
Hand infection
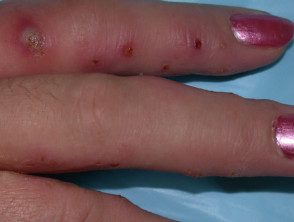
Infected staphylococcal eczema
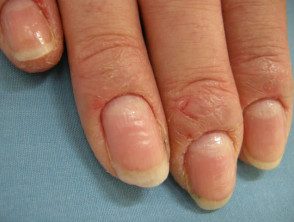
Paronychia
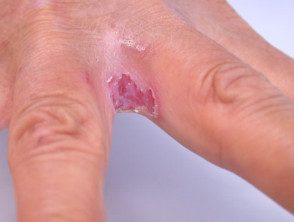
Erosio interdigitalis blastomycetica
Tips to preserve the skin of the hands
Disinfectants
Evidence-based Cochrane reviews reveal that alcohol-based hand sanitizers are higher to regular hand washing to reduce the transmission of diseases in hospitals and health services. They can also minimize irritation compared to soap and water.
- At work, choose a colorless alcohol-based hand cleaner that is fragrance- and perfume-free.
- Wash with soap and water only when skin is visibly dirty or contaminated with blood or other body fluids.
- Note that cream cleaners are not antimicrobial; Soap and water or a disinfectant is needed to wash your hands in order to destroy pathogens such as the SARS-CoV-2 virus responsible for COVID-19.
Gloves
Gloves provide a barrier to the skin, but no glove will resist all chemicals indefinitely. Choosing the right glove design and construction will provide the best protection, as long as it also fits well. Similarly, protection against mechanical hazard varies with different gloves providing different resistance to abrasion, blade cut, tear resistance and puncture resistance.
- Latex gloves provide the best protection against viruses for healthcare workers.
- Powder-free gloves are less irritating and dry than powder gloves.
-
Nitrile gloves are a suitable alternative for people with latex. allergy.
- Vinyl gloves are not suitable for healthcare workers in direct contact with bodily excretions.
- Avoid petroleum based emollients under latex gloves as they weaken the rubber
- If you use occlusive gloves for more than 20 minutes, wear tight-fitting cotton gloves underneath to reduce irritation from sweating.
Healthcare facilities often have a health and safety officer with knowledge of proper gloves. Security shops also offer advice and a wide variety.
What investigations are appropriate in dermatitis of the hand?
If hand eczema slowly improves, seek a referral for a dermatologist for patch testing Patch testing helps decide if a contact allergy is contributing. About 60% of patients with chronic hand eczema has one or more positive contacts Allergens in patch testing. Loss of barrier function due to irritant contact dermatitis increases the risk of developing a contact allergy.
Common occupational allergens in healthcare workers include nickel, perfume / fragrance, rubber antioxidants, antiseptics, antibacterial soap, and preservatives.
Latex allergy causes immediate redness and swelling of the hands when wearing gloves and is diagnosed by puncture tests and specific IgE tests.
Allergy to rubber gloves.
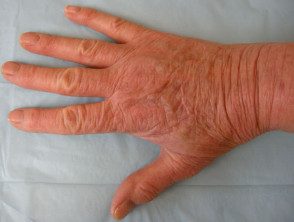
Hand dermatitis caused by gloves
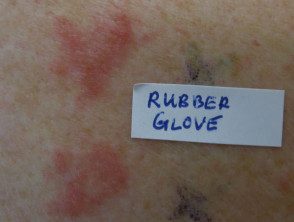
Positive patch tests on gloves.
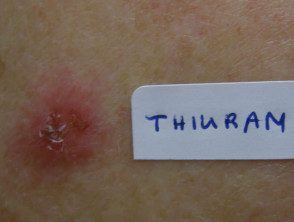
Positive patch test for thiuram, gum antioxidant
What is the treatment for hand eczema?
Managing eczema of the hand involves:
- Minimizing contact with irritants
- Avoid known contact allergens.
- Optimizing the skin barrier with suitable emollients at work and at home
- Powerful courses current corticosteroids for flare-ups
-
Antibiotics for secondary infection.

