What is it intertrigo?
Intertrigo describes a eruption at push-ups, such as behind the ears, in the folds of the neck, under the arms, under a protruding abdomen, in the groin, between the buttocks, in the webs of the fingers or in the spaces of the toes. Although intertrigo can affect only one skin fold, intertrigo commonly involves multiple sites. Intertrigo is a sign of inflammation or infection.
Who gets intertrigo?
Intertrigo can affect men or women of any age. Intertrigo is particularly common in people who are overweight or obese (see Metabolic syndrome)
Other contributing factors are:
- Genetic tendency to skin diseases
- Hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating)
- Years
- Diabetes
- Of smoking
-
Alcohol.
In infants, napkin dermatitis It is a type of intertrigo that occurs primarily due to skin exposure to sweat, urine, and feces in the diaper area.
The intertrigo of the toe web is associated with closed or tight shoes. Lymphedema is also a cause of intertrigo in the toe box.
What are the clinical features of intertrigo?
Intertrigo can be acute (recent onset), relapse (recurrent) or chronic (present for more than six weeks). The exact appearance and behavior depend on the underlying causes.
Intertrigo-affected skin is swollen, red, and uncomfortable. The affected skin can become moistened and macerated, leading to fissure (cracks) and flaking.
Intertrigo with secondary bacterial Infection (eg, pseudomonas) can cause a bad odor.
What Causes Intertrigo?
Intertrigo is due to genetic and environmental factors.
- Flexural The skin has a relatively high surface temperature.
- Moisture from insensitive water loss and sweating can not evaporate due to occlusion.
- Friction of movement of adjacent The skin produces chafing.
- Intertrigo occurs more easily in environments that are warm and damp.
-
Diabetes, alcohol, and smoking increase the likelihood of intertrigo, especially the infectious form.
the microbiome (microorganisms normally resident in the skin) in the skin in flexion includes Corynebacteriumother bacteriaand yeasts. Microbiome overgrowth in warm, humid environments can cause intertrigo.
Intertrigo is classified as infectious and inflammatory origins, but they often overlap.
- Infections tend to be unilateral and asymmetric.
- Atopic dermatitis is generally bilateral and symmetrical, affecting the flexion of the neck, knees and elbows.
- Other inflammatory disorders also tend to be symmetrical and affect the armpits, groins, under the breasts, and abdominal folds.
Infections that cause intertrigo
Thrush: Candida albicans
- Characterized by its rapid development.
- Itching, damp, peeling, red and white skin.
- Small shallow papules and pustules
Candida albicans
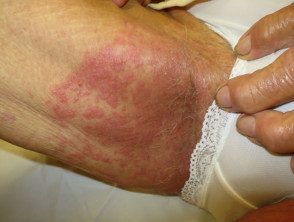
Intertrigo from candida infection
Erythrasma Corynebacterium minutissimum
- Persistent brown spots
- Minimum scale
- Asymptomatic (painless and itchy)
Erythrasma
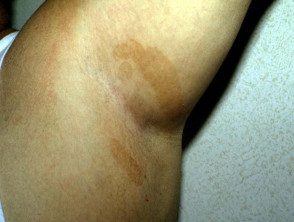
Axillary erythrasma
Tub: Trichophyton rubrum + T. interdigitale
-
Jock itch (groin) and athlete's foot (between the toes)
- It spreads slowly over weeks or months.
- Irregular cancel plates
- Peeling, climbing
Ringworm
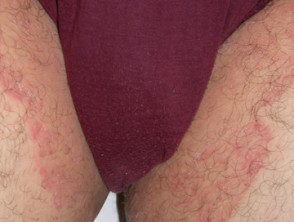
jock itch
Impetigo: Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes
- Rapid development
- Moist blisters and scabs on a red base
- Contagious, so other family members can also be affected
Impetigo
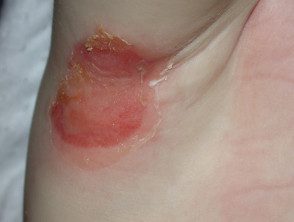
Blistering impetigo
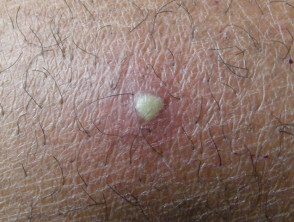
Boils: Staphylococcus aureus
- Rapid development
- Very painful follicular papules and nodules
- Central pustule or abscess
Boil
Folliculitis: Staphylococcus aureus
- Acute or chronic
- Superficial tender red papules
- Pustules centered on hair follicles
- It can be triggered by shaving, waxing, waxing.
Folliculitis
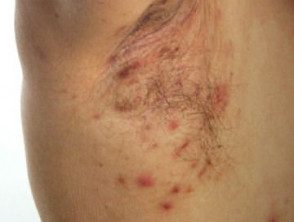
Folliculitis in the armpit
Inflammations of the skin that cause intertrigo
Flexural psoriasis
- Well definedsmooth or shiny red patches
- Very persistent
- Common in submammary and groin wrinkles
- Symmetric implication
- May fissure (crack) in the fold
- The red patches at other sites are scaly
Flexural psoriasis
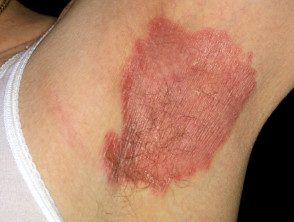
Flexural psoriasis
Seborrheic dermatitis
- Thin, ill-defined salmon-pink patches
- Common in armpit and groin wrinkles
- Fluctuates in severity
- Can be asymmetrical
- Often unnoticed
- Red spots on the face and scalp tend to be flaky.
Seborrheic dermatitis
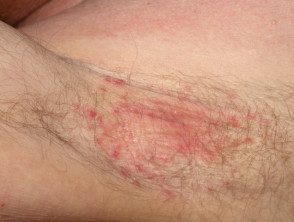
Intertrigo due to seborrheic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis
- It first occurs in childhood
- Common in the folds of the elbow and knee.
- Characterized by flares
- Itch
- Acute eczema is red, blistered, swollen
- Chronic eczema is dry, thickened, streaked (lichenified).
Atopic dermatitis
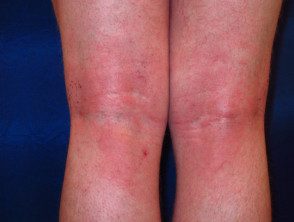
Flexural eczema
Contact irritating dermatitis
- Acute, recurrent or chronic.
Irritants include:
- Body fluids: sweat, urine.
- Friction from movement and clothing.
- Antiperspirant dryness
- Soap
- Excessive washing.
Irritant contact dermatitis
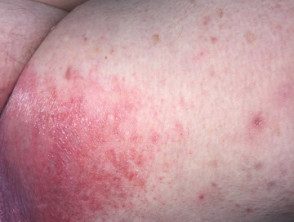
Irritant contact dermatitis in urine. Napkin dermatitis in adults.
Allergic contact dermatitis
- Acute or recurrent
- the allergen maybe:
- Fragrance, preservative, or medication in deodorant, wipe, or other product
- Underwear component (rubber on elastic, nickel on bra wire).
Allergic contact dermatitis
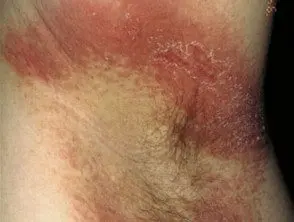
Hidradenitis suppurativa
- Chronic disorder
- Boiling papules and follicular nodules.
- Breast discharge and scars
Hidradenitis suppurativa
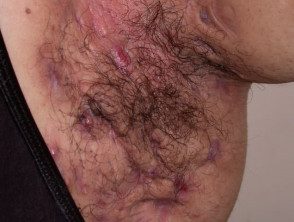
Intertrigo due to
Hailey-Hailey disease
- Intermittent painful superficial blisters that break down quickly
- Rare hereditary condition
- It often begins between the ages of 20 and 40.
- Most troublesome during the summer months.
Hailey-Hailey disease
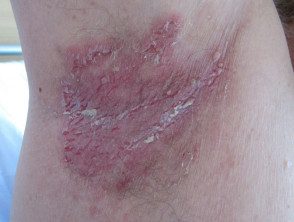
Intertrigo due to Hailey-Hailey disease
Granular parakeratosis
- Red-brown scaly rash
- Can sting
- Rare
- A biopsy It is essential for diagnosis.
Granular parakeratosis
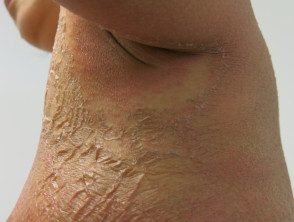
granular parakeratosis 02
Fox-Fordyce disease
- Dome-shaped follicular papules in the armpits
- Often persistent
- Asymptomatic or itchy
- Reduced sweating
- Excoriations and lichenification it eventually occurs as a result of scratching.
Fox-Fordyce disease
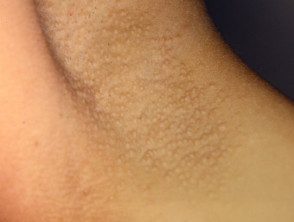
Fox-Fordyce axillary disease
Intertrigo toe web
- Common in people who wear tight shoes
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa is the most common organism
- Mild intertrigo on the toe is presented with erythema and scales (athlete's foot)
- Chronic intertrigo (more than six months) causes burning, oozing, macerationand inability to move the toes
- A serious complication is cellulite, which often spreads to the ankles and knees.
Intertrigo toe web
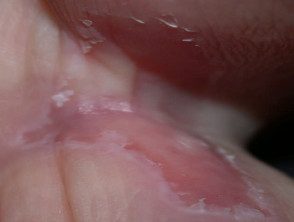
Athlete's foot
What research should be done?
Investigations may be necessary to determine the cause of intertrigo.
- A swab for microscopy and culture bacteria (microbiology)
- A scraping for microscopy and fungal culture (mycology)
- A skin biopsy may be done to histopathology If the skin condition is unusual or does not respond to treatment.
What is the treatment for intertrigo?
- Treatment depends on the underlying cause if it is identified, and what micro-organisms are present in the rash. Combinations are common.
- Zinc oxide paste can be used for napkin dermatitis or irritant contact dermatitis associated with incontinence.
- The physical effort should be followed by a bath and a complete drying of the skin flexes. A hair dryer in a cold environment is an effective approach to drying your armpits and breasts.
- Sweating can be reduced with an antiperspirant. cream or dust.
-
Bacterial infection can be treated with current antibiotics such as fusidic acid cream, mupirocin ointmentor oral antibiotics such as flucloxacillin and erythromycin.
-
Yeasts and fungi can be treated with topical antifungals such as clotrimazole and terbinafine cream or oral antifungal agents such as itraconazole or terbinafine.
- Inflammatory skin conditions are often treated with low-potency topical steroid creams like hydrocortisone. Stronger steroids are best avoided in push-ups because they can cause thinning of the skin, leading to stretch marks (atrophic stretch marks) and, in rare cases, ulcers. Calcineurin inhibitors, such as tacrolimus ointment or pimecrolimus cream, are also effective on skin folds.
