What is it papular urticaria?
Papular urticaria is a common reaction to insects and arachnid bites It is more common in children than in adults. [one]. It occurs during the summer or autumn months as very pruritic red crops. papules and vesicles.
Despite the name, papular urticaria is not a true urticaria, characterized by temporary scarring that resolves within hours. Weals in papular urticaria they last from days to weeks. Papular urticaria is not associated with an internal complaint.
Also called persistent insect sting reaction.
Papular urticaria
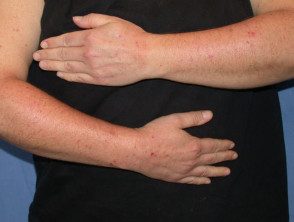
Papular urticaria
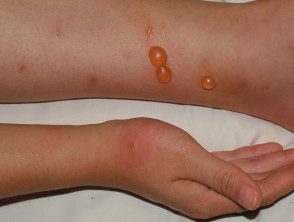
Papular urticaria
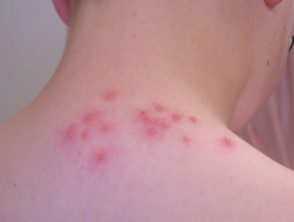
Papular urticaria
Who gets papular urticaria?
Papular urticaria occurs more frequently in children. This is because desensitization to insect bites has not yet developed. [one].
It can also occur in adults, especially in travelers to new settings.
What is the cause of papular urticaria?
Papular urticaria is believed to be a immune reaction to insect bites. The reaction subsides after a few months or years, as the person becomes insensitive to them. The initial bite is rarely noticeable.
Fleas and Mites Living cats and dogs are often responsible [4].
- Fleas are easily seen with the naked eye, but can be difficult to remove. Fleas produce many eggs, which develop into larvae and pupae. The average cat has only twenty fleas, but it can be surrounded by 20,000 of them.
- Mites are too small to see but are an equally common cause of papular urticaria.
- Animals are repeatedly infested and should be treated every few weeks with an insecticide without rinsing.
Not everyone with papular urticaria has pets, and it can be nearly impossible to determine what a patient reacts to. There have been reports of allergy mosquitoes, mosquitoes, mites, beetles, caterpillars and other insects [1].
A similar disorder, prurigo simplex, sometimes called 'chronic Papular urticaria 'and affects adults and children. The cause is unknown. It can be a variant of atopic dermatitis.
What are the clinical characteristics of papular urticaria?
Papular urticaria presents with very itchy clusters of red bumps.
- Very often they arise on the legs and other uncovered areas, such as forearms and face.
- Sometimes the papules are scattered in small groups throughout the body. [3].
- They appear every few days during the summer or fall months.
- They vary from 0.2 to 2 cm in diameter.
- Every papule It has a central punctum.
- Papular urticaria can present as fluid-filled blister cultures.
- New lesions develop just as old ones begin to disappear.
When scratching the papular urticaria, the spots form crusts.
-
Secondary bacterial infection painful cause pustules and scabs (impetiginization)
- Sometimes a new stain causes old ones to reappear and itch intensely [3].
The spots remain for a few days to a few weeks and can leave persistent. hyperpigmented brands (post-inflammatory pigmentation) or hypopigmented scars, especially if they have been deeply scratched.
What are the complications of papular urticaria?
Papular urticaria is not dangerous.
Bites from infected insects can cause cellulite and rarely bacteremia (septicemia) Located cutaneous vasculitis It can also happen.
Which is the differential diagnosis Papular urticaria?
The differential diagnosis of papular urticaria includes:
- Scabies
- Atopic eczema
- Other forms of prurigo
- Go reaction
- Pityriasis lichenoids
- Lymphomatoid papulosis
How is papular urticaria diagnosed?
Papular urticaria is usually a clinical diagnosis. A biopsy can support diagnosis, since insect bites have a characteristic microscopic appearance.
the histopathology Papular urticaria includes mild dermal edema, extravasation of erythrocytes, interstitial eosinophilsand exocytosis of lymphocytes. Vasculitic features can be observed.
What is the treatment for papular urticaria?
- Current steroid cream - this should be applied as soon as the itchy spots appear.
-
Antihistamine tablets: They can reduce the size and severity of the spots and reduce itching.
-
Antiseptic cream can reduce or prevent a secondary infection.
- Wear clothing that covers completely.
-
Insect repellents can be applied to exposed skin to prevent insect bites outdoors.
- Insecticides can remove insects from the home, workplace, or school. Get professional help from a pest control company if necessary.
Seek veterinary advice on handling infested animals.
- Keep pets outside.
- Use a pyrethroid kennel and a rug spray - This should be followed by vacuuming.
- Apply a long-lasting insect growth regulator to the neck of cats and dogs.
What is the result of papular urticaria?
Papular urticaria is usually self-limiting. The immune basis of this reaction means that it can take months or even years for children to become insensitive to the offending insect. [two]. Papular urticaria can go away on vacation or on the move.
Occasionally the eruption it can erase for years and then repeat itself unexpectedly.

