What is pilomatricoma?
Pilomatricoma is an unusual, harmless, hair follicle tumor derived from the cells of the capillary matrix. Also spelled 'pilomatrixoma', and sometimes referred to as 'calcifying epithelioma de Malherbe.”
Who gets pilomatricoma?
Pilomatricoma is most often diagnosed in young children, but it can affect adults as well. It appears to be slightly more common in women than in men.
What causes pilomatricoma?
It is now known that the cause of pilomatricoma is due to a located mutation in a capillary matrix cell. A hyperactive protocoloncogene called BCL-2 suggests that the normal process of cell death is suppressed, and mutations in CTNNB1 in most cases suggests loss of regulation of a protein complex called beta-catenin/LEF-1.
What are the clinical features of pilomatricoma?
Pilomatricoma presents as a single skin color or purple injury.
- They are usually found on the head and neck, but can occur anywhere.
- They usually don't cause any symptoms, but they can be sensitive.
- They can be skin-colored, white, or red.
- They can be regular or irregular.
- Most pilomatricomas are 5 to 10 mm in diameter.
- They can remain stable for years or slowly grow in size up to several centimeters in diameter.
- Pilomatricoma is characterized by calcification inside the lesion, making it feel hard and bony, often resulting in an angled shape (the “tent” sign)
Pilomatricoma
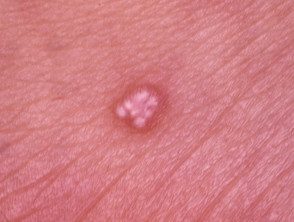
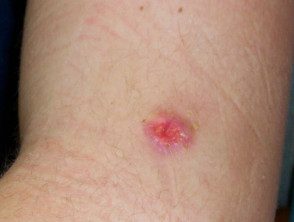
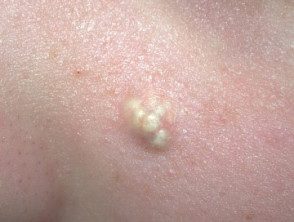
Pilomatrixoma
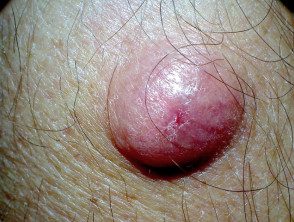
giant pilomatrixoma
What are the complications of pilomatricoma?
Complications of pilomatricoma are rare. However, they occasionally grow to a giant size (several centimeters in diameter) and pilomatrix carcinoma (Cancer) has been reported very rarely.
A few cases of multiple pilomatricomas have been reported in association with the rare neurological myotonic condition dystrophy. Individual cases of pilomatricomas arising in patients with a variety of other genetic disorders. The vast majority are not associated with any other abnormality.
How is the diagnosis of pilomatricoma made?
If pilomatricoma is suspected, dermatoscopy may be helpful, showing a central whitish or blue-gray structureless area. Erythema and telangiectasia are sometimes seen
Pilomatricoma with dermatoscopic appearance.
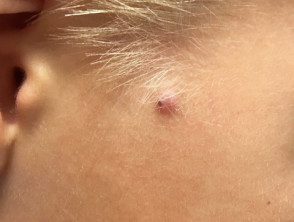
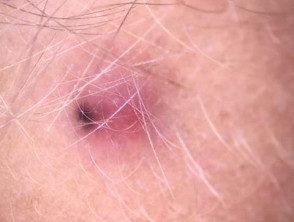
Pilomatricoma dermatoscopy
If the nature of the skin lesions is uncertain, ultrasound Scanning may be recommended. Pilomatricoma examination is described as a donut within the dermis (middle layer of skin) with a tail (tail denotes calcification). Alternatively, calcification can be detected by X-ray.
A biopsy will help establish the cause of the injury. Alternatively, the entire lesion can be removed, providing diagnosis and treatment. the histology of pilomatricoma is surprising. can show a strong demarcated tumor surrounded by a fibrous capsule or a poorly demarcated tumor without a capsule. There are dark spots'basophilic'cells and 'shadow cells' with missing nuclei. Calcium deposits are found in most injuries.
What is the treatment for pilomatricoma?
Pilomatricomas are usually removed surgically. They do not go away on their own, and if they are incompletely removed, they can reappear.


