What is elastic pseudoxanthoma?
Elastic pseudoxanthoma (PXE) is the name given to a group of connective tissue disorders that affect the elastic tissue of the skin, blood vesselsand the eyes. PXE is also known as Gronblad-Strandberg syndrome.
Elastic pseudoxanthoma
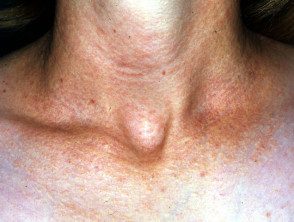
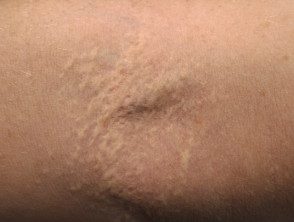
Elastic pseudoxanthoma of antecubital fossa
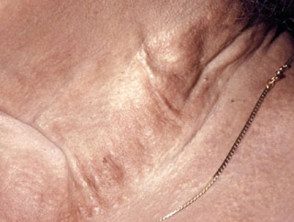
What is the cause of elastic pseudoxanthoma?
The basic flaw in PXE seems to be related to genetic abnormalities in chromosome 16p13.1. The disease involves the transporter. genes MRP6 or ABCC6 in at least some affected families. There is good evidence that collagen and soil substance they are abnormal in affected individuals. Calcium accumulates abnormally elastic fibers on the skin, blood vessels, eyes and heart.
PXE affects about 1 in 160,000 people. There are several PXE subtypes, each with a slightly different clinical presentation and inheritance pattern. Two are inherited as one autosomal dominant characteristic; This means that half of the children of an affected individual are affected. Three types of PXE are autosomal recessive, in which 1 in 4 children are affected.
Clinical characteristics of elastic pseudoxanthoma
People with PXE have distinctive skin lesions, changes in blood vessels, and eye abnormalities. These may vary in distribution and severity
Skin lesions
PXE skin lesions are characteristic. They consist of small yellowish bumps in rows or a lace pattern, which can join together to form large patches. The skin is soft, loose and slightly wrinkled. The patches may have a slightly stony appearance, which has been described as cobblestone.
The common sites affected in PXE are the sides of the neck, below the clavicles, armpits, abdomen, groin, perineum and thighs
These skin changes can develop in childhood, but generally develop in early adulthood (before age 30). They can, in some cases, appear for the first time in old age. Once they appear, they generally persist without change indefinitely.
Similar changes can occur in the soft palate, inside the lips and lining of the stomach, rectum, and vagina.
Heart and blood vessels
The connective tissue in the arteries of the heart and throughout the body are abnormal in elastic pseudoxanthoma. This can cause leg pain when walking (claudication), stroke, heart pain (angina pectoris) and cardiomyopathy (heart muscle disease). Mitral valve prolapse occurs in approximately 5 to 8% of cases.
Eye
Vascular Injuries known as angioid streaks affect the retina of most PXE patients. They usually appear between 20 and 40 years old. Angioid streaks can lead to progressive visual failure and occasionally blindness.
Obstetric risk associated with elastic pseudoxanthoma
PXE patients are at increased risk of miscarriage in the first three months of pregnancy. Stretch marks develop during pregnancy in virtually all patients.
Elastic acquired pseudoxanthoma
There have been occasional reports of late start or acquired PXE.
- The acquired PXE has been associated with the drug penicillamine.
- Some cases have followed liver transplant.
- It has also been reported in patients with beta thalassemia.
How is elastic pseudoxanthoma diagnosed?
Diagnosis of PXE is usually straightforward on the skin. biopsy. the pathology PXE is characteristic.
Imaging studies are done to determine its effect on the blood vessels and the heart.
What is the treatment for elastic pseudoxanthoma?
The most important aspect of treatment is to ensure that complications from blood vessel participation is prevented or promptly treated by the appropriate specialist. Regular follow-up with a specialist vascular surgeon and / or cardiologist is recommended.
- There is currently no effective treatment for skin lesions.
- Dietary calcium restriction has been proven with some benefit, but this is controversial.
- To be Photocoagulation can be helpful in preventing further bleeding from the back of the eye.
- Since there is a risk of passing this condition on to the next generation, genetic counseling may be helpful.

