What is Reiter? syndrome?
Reiter's syndrome has been reclassified as reactive arthritis and it is a type of spondyloarthropathy. This page will be revised to reflect the name change.
Reiter's syndrome is a collection of symptoms, but it generally has three main characteristics: arthritis, symptoms of the genitourinary tract, and conjunctivitis. Skin lesions and mucous The membranes also develop in some patients.
Some or all of these symptoms usually occur 1 to 3 weeks after a infection of the genitourinary tract or bacterial gastrointestinal infection that causes diarrhea. Arthritis is sometimes known as reactive arthritis, which means that arthritis occurs as a reaction to an infection that started in another part of the body.
Reiter's syndrome usually lasts for several months. The symptoms are the same regardless of the origin of the triggering infection.
What causes Reiter's syndrome?
The exact cause of Reiter's syndrome remains unknown, but people with a genetic guy called HLA-B27 has a higher probability of developing the syndrome (approximately 80% of people with Reiter's syndrome have this disease) gene) Having this gene does not mean you will develop Reiter syndrome, but it can predispose to you if you have certain infections.
Genitourinary Reiter's syndrome is often a reaction to a urethral infection that has been passed from one person to another through sexual intercourse. The infection is more commonly chlamydia.
Gastrointestinal or enteric Reiter's syndrome can develop after acute bacterial diarrhea caused by eating food contaminated with bacteria such as salmonella, shigella, or campylobacter.
How common is Reiter's syndrome and who gets it?
People of all races, ages and sex You can get Reiter's syndrome, however, it is more common in young men. It is the most common form of arthritis that affects men between 20 and 40 years old.
HIVPositive men who carry the HLA-B27 gene and are exposed to the appropriate triggers develop Reiter's syndrome in 75% cases. For this reason, a newly diagnosed patient with Reiter's syndrome should have their HIV status verified and undergo a urological and gastrointestinal examination for infection.
What is the clinical presentation of Reiter's syndrome?
Reiter's syndrome generally affects the genitourinary tract, joints, and eyes in that time sequence. Less frequently, skin and mucous membrane Lesions may be present.
| Site | Clinical characteristics of Reiter's syndrome. |
|---|---|
| Genitourinary tract |
|
| Joints |
|
| Eyes |
|
| Skin and mucous membranes |
|
Reiter's syndrome
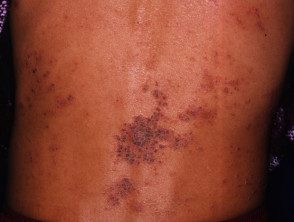
Reiter's syndrome
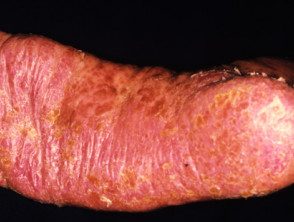
Blenorrhagic keratoderma
What treatment is available for Reiter's syndrome?
There is no cure for Reiter's syndrome. However, in many patients the symptoms resolve completely over long periods of time. About 65% of patients will resolve in 6 months. Approximately 40% of patients will experience reappearance after the initial flare has been established.
During an active phase of the disease, treatment may include:
- Antibiotics to eliminate the original bacterial infection, especially if it is genitourinary.
- Nonsteroidal anti-steroidsinflammatory drugs (NSAID) to reduce inflammation and joint pain
- Drainage of inflamed joints, injections of corticosteroids into painful joints.
- Bed rest in acute early stages
- Strengthening exercises to maintain mobility.
In many ways, Reiter's syndrome can resemble psoriasis in appearance. Treatment of the skin condition is similar to that recommended for psoriasis and may include ointments (emollients, coal tar, calcipotriol, current steroids), Ultraviolet radiation (phototherapy). Oral medications (acitretin, methotrexate, cyclosporine, azathioprine) may be required to control skin lesions and for patients with severe joint disease.
In severe cases of Reiter's syndrome, symptoms can interfere with work and daily activities. In rare cases, the heart and nervous system may be involved.
