What are antitumor necrosis alpha drugs?
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is a cytokine associate with inflammatory disorders of the skin, joints and gastrointestinal tract.
The most active anti-TNF drugs are monoclonal antibodies directed against TNF-alpha (TNFα). Anti-TNFα drugs control inflammation in inflammatory skin diseases, arthritisand intestinal disease. They were among the first biological agents on the market.
Anti-TNFα monoclonal antibodies include:
- Infliximab
- Adalimumab
- Etanercept
- Golimumab
- Certolizumab
Other anti-TNF drugs
Other drugs with activity against TNF include:
- Thalidomide
- Sulfasalazine
- Pentoxifylline
- Bupropion
Natural compounds that act against TNF include:
- Catechins
- Curcumin
- Cannabis
- Echinacea purpurea
For what skin conditions are anti-TNFs used?
Anti-TNF monoclonal antibodies are mainly used in the treatment of serious diseases. chronic license plate psoriasis. They are also used for other severe inflammatory skin conditions when conventional therapies have failed. Examples include:
- Hidradenitis suppurativa
- Skin disease associated with Crohn's disease.
- Pyoderma gangrenous and PAPA syndrome (without brand)
Skin conditions treated with tumor necrosis factor inhibitors
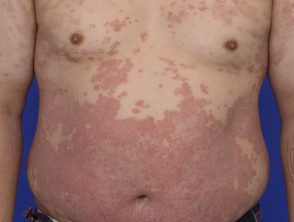
Severe psoriasis
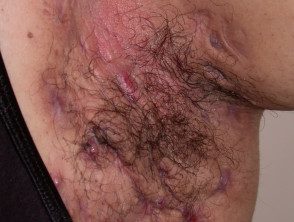
Hidradenitis suppurativa
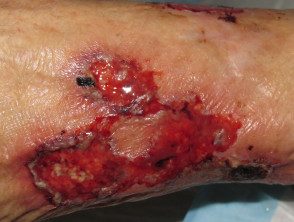
Gangrenous pyoderma
What are the risks of anti-TNF medications?
Anti-TNF biologics are administered by injection. They can sometimes cause injection site reactions or infusion reactions. They should be avoided in patients with severe heart failure.
The main risk of anti-TNF therapy is reduced immunity to bacterial, fungal, viral, and parasitic infections, including:
- Tuberculosis
- Histoplasmosis
- Coccidioidomycosis
- Blastomycosis
They can also increase the risks of skin cancer and autoimmune diseases, including demyelinating conditions.
Anti-TNF drugs can lose their effect over time, possibly due to the induction of antibodies against them. Paradoxically, anti-TNF can sometimes cause dermatological side effects, such as:
- Palmoplantar pustulosis
- Various forms of psoriasis
- Eczema
- Lupus erythematosus
- Morph
- Alopecia areata
- Vitiligo
- Granuloma cancel
- Sarcoidosis
- Erythema multiform
- Vasculitis
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome - toxic epidermal necrolysis
-
Numular drug-induced dermatitis
Dermatological side effects of tumor necrosis factor inhibitors
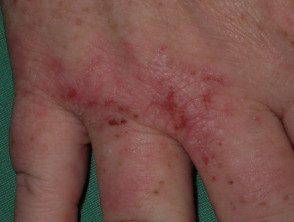
Dermatitis of the hand
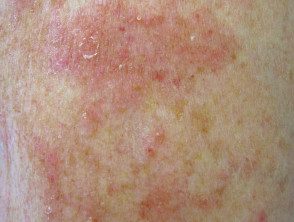
Nummular dermatitis
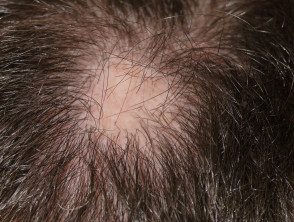
Alopecia areata

