What is it acanthosis nigricans?
Acanthosis nigricans is a skin disorder characterized by darkening (hyperpigmentation) and thickening (hyperkeratosis) of the skin, which occurs primarily in the skin folds in the armpit (armpit), groin and back of the neck.
Acanthosis nigricans is not a skin disease per se but a cutaneous sign of an underlying condition or disease.
There are two major types of acanthosis: benign and evil one. Although it is classically described as a sign of internal malignancyThis is very extrange. The benign types, sometimes described as “pseudoacanthosis nigricans,” are much more common.
What causes acanthosis nigricans?
The cause of acanthosis nigricans is not yet clearly defined, but it appears to be related to insulin endurance. It has been associated with several benign and malignant conditions. According to the predisposing conditions, acanthosis nigricans has been divided into 7 types.
| Types of acanthosis nigricans | |
|---|---|
| Kind | Characteristics |
| Acanthosis nigricans associated with obesity |
|
| Syndromic acanthosis nigricans |
|
| Benign acanthosis nigricans |
|
| Drug-induced acanthosis nigricans |
|
| Hereditary benign acanthosis nigricans |
|
| Malignant acanthosis nigricans |
|
| Acanthosis nigricans mixed type |
|
What are the characteristics of acanthosis nigricans?
- Thick patches of brown skin with a velvety texture that can appear anywhere but most often appear in skin folds in the armpit, groin, and back of the neck.
- Papillomatosis (multiple finger-like growths) is common in cutaneous and mucous membrane surfaces
- Skin tags are often found in and around the affected areas.
- Pruritus (itching) may be present, particularly in acanthosis nigricans associated with malignancy (paraneoplastic pruritus).
- Acanthosis nigricans Lesions may also appear in the mucous membranes of the oral, nasal and laryngeal cavities mucous membrane and esophagus
- Lesions involving the mucosa, palms, and soles tend to be more extensive and more severe when malignant. acanthosis nigricans.
- Patients with malignancy acanthosis nigricans They tend to be middle-aged, non-obese, and the lesions develop abruptly.
Acanthosis nigricans
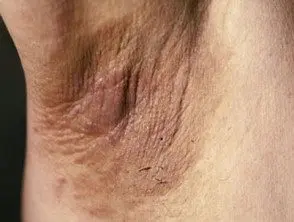
Acanthosis nigricans
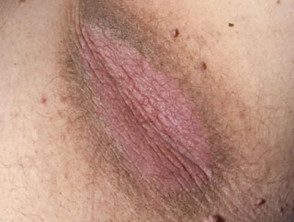
Acanthosis nigricans
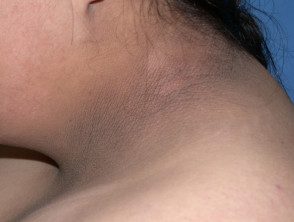
Acanthosis nigricans
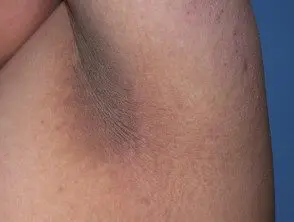
Acanthosis nigricans
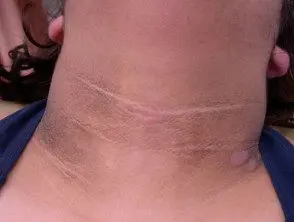
Acanthosis nigricans
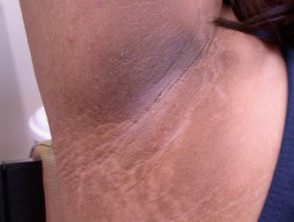
Acanthosis nigricans
What is the work for acanthosis nigricans?
It is very important to differentiate acanthosis nigricans related to malignancy from that related to benign conditions. Malignant tumors acanthosis nigricans They are usually very aggressive and spread quickly. Death often occurs shortly afterward. If it is malignant acanthosis nigricans It is suspected that in a patient without known cancer, it is extremely important to perform a thorough workup of the underlying malignancy and identify an occult tumor. If the tumor can be treated successfully, the condition may resolve.
Other causes of acanthosis nigricans It can be identified by detecting insulin resistance and diabetes mellitus.
What is the treatment for acanthosis nigricans?
the primary The goal of treatment is to correct the underlying disease process. Correcting the underlying cause often results in resolution of the injuries.
- Correct hyperinsulinemia through diet and medications.
- Lose weight with associated obesity acanthosis nigricans
- Excise or treat the underlying tumor
- Stop Offending Drug-Induced Medications acanthosis nigricans
in hereditary acanthosis nigricans, lesions tend to gradually enlarge before stabilizing and/or returning on their own.
There is no specific treatment for acanthosis nigricans. The treatments considered are primarily used to improve cosmetic appearance and include current retinoids, dermabrasion and To be therapy.
Final result of acanthosis nigricans varies depending on the cause of acanthosis nigricans. Benign conditions, either on their own or through lifestyle changes and/or treatment, have good outcomes. However the forecast for patients with malignancy acanthosis nigricans He is often poor. The associated cancer is often advanced and the average survival of these patients is approximately 2 years.

