What is Nodular Chondrodermatitis?
Nodular chondrodermatitis is common inflammatory condition that affects the skin and cartilage of the helix or anthelix of the ear.
Chondrodermatitis nodularis is sometimes called Winkler's disease, after dermatologist who described it in 1915. It is also called nodular chondrodermatitis, chondrodermatitis nodularis helicis and chondrodermatitis nodularis chronicle helicis
Who gets chondrodermatitis nodularis?
Chondrodermatitis nodularis occurs more frequently in older fair-skinned, middle-aged men, with 10 to 35% of reported cases in women. It is rarely reported in children.
What causes nodular chondrodermatitis?
The exact cause of chondrodermatitis nodularis is still unknown. There are several factors that contribute to its development.
- Repeated pressure and compromised blood supply to the ear (predominantly in people who sleep on one side)
- Exposure to cold and sun.
- Trauma headphones, mobile devices, or headphones
- Connective tissue disease (eg, lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis, and scleroderma)
Nodular chondrodermatitis
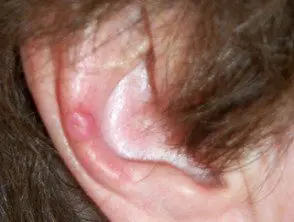
Chondrodermatitis
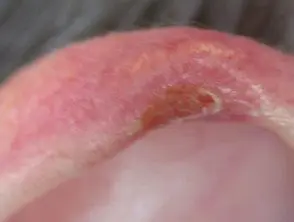
Chondrodermatitis
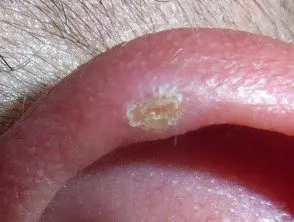
Image provided by Dr. Trevor Evans
What are the clinical features of nodular chondrodermatitis?
Chondrodermatitis nodularis is a solitary, firm and oval-shaped nodule, 4–6 mm in diameter, with center Cortex and surroundings erythema.
- In men, the most common site for CNH is the helix, while in women it is most often found in the anthelix.
- It is typically unilateral, located on the sleeping side, but can be bilateral.
- CNH is painful and tender. Night pain can prevent sleeping on the affected side.
- the injury may bleed or download a small amount of scaly material.
How is chondrodermatitis nodularis diagnosed?
In most cases, the diagnosis of chondrodermatitis nodularis is done clinically, depending on the characteristic location of the helix or anthelix, and a typical history of pain and tenderness.
Sometimes a excision biopsy may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis (see Chondrodermatis nodularis pathology)
Which is the differential diagnosis for nodular chondrodermatitis
The differential diagnosis for CNH depends on the clinical findings. Other diagnoses to consider include:
- Scaly cell carcinoma
- Keratoacanthoma
- Viral wart
- Gouty tophus
- Calcinosis skin
- Basal cell carcinoma
- Actinic keratosis.
What is the treatment for nodular chondrodermatitis?
General measures
Protective padding at night can relieve pressure on the CNH affected area.
- Try to avoid sleeping on one side only.
- Select a soft pillow.
- Consider designing a "hole" in the pillow to avoid pressure on the painful area.
- You can use rubber foam or a bath sponge to make a cchondrodermatitis Nodularis hearing protector to wear at night, held in place with an elastic headband (or buy a hearing protector from a medical supply company).
- Wear a warm hat over your ears when you're out in the cold and wind.
- Apply petroleum jelly or an antiseptic ointment under a light dressing, especially if the chondrodermatitis nodularis is ulcerated or infected.
Intralesional steroid injection
A triamcinolone acetonide steroid injection can reduce locally inflammation.
Implant
A filler like collagen Or hyaluronic acid can be injected under the skin over the cartilage to provide a cushioning layer.
Current nitroglycerine
Nitroglycerin ointment (containing 1–2% glyceryl trinitrate) causes relaxation and vasodilation of arteriolar smooth muscle and can reverse the ischemic changes observed in nodular chondrodermatitis.
- Apply twice a day to the affected area.
- Side effects include transient headache and skin irritation.
Surgery
Surgical options may include:
- Removal of skin and cartilage with minimal margins.
- Excision by puncture biopsy, with full-thickness skin graft
- Curettage to remove the affected tissue, which is allowed to heal by second intention.
Unfortunately, CNH has a 10-30% reappearance rate after surgery.
What is the result of nodular chondrodermatitis?
CNH is usually resolved in a few months. It may reappear.
