What is dermatomyositis?
Dermatomyositis is a rare acquired muscle disease that is accompanied by a eruption. It is one of a group of muscle diseases called inflammatory myopathies
Dermatomyositis
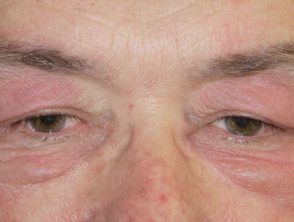
Dermatomyositis of the eyelids.
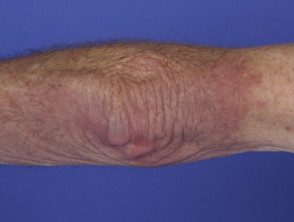
Dermatomyositis of the arm.
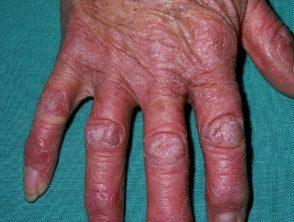
Dermatomyositis of the hand.
Classification of inflammatory myopathies.
- Dermatomyositis (DM): inflammation of voluntary musclesmyositis) in association with a rash
- Polymyositis (PM): myositis without rash
- Youth DM/PM: myositis and skin rash in children <18 años
- Amyopathic DM: The typical skin rash develops without evidence of muscle involvement. Also called dermatomyositis, sinusoidal myositis.
Anti-synthase syndrome: myositis, arthritis, interstitial lung disease, mechanic's hands and Raynaud's phenomenon
Who gets dermatomyositis?
Dermatomyositis can affect people of any race, age, or sex, although it is twice as common in women as in men. The onset of the disease is more common in people aged 50 to 70 years.
What causes dermatomyositis?
Dermatomyositis is considered one of the connective tissue diseases like systemic sclerosis and lupus erythematosus. Dermatomyositis is thought to be caused by a microangiopathy that affects the skin and muscles.
Factors that may play a role in its development are listed below.
- Genetic predisposition
- Underlying Cancer (more likely in older people)
- Autoimmune defect (an immune reaction against oneself)
- infectious or toxic agents that act as triggers
- Certain medications, including hydroxyurea, penicillamine, statins, quinidine, and phenylbutazone.
What are the clinical features of dermatomyositis?
Dermatomyositis is characterized by cutaneous characteristics and myositis.
Skin characteristics
In many patients, the first sign of dermatomyositis is the presence of a symptomless, itchy or burning rash. The rash often, but not always, develops before the muscle weakness.
- The reddish or bluish-purple patches primarily affect sun-exposed areas.
- A violaceous The rash can also affect the cheeks, nose, shoulders, upper chest, and elbows.
Dermatomyositis on sites exposed to the sun.
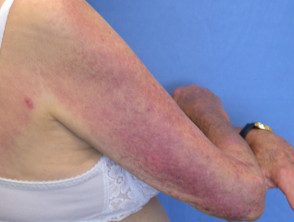
Dermatomyositis
- Purple eyelids, which are described as heliotrope as they resemble heliotrope flower, Heliotropium peruvianum, which has small purple petals.
heliotrope eyelids
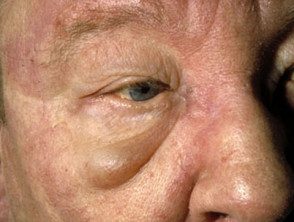
Dermatomyositis
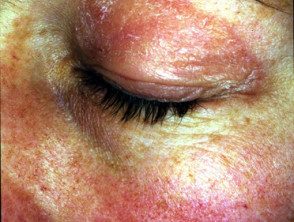
Dermatomyositis
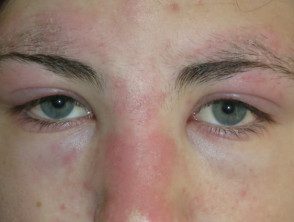
dermatomyositis eyelids 01
- A scaly scalp and thinning hair it can happen.
- Less commonly, there poikiloderma, in which is the skin atrophic (pale and thin skin), red (dilated blood vessels) and brown (post-inflammatory pigmentation)
Dermatomyositis of the scalp and neck.
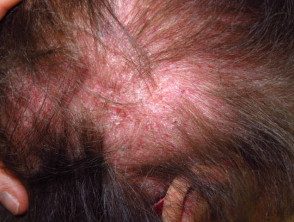
Dermatomyositis of the scalp.
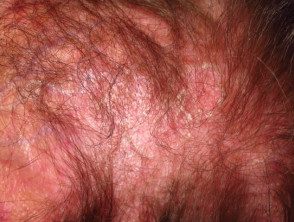
Dermatomyositis of the scalp.
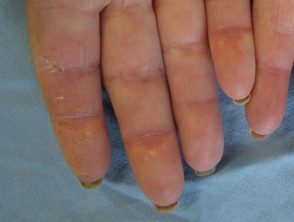
- Purple papules or plates they are found on bony prominences, especially the knuckles (Gottron's papules).
Gottron papules
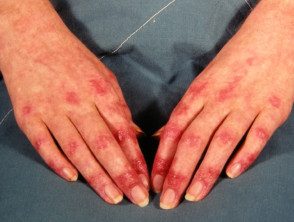
Dermatomyositis of the hand.
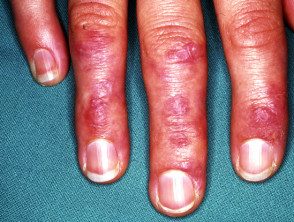
Gottron papules
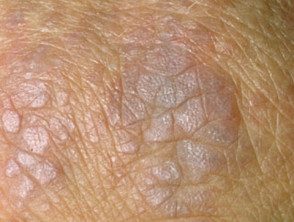
Gottron papules
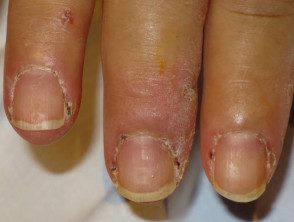
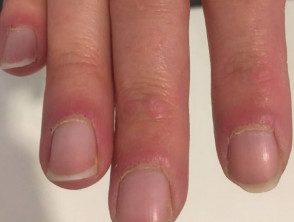
- Irregular cuticles and prominent blood vessels in nail folds are best seen by capillaroscopy or dermoscopy.
Nail folds in dermatomyositis
pulmonary alveolar hemorrhage, positive antiRo520
Nail fold dermatomyositis
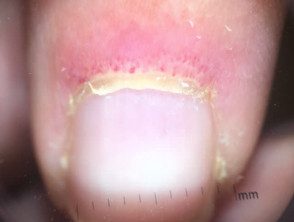
Dermoscopy view
See more images of dermatomyositis.
myositis
Muscle weakness may develop at the same time as the dermatomyositis rash, or it may occur weeks, months, or years later. Proximal muscles are affected, i.e. those closest to the trunk (upper arms, thighs). The first indication of myositis is when the following everyday movements become difficult.
- Climb stairs or walk
- Getting up from a sitting or crouching position
- lift objects
- Raise arms over shoulders, as when combing hair
- Difficulty to swallow (dysphagia)
Occasionally, the affected muscles are sore and tender to the touch.
What are the complications of dermatomyositis?
Calcinosis affects some people, especially children and adolescents.
- It presents as hard yellow or white lumps under the skin.
- These usually appear on the fingers or over the joints.
- sometimes these nodules it can poke through the skin and ulcerate.
- the ulcers can get infected
Some patients have swollen joints (arthritis) and Raynaud's phenomenon (this term refers to fingers that become very white and stiff in cold conditions, then purple when warm again).
Complications of dermatomyositis.
Calcinosis
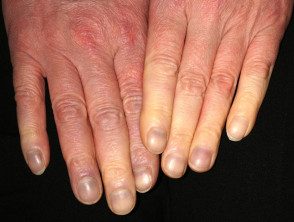
Raynaud
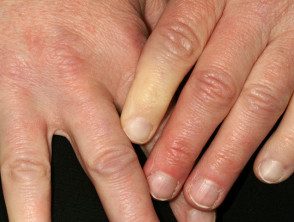
Raynaud
How is dermatomyositis diagnosed?
The following tests usually confirm the diagnosis of dermatomyositis.
- A blood test to detect elevated circulating muscle. enzymes: creatine kinase (CK) and sometimes aldolase, aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and lactic dehydrogenase (LDH)
- A blood test to detect autoantibodies: non-specific antinuclear antibody (ANA) is found in the majority of patients, the specific Anti-Mi-2 is found in a quarter and Anti-Jo-1 in a few, generally those who have lung disease, and are diagnostic of antisynthetase syndrome.
Skin biopsy of the eruption: microscopic appearance of an interface dermatitis is similar to systemic (acute) lupus erythematosus
- Biopsy of an affected muscle.
- Electromyography (EMG) test
- Magnetic resonance imaging (Magnetic resonance) examination of the muscles
In those over 60 years of age, a full-body exam and test, looking for underlying cancer, is recommended.
What is the treatment of dermatomyositis?
the primary the goal of treatment is control Skin disease and muscle disease. An oral corticosteroid such as moderate to high dose prednisone is the mainstay of medical treatment and is given to slow the rate of disease progression.
Hydroxychloroquine can reduce the photosensitive rash. Note that adverse skin reactions to hydroxychloroquine are reported to affect more than 30% of patients with dermatomyositis, compared to a lower risk of rash in patients with cutaneous lupus erythematosus [1].
immunosuppressive or cytotoxic Medications such as methotrexate, mycophenolate mofetil may also be used, azathioprine, cyclophosphamide, cyclosporine, high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin and experimentally, biological products such as rituximab.
- Diltiazem, a calcium channel blocker usually prescribed for high blood pressure, can reduce calcinosis.
Colchicine has also been reported to reduce calcinosis.
- Patients should strictly avoid excessive sun exposure and use sun protection, including full-coverage clothing and broad-spectrum sunscreens to minimize the sun's harmful effects on already damaged and photosensitive skin.
- Bed rest may be required for severely inflamed muscles
- Physical therapy and activity are recommended to keep muscles and joints moving.
- People with difficulty swallowing shouldDo not eat food before bedtime and raise the head of the bed to sleep.
What is the outcome for patients with dermatomyositis?
Most patients will require lifelong treatment, but dermatomyositis resolves completely in about one in five patients. Patients who have a disease that affects their heart or lungs, or who also have underlying cancer, fare worse and may ultimately die from their disease.

