Ad
Skin cancer
Application to facilitate skin self-examination and early detection. read more.
What is a atypical solar lentigo?
An atypical solar lentigo is a solar lentigo with unusual characteristics. The term can be used when a doctor is not sure if a flat brown mark (a lentigo) is a benign solar lentigo or melanoma in the place (an early form of melanoma, a type of skin Cancer) The plural of lentigo is lentigines.
Byrom et al gave the name unstable solar lentigo to a specific type of atypical solar lentigo on sun damaged skin [1]. Unlike the usual solar lentigo, which is predominantly keratinocytic, the unstable lentigo has areas of melanocytic proliferation in histology.
Atypical solar lentigo
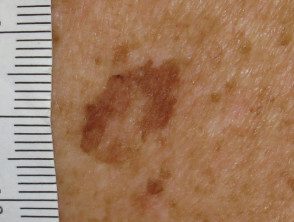
Atypical solar lentigo
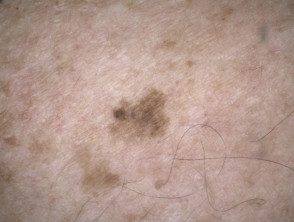
Atypical solar lentigo
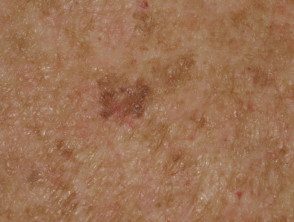
Atypical solar lentigo
Atypical solar lentigines are large flat brown markings with irregular shape, structure and color.
Who receives atypical solar lentigines?
Atypical and typical solar lentigines arise on sun-damaged and aged skin. Lentigines most commonly affect people over 50 with fair skin (Fitzpatrick skin types I and II) who spend a lot of time doing outdoor work or outdoor recreation.
Atypical solar lentigines can also arise in people with genetic disorders in which sun damage occurs at an early age (eg, xeroderma pigmentosum) or when taking immunosuppressive medications.
Other characteristics of sun damage may be present on the surrounding mottled skin. [two]. These may include:
- Freckles (ephelides)
- Guttate hypomelanosis
- Solar elastosis
- Actinic keratosis
- Lentigo solar
- Other forms of lentigo
- Seborrheic keratosis
-
Skin cancer (eg. basal cell carcinoma, scaly cell carcinoma and melanoma).
What is the cause of atypical solar lentigines?
Atypical solar lentigines are believed to be caused by genetic changes in keratinocytes and in melanocytes due to exposure to Ultraviolet radiation. A lichenoid Keratosis is due to a local immune reaction.
What are the clinical characteristics of an atypical solar lentigo?
An atypical solar lentigo arises on the face, ears, neck, hands, forearms, or upper back. It is a lonely and different taint.
Compared to surrounding solar lentigines, an atypical solar lentigo can:
- Be bigger and more irregular in shape.
- Have a sharper or less defined margin
- Be darker in color and have greater color variation.
- Be inflamed (red) or there may be areas of hypopigmentation (loss of color)
- You have gray or purple discoloration due to inflammatory reaction.
An atypical solar lentigo can be adjacent to a more typical solar lentigo, a melanoma in situ (either a lentigo malignant or a lentiginous melanoma), or both.
Which is the differential diagnosis of an atypical solar lentigo?
Differential diagnoses for an atypical solar lentigo may include:
- Lentigo solar
- Melanoma in situ
- Lichenoid keratosis
- Seborrheic keratosis
- Pigmented actinic keratosis
- Other forms of lentigo
- Melanocytic junction nevus.
What are the complications of an atypical solar lentigo?
The main complication of an atypical solar lentigo is the lack of a diagnosis of melanoma in situ. Some atypical solar lentigines can also be precursors of melanoma in situ, especially the histological variant, unstable solar lentigo.
How is an atypical solar lentigo diagnosed?
An atypical solar lentigo is evaluated clinically and by dermoscopy. Pathological examination often leads to a more accurate diagnosis, such as solar lentigo, lichenoid keratosis, unstable solar lentigo, atypical lentigo hyperplasia, atypical junctional melanocytic nevi or melanoma in situ.
If there is melanocytic proliferation within an atypical solar lentigo, the whole injury they must be excised and the multiple layers of the samples must be examined by histology. Please note that a single atypical solar lentigo may display characteristics of solar lentigo, unstable solar lentigo, actinic keratosis, and melanoma in situ (and even invader melanoma).
What is the treatment for an atypical solar lentigo?
An atypical solar lentigo is often removed.
Lesions that are not removed should be carefully followed up, preferably by serial sequential dermoscopy (mole mapping). The observed changes may include an increase in size and a change in shape, structure, and color.
Greater asymmetry in the distribution of structures and colors in dermoscopy should lead to excision of injury Stable injuries can still be observed.
What is the result of atypical solar lentigo?
The result depends on the actual diagnosis.
Solar lentigo and lichenoid keratosis are harmless. Melanoma in situ can progress to invasive melanoma.


