What is it primary cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma?
Primary cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma is a type of low-grade cutaneous B-cell lymphoma that originates in the mucous membrane-associated lymphoid fabric (MALT). Is a heterogeneous proliferation of cells in the marginal zone, B cells, little lymphocytesand plasma cells.
Cutaneous lymphoma of the marginal zone
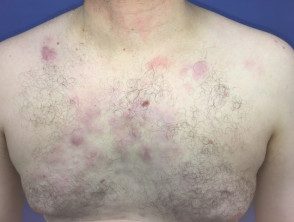
Cutaneous lymphoma of the marginal zone
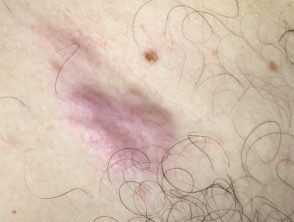
Cutaneous lymphoma of the marginal zone
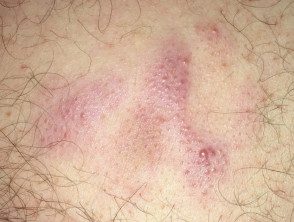
Cutaneous lymphoma of the marginal zone
Who gets primary cutaneous lymphoma of the marginal zone?
Cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma affects all ages, but tends to affect younger patients compared to other types of B-cell lymphoma [1]. The median age of diagnosis is 55 years. Men are twice as likely to contract this type of lymphoma as women [2].
What causes primary cutaneous lymphoma of the marginal zone?
It is not clear whether cutaneous lymphoma of the marginal zone is the result of a de novo neoplastic process (the beginnings of a tumor) or a reaction to exogenous me endogenous agents [3]. A small number of cases have been associated with Borrelia burgdorferi (the cause of Lyme disease), and hepatitis C infection [1–4].
What are the clinical characteristics of primary marginal zone lymphoma?
Cutaneous lymphoma of the marginal zone presents as papules, platesor nodules that color range from red to violet. The lesions can be solitary or multifocal and are most often seen on the trunk or arms of the patient. [1,2,4]. Dermoscopy is vascular but the characteristics are not specific to the disease.
Dermoscopy of marginal zone lymphoma
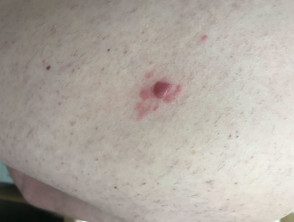
Marginal zone lymphoma.
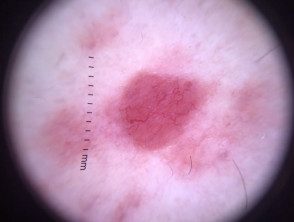
Dermoscopy of marginal zone lymphoma
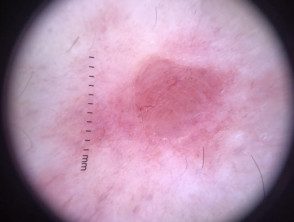
Dermoscopy of marginal zone lymphoma
How is primary cutaneous lymphoma of the marginal zone diagnosed?
After obtaining a complete history of the patient and performing a physical exam and a skin exam, the diagnosis is made based on a suitable full thickness biopsy of the affected skin.
A 4–6 mm punch, incisional or excision biopsy must be obtained The biopsy sample must include the lattice dermis and fat [2].
Histologically, show cutaneous lymphomas of the marginal zone nodular to diffuse dermal infiltration of marginal zone B cells, lymphocytes, lymphoplasmocytoid cells and plasma cells combined with centroblast type cells or immunoblasts and reagents T cells. The marginal cells in zone B are small to medium in size and have irregularities. nucleidiscreet nucleoli and abundant pale cytoplasm [2].
Immunohistochemistry The tests for cutaneous lymphomas of the marginal zone are positive for CD20, CD79a and BCL-2 and negative for CD 10 and BCL-6 cells [2].
Other essential investigations include a complete blood count, a complete metabolic profile, and lactate dehydrogenase studies. A test for Borrelia burgdorferi it can also be done, particularly in endemic regions [2].
Additional blood tests that can be performed for disease evaluation and staging include antinuclear antibody, rapid plasma reagin, viral hepatitis serologies, flow cytometry, serum protein electrophoresisand quantitative immunoglobulin evaluation [2].
Images may include Positron emission tomography (PET) me computed tomography (Connecticut) [2].
None lymph node With high PET activity, or measuring> 1.5 cm in length by an imaging study, a biopsy should be done. A bone marrow biopsy is optional. [two].
Which is the differential diagnosis for primary cutaneous lymphoma of the marginal zone?
The differential diagnosis for cutaneous lymphoma of the marginal zone may include:
- Other types of cutaneous B-cell lymphoma
- Cell Brich in cutaneous lymphoids hyperplasia
- Cutaneous pseudolymphoma
- Arthropod bites
- Urticaria
- Leukemia skin
- Basal cell carcinoma [1,2,4].
It is important to distinguish primary cutaneous lymphoma from the marginal zone from non-Hodgkin systemic B-cell lymphoma with skin involvement. [1,2].
What is the treatment for primary marginal zone cutaneous lymphoma?
Spontaneous resolution of cutaneous lymphoma of the marginal zone may occasionally occur, particularly in the first few months. [two]. A lonely license plate or located the disease can be treated with radiotherapy or surgical excision, with curative intention [1,5].
Multifocal disease can be treated with:
- Observation
- Radiotherapy
- Class 1 current corticosteroids (eg, clobetasol propionate)
- Nitrogen mustard
-
Imiquimod cream
- Cryotherapy
-
Intralesional steroids
- Interferon-α
-
Rituximab
- Intravenous rituximab
- Chlorambucil [1,5].
Patients who develop disseminated skin lesions are treated with multiple agents chemotherapy [5].
Antibiotic therapy may be indicated in patients who are positive for Borrelia burgdorferi antibodies [5].
What is the prognosis for primary marginal zone lymphoma of the skin?
the forecast it is excellent for primary cutaneous lymphoma of the marginal zone, with a 5-year survival rate of up to 99% [5]. However, the cutaneous relapse the rate is high at approximately 40% [2], but the extracutaneous the spread of the disease is rare [2].

